Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts - 1 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page No - 66)
Question 1:
What colour do the following indicators turn when added to a base or alkali (such as sodium hydroxide)?
(a) methyl orange
(b) litmus
(c) red cabbage extract
 Red Cabbage ExtractSolution:
Red Cabbage ExtractSolution:
(a) When methyl orange is added to a base it turns colour into yellow
(b) Litmus paper changes into blue when dipped in base solution. It changes colour from red to blue as the solution is alkali
(c) Red cabbage extract turns into green colour when added to a base
Question 2:
What colours do the following indicators turn when added to an acid (such as hydrochloric acid)?
(a) litmus
(b) methyl orange
Solution :
(a) Litmus paper is an indicator used to identify the whether the solution is acidic or basic. Here when this is dipped in acidic solution like hydrochloric acid it turns blue colour to red.
(b) Methyl orange is also an indicator shows colour change in different solutions. In acid solutions it changes its colour to red.
Question 3:
Name an indicator that is red in acid solution but turns blue in basic solution.
Solution :
Litmus is used as an indicator to identify the solution is acidic or basic by changing its colour from solution to solution. In acidic solution the litmus colour changes from blue to red and in alkali solutions the colour changes from red to blue.
Question 4:
Name an indicator that is pink in alkaline solution but turns colourless in acidic solution.
Solution :
Phenolphthalein is used as an indicator in acid-base titrations and it turns colourless in acidic solutions and turns into pink in basic solutions.
Question 5:
When a solution is added to a cloth strip treated with onion extract, then the smell of onion cannot be detected. State whether the given solution contains an acid or a base.
Solution :
The given solution contains base because onion extract loses its smell when added to a base, but its smell does not change when added to acid.
Question 6:
When a solution is added to vanilla extract, then the characteristic smell of vanilla cannot be detected. State whether the given solution is an acid or a base.
Solution :
The given solution will be base because when a basic solution is added to vanilla it completely destroys the characteristic smell of vanilla and when in acidic solution it does not change
Question 7:
How will you test for the gas which is liberated when hydrochloric acid reacts with an active metal ?
Solution :
When hydrochloric acid reacts with active metal hydrogen gas will be evolved at the surface of the metal in the form of bubbles and thus formed gas is passed through soap and bring candle near the bubble formed. If the gas burns with a pop sound then it can be concluded that it is hydrogen.
Question 8:
Name the gas evolved when dilute HCl reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate. How is it recognised ?
Solution :
Carbon dioxide gas is liberated when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. The gas liberated thus will pass through lime water and lime water turns milky due to the presence of carbon dioxide and further more if we do the same the solution becomes clear.
Question 9:
Give the names and formulae of two strong acids and two weak acids.
Solution :
Strong acids are those which dissociates into ions in water. Eg: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) Acetic acid (CH3COOH) and Citric acid (C6H8O7) are weak acids which are partially dissociates into its ions in water
Question 10:
Name one natural source of each of the following acids :
(a) Citric acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Lactic acid
(d) Tartaric acid
Solution :
(a) The natural source of citric acid is from Lemon
(b) The natural source of oxalic acid is from tomatoes
(c) The natural source of Lactic acid is from sour milk or curd.
(d) The natural source of Tartaric acid is from tamarind
Question 11:
Name one animal and one plant whose stings contain formic acid (or methanoic acid).
Solution :
Animal sting containing Formic acid : Ants
Plant sting containing Formic acid : Nettle leaf sting
Question 12:
How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when the solution of an acid is diluted ?
Solution :
The concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+) decreases on diluting an acid. Thus the strength of the acid decreases. Concentration of hydronium ions = Volume of solute (acid)/Volume of solution
Question 13:
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reactions taking place when :
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Solution :




(Page No - 67)
Question 14:
Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
(a) Zn (s) + HCl (aq) ——- >
(b) Na2C03 (s) + HCl (aq) ———>
(c) NaHC03 (s) + HCl (aq) ——–>
(d) NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) ———>
(e) CuO(s) + HCl (aq) ———->
Solution :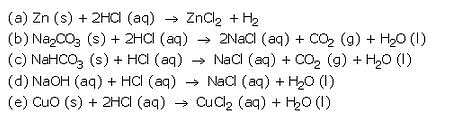
Question :15
Fill in the blanks in the following sentences :
(a) Acids have a…………….. taste and they turn…………… litmus to……………….
