Bonding in Metal Complexes & Applications of Coordination Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Bonding in Metal Complexes
Complexes in which carbon monoxide acts as ligands are metal carbonyls
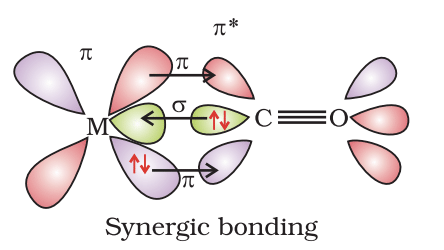
Example: [Ni(CO)4] Tetracarbonyl Nickel (0) and [Fe(CO)5] Penta Carbonyl Iron (0) In these complexes, complexes, a′σ‘ bond is formed by the overlapping of vacant ‘d’ orbital of metal ion and filled orbital of C-atom (carbon).
A π bond is formed by the lateral overlapping of filled inner orbitals of metal ion and vacant of the carbon atom. Thus synergic bonding exists in metal carbonyls.
Applications of Coordination Compounds
The complexes are of immense importance on account of their applications in various fields. During complex formation there are drastic changes in the properties of metal atom/ion these changes in properties are made use of in the application of metal complexes.
(i) The detection and estimation of Ni2+ is based on the formation of a scarlet red complex with dimethyl glyoxime.
(a) Fe3+ is detected by formation of a blood red coloured complex with KSCN.
(b) Many ligands (organic reagents) are used for the gravimetric estimation of number of metal ions.
Metal ion to be estimated | Cu2+ | Ni2+ | Fe3+ | Al3+ | Co2+ |
Organic reagents used | Benzoin oxime | Dimethyl glyoxime | 1,20-phena- nthroline | 8-hydroxy quinoline | α-nitroso β-naphthol |
(c) EDTA is used as a complexing agent in volumeter analysis of metal ions like Ca2+ , Mg2+ and Zn2+ .
(d) The co-ordination compounds of the transition metals exhibit a variety of colours. This property is utilised in colorimetric analysis for the estimation of many metals.
(ii) (a) Metallurgical process :
Silver and gold are extracted by the use of complex formation. Silver ore is treated with sodium cyanide solution with continuous passing of air through the solution. Silver dissolves as a cyanide complex and silver is precipitated by the addition of scrap zinc.
b) Native Gold and Silver also dissolve in NaCN solution in presence of the oxygen (air).
4 Ag + 8NaCN + O2 + 2H2O 3Na[Ag(CN)2] + 3NaOH
Silver and Gold are precipitated by addition of scrap zinc. Nickel is extracted by converting it into a volatile complex, nickel carbonyl, by use of carbon monoxide (Mond's process). The complex decomposes on heating again into pure nickel and carbon monoxide.
Ni + 4CO Ni(CO)4
Ni + 4 CO
(iii) Photography
In photography, the image on the negative is fixed by dissolving all the remaining silver bromide with hypo solution in the form of a soluble complex.
AgBr + 2Na2S2O3 Na3[Ag(S2O3)2 ] + NaBr
(soluble) (soluble)
(iv) Electroplating
Metal complexes release metal slowly and give a uniform coating of the metal on the desired object Cyano complexes of silver, gold copper and other metals are used for the electrodeposition of these metals.
(v) Biological processes
Metal complexes are of immense importance in biological processes. Haemoglobin, the red blood pigment, which acts as oxygen carrier to different parts of the body is a complex of iron (II). Vitamin B12 is a complex of cobalt metal. The green colouring matter of plants, called chlorophyll, is a complex of magnesium. It acts as a catalyst in photosynthesis.
Organometallic compounds
Organometallic compounds are defined as those compounds in which the carbon atoms of organic (usually alkyl or aryl) groups are directly bonded to metal atoms. The compounds of elements such as boron, phosphorus, silicon, germanium and antimony with organic groups are also included in organometallics. Many organometallic compounds are important reagents that are used for the synthesis of organic compounds.
Classification of Organometallic Compounds
Organometallic compounds are classified in three classes.
(i) Sigma bonded organometallic compounds: In these complexes, the metal atom and carbon atom of the ligand are joined together with a sigma bond, For Examples:
(a) Grignard reagents, R - Mg - X where R is an alkyl or aryl group and X is a halogen.
(b) Zinc compounds of the formula R2Zn such as (C2H5)2Zn. (isolated by Frankland).