(b) Substances do not show their acidic properties without……………….
(c) Acids produce…………… ions on dissolving in water.
(d) Those substances whose smell (or odour) changes in acidic or basic solutions are called
(e) Onion and vanilla extract are…………..
Solution :
(a) Sour; blue; bed.
(b) Water.
(c) Hydrogen.
(d) Olfactory.
(e) Olfactory.
Question 16:
(a) What is an indicator ? Name three common indicators.
(b) Name the acid-base indicator extracted from lichen.
(c) What colour does the turmeric paper turn when put in an alkaline solution ?
Solution :
(a) An indicator is a ‘dye’ that changes colour when it is put in an acid or a base. The three most common indicators are: Litmus, Methyl orange and Phenolphthalein.
(b) Litmus is the acid-base indicator extracted from lichen. It will show colour change blue to red when in acid and red to blue in base.
(c) When turmeric paper is dipped in alkaline solution it will turn to red.
Question 17:
What is an olfactory indicator ? Name two olfactory indicators. What is the effect of adding sodium hydroxide solution to these olfactory indicators ?
Solution :
Olfactory indicators are those smell or odour changes when it is mixed in an acidic or basic solution. It can be used in laboratory to test whether the solution is base or acid and can perform olfactory titration Onion and vanilla extracts are the olfactory indicators When a basic solution like sodium hydroxide solution is added to a cloth strio treated with onions the smell cannot be detected
Question 18:
(a) What happens when an acid reacts with a metal ? Give chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal ? How will you test for the presence of this gas ?
Solution :
(a) When an acid reacts with a metal, then a salt and hydrogen gas are formed.
(b) While diluting an acid, it should be done always in a slow manner with a constant stirring and in small amount. The dilution of an acid is an exothermic reaction. When we add acid to water the heat that evolved gets absorbed by the water but if doing reverse, which is water added to acid a large amount of heat evolved and chances of acid splashing to the person handling will be more.
Question 19:
While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid ?
Solution :
While diluting an acid, it should be done always in a slow manner with a constant stirring and in small amount. The dilution of an acid is an exothermic reaction. When we add acid to water the heat that evolved gets absorbed by the water but if doing reverse, which is water added to acid a large amount of heat evolved and chances of acid splashing to the person handling will be more.
Question 20:
What happens when an acid reacts with a metal hydrogencarbonate ? Write equation of the reaction which takes place.
Solution :
When an acid reacts with a metal hydrogen carbonate, then a salt, carbon dioxide gas and water are formed.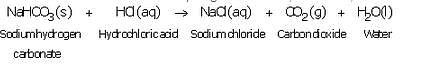
Question 21:
(a) What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate ? Write a balanced chemical
equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Which gas is liberated when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate ? How will you test for the presence of this gas ?
Solution :
(a) When dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate, then sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and water are formed.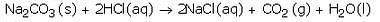
(b) CO2 gas is liberated during the reaction.
When carbon dioxide gas formed in the form of brisk effervescence is passed through lime water, it turns the lime water milky. If excess of carbon dioxide gas is passed through the milky lime water, the solution becomes clear again. This confirms the presence of carbon dioxide gas.
Question 22:
What happens when an acid reacts with a base ? Explain by taking the example of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide. Give equation of the chemical reaction which takes place. What is the special name of such a reaction ?
Solution :
When an acid reacts with a base, then a salt and water are formed. When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide solution, then a neutralisation reaction takes place to form sodium chloride and water.
Such a reaction is termed as neutralisation reaction.
Question 23:
What happens when an acid reacts with a metal oxide ? Explain with the help of an example. Write a balanced equation for the reaction involved.
Solution :
Acids react with metal oxides to form salt and water.
For example: Copper (II) Oxide, a metal oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form copper chloride and water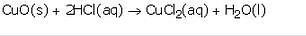
Question 24:
(a) What are organic acids and mineral acids ?
(b) Give two examples each of organic acids and mineral acids.
(c) State some of the uses of mineral acids in industry.
Solution :
(a) Organic acids are acids present in plant materials and animals. These are naturally occuring acids.
A mineral acid (or inorganic acid) is an acid derived from one or more minerals of the earth.
(b) Organic acids: Citric acid, lactic acid;
Mineral acids: Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid.
(c) Uses of mineral acids in industry:
- Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, paints, dyes, detergents etc.
- Nitric acid is used for making fertilizers, explosives, dyes and plastics.
- Hydrochloric acid is used for removing oxide film from steel objects, in textile, food and leather industries.
Question 25:
What is meant by strong acids and weak acids ? Classify the following into strong acids and weak acids :
HCl, CH3COOH, H2SO4, HNO3, H2CO3, H2SO3
Solution :
A strong acid is one that completely ionises in water to form a large amount of hydrogen ions whereas a weak acid only partially ionises in water and thus produces a small amount of hydrogen ions.
HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 are strong acids; CH3COOH, H2CO3, H2SO3 are weak acids.
Question 26:
Why do HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc., show acidic character in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like C6H12O6 (glucose) and C2H5OH (alcohol) do not show acidic character ?
Solution :
The acidic character of a substance is due to the presence of hydrogen ions [H+(aq) ions] in its aqueous solution. HCl, H2SO4 etc show acidic properties because they produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. The solution of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character because they do not ionize in water to produce hydrogen ions or any other ions in solution.
Question 27:
What is a neutralisation reaction ? Explain with an example. Give the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place.
Solution :
The reaction between an acid and a base to form salt and water is called a neutralisation reaction. When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide solution, then a neutralisation reaction takes place to form sodium chloride and water.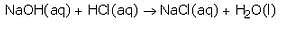
Question 28:
Why should curd and other sour foodstuffs (like lemon juice, etc.) not be kept in metal containers (such as copper and brass vessels) ?
Solution :
Curd and other sour substances contains acids which can react with the metals of brass and copper vessels to form toxic (poisonous) metal compounds which can cause food poisoning and damage our health.
Question 29:
(a) What is produced if an acid is added to a base ?
(b) Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of dry litmus paper ?
(c) What colour does phenolphthalein indicator turn when added to an alkali (such as sodium hydroxide) ?
Solution :
(a) Salt and water.
(b) Because dry HCl does not undergo dissociation to form ions because of the absence of aqueous medium. Colour of the litmus paper changes when ions are present. Hence it does not change the colour of litmus paper
(c) Pink.
Question 30:
(a) Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water ?
(b) Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity ?
(c) Why does distilled water not conduct electricity whereas rain water does ?
Solution :
(a) The acidic behavior of an acid is due to the presence of hydrogen ions [H+ (aq) ions] which are produced only when acids are dissolved in water. In the absence of water, acids do not produce hydrogen ions and hence do not show acidic behavior.
(b) The aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity due to the presence of charged particles called ‘ions’ in it. These ions carry electric current.
(c) Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it does not contain any ionic compounds dissolved in it whereas rain water does.
Reason: When rain water falls on earth through the atmosphere, it dissolves an acidic gas ‘carbon dioxide’ from the air and forms carbonic acid (H2CO3). The carbonic acid provides some hydrogen and carbonate ions to the rain water. Due to the presence of these ions, rain water conducts electricity.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts - 1 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 2. How can we identify whether a substance is an acid or a base? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 4. How do acids and bases react with each other to form salts? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of acids, bases, and salts in daily life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|