Other similar compounds are (CH3)4Sn, (C2H5)4Pb, Al2(CH3)6, Al2(C2H5)6, Pb(CH3)4 etc.
Al2(CH3)6 is a dimeric compound and has a structure similar to diborane, (B2H6). It is an electron-deficient compound and two methyl groups act as bridges between two aluminium atoms.
(ii) Pi-bonded organometallic compounds: These are the compounds of metals with alkenes, alkynes, benzene and other ring compounds. In these complexes, the metal and ligand form a bond that involves the p-electrons of the ligand. Three common examples are Zeise's salt, ferrocene and dibenzene chromium.
These are shown below:
The number of carbon atoms bonded to the metal in these compounds is indicated by the greek letter h(eta) with a number. The prefixes η2, η5 and η6 indicate that 2, 5 and 6 carbon atoms are the metal in the compound.
(iii) Sigma and Pi bonded organometallic compounds: Metal carbonyl compounds formed between metal and carbon monoxide, belong to this class. These compounds possess both s-and p-bonding. Generally, the oxidation state of metal atoms in these compounds is zero. Carbonyls may be mononuclear, bridged or polynuclear.
In a metal carbonyl, the metal-carbon bond possesses both the s-and p-character. An s-bond between metal and the carbon atom is formed when a vacant hybrid orbital of the metal atom overlap with an orbital on a C atom of carbon monoxide containing a lone pair of electrons.
Formation of p-bond is caused when a filled orbital of the metal atom overlaps with a vacant antibonding p* orbital of C atom of carbon monoxide. This overlap is also called back donation of electrons by metal atom to carbon.
The p-overlap is perpendicular to the nodal plane of the s-bond.
In olefinic complexes, the bonding p-orbital electrons are donated to the empty orbital of the metal atom and at the same time to the back bonding p-orbital of the olefin.
Applications of Organometallic Compounds
(i) Tetraethyl lead (TEL) is used as an antiknock compound in gasoline.
(ii) Wilkinson's catalyst [Rh(PPh3)3Cl] is used as a homogeneous catalyst in the hydrogenation of alkenes.
(iii) The extraction and purification of nickel are based on the formation of organometallic compound Ni(CO)4. The formation of Ni(CO)4 at 50-80ºC and its decomposition at 150-180ºC is used in the extraction of nickel by MOND's Process.
(iv) Zeigler Natta catalyst (trialkyl aluminium titanium tetrachloride) acts as a heterogeneous catalyst in the polymerisation of ethylene into polyethene polymer.
Points to be remembered:
(i) CH3B(OCH3) is an organometallic compound but B(OCH3) is not.
(ii) The closed ring complexes formed by polydentate ligands are called Chelates. Chelation leads to stability.
(iii) Estimation of nickel (II) is done by complexing with dimethyl glyoxime (DMG) whereas that of Ca 2 and Mg2 ions is done by titrating against EDTA.
(iv) Complex in which ligands can be substituted by other ligands is called labile complexes. For example [Cu(NH3)4]2 is a labile complex because NH3 ligands can be substituted by CN- ligands.
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ + 4CN- → [Cu(CN)4]2 + 4NH3
(less stable) (more stable)
(v) Another type of geometrical isomerism is also shown by octahedral complexes of the type Ma3b3.
if each trio of donor atoms occupy adjacent positions at the corner of an octahedral face, then it is called facial (fac) isomer and when the position are around the meridian of the octahedron, then it is called meridional (mer) isomer.
(vi) Haemoglobin is a complex of Fe, chlorophyll is a complex of Mg, vitamin B12 is a complex of Co.
(vii) s-bond organometallic compounds generally contain a non-transition metal linked to a carbon atom of an alkyl group by s bond. For example eg. R-MgX.
(viii) p-bonded organometallics are formed by the donation of p-electrons of the double bond to the metal atom. For example Zeise's salt K[PtCl3h2 C2H4] and Ferrocene Fe(h5-C5H5)2
(ix) Grignard's reagent is one of the most useful organometallic compounds. Due to the high polarity of (Cd-Mgd ) bond, it can be used to synthesise many organic compounds.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Bonding in Metal Complexes & Applications of Coordination Compounds - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the bonding in metal complexes? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of coordination compounds? |  |
| 3. What are organometallic compounds? |  |
| 4. What is the crystal field theory? |  |
| 5. How does ligand field theory differ from crystal field theory? |  |