NCERT Summary: Soils- 1 | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Soil
Technically, the soil is a mixture that contains minerals, organic matter, and living organisms. But broadly speaking, soil can refer to any loose sediment.
- Soil is the most important layer of the earth’s crust. It is a valuable resource.
- Soil is the mixture of rock debris and organic materials which develop on the earth’s surface.
Factors affecting the Formation of Soil
- The major factors affecting the formation of soil are relief, parent material, climate, vegetation, and other life-forms and time.
- Besides these, human activities also influence it to a large extent. Components of the soil are mineral particles, humus, water, and air.
- The actual amount of each of these depends upon the type of soil. Some soils are deficient in one or more of these, while there are some others that have varied combinations.
Soil Profile
“Soil profile is defined as the vertical section of the soil from the ground surface downwards to where the soil meets the underlying rock.”
- If we dig a pit on land and look at the soil, we find that it consists of three layers which are called horizons.
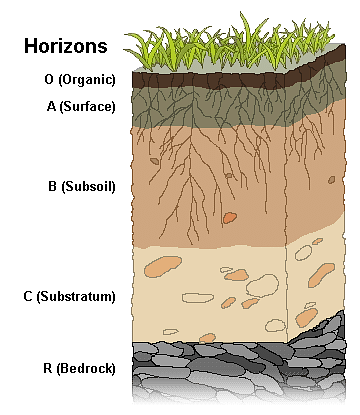
- ‘Horizon A’ is the topmost zone, where organic materials have got incorporated with the mineral matter, nutrients and water, which are necessary for the growth of plants.
- ‘Horizon B’ is a transition zone between the ‘horizon A’ and ‘horizon C’, and contains matter derived from below as well as from above.
- It has some organic matter in it, although the mineral matter is noticeably weathered. ‘Horizon C’ is composed of the loose parent material.
- This layer is the first stage in the soil formation process and eventually forms the above two layers.
- This arrangement of layers is known as the soil profile. Underneath these three horizons is the rock which is also known as the parent rock or the bedrock. Soil, which is a complex and varied entity, has always drawn the attention of scientists.
Classification of Soil
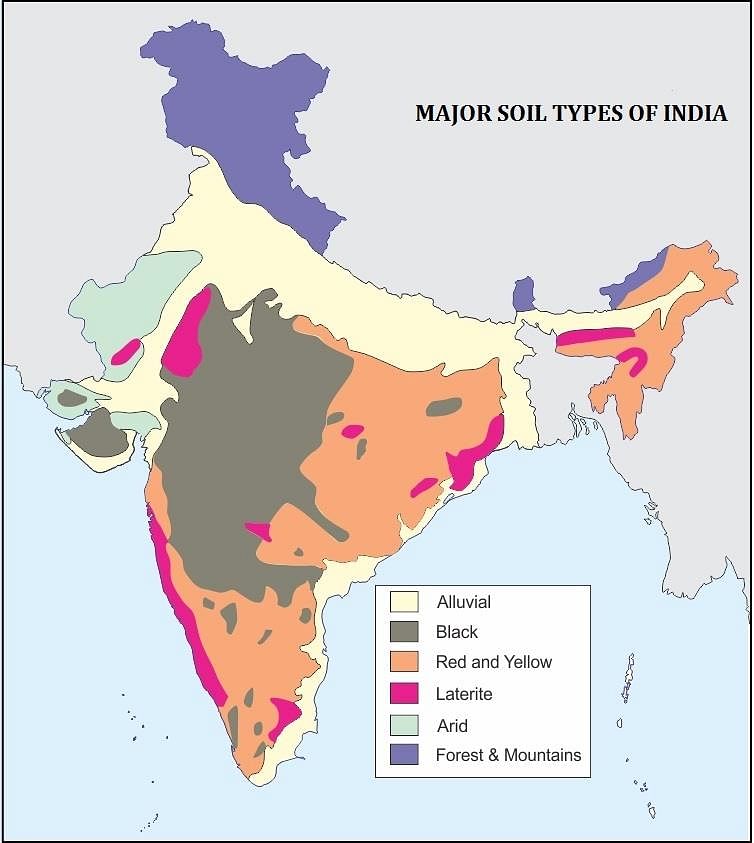
- India has varied relief features, landforms, climatic realms and vegetation types. These have contributed in the development of various types of soils in India.

- On the basis of genesis, colour, composition, and location, the soils of India have been classified into:
Alluvial soils
Black soils
Red and Yellow soils
Laterite soils
Arid soils
Saline soils
Peaty soils
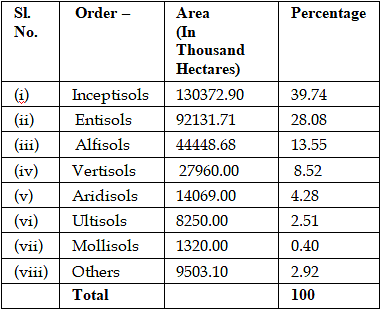
Forest soils - ICAR has classified the soils of India into the following order as per the USDA soil taxonomy
Alluvial Soils
- Alluvial soils are widespread in the northern plains and the river valleys. These soils cover about 40 percent of the total area of the country. They are depositional soils, transported and deposited by rivers and streams.
- Through a narrow corridor in Rajasthan, They extend into the plains of Gujarat. In the Peninsular region, they are found in deltas of the east coast and in the river valleys.
- The alluvial soils vary in nature from sandy loam to clay. They are generally rich in potash but poor in phosphorous.
- In the Upper and Middle Ganga plain, two different types of alluvial soils have developed, viz. Khadar and Bhangar. Khadar is the new alluvium and is deposited by floods annually, which enriches the soil by depositing fine silts.
- Bhangar represents a system of older alluvium, deposited away from the flood plains. Both the Khadar and Bhangar soils contain calcareous concretions (Kankars).
- These soils are more loamy and clayey in the lower and middle Ganga plain and the Brahmaputra valley. The sand content decreases from the west to the east.
- The colour of the alluvial soils varies from light grey to ash grey. Its shades depend on the depth of the deposition, the texture of the materials, and the time taken for attaining maturity. Alluvial soils are intensively cultivated.
Black Soils
- Black soil covers most of the Deccan Plateau which includes parts of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and some parts of Tamil Nadu.
- In the upper reaches of the Godavari and the Krishna, and the northwestern part of the Deccan Plateau, the black soil is very deep.
- These soils are also known as the ‘Regur Soil’ or the ‘Black Cotton Soil’. The black soils are generally clayey, deep, and impermeable.
- They swell and become sticky when wet and shrink when dried. So, during the dry season, these soils develop wide cracks.
- Thus, there occurs a kind of ‘self ploughing’. Because of this character of slow absorption and loss of moisture, the black soil retains the moisture for a very long time, which helps the crops, especially; the rain-fed ones, to sustain even during the dry season.
- Chemically, the black soils are rich in lime, iron, magnesia, and alumina. They also contain potash. But they lack phosphorous, nitrogen, and organic matter. The color of the soil ranges from deep black to grey.
Red and Yellow Soil
- Red Soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern part of the Deccan Plateau. Along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghat, a long stretch of area is occupied by red loamy soil. Yellow and red soils are also found in parts of Odisha and Chhattisgarh and in the southern parts of the middle Ganga plain.
- The soil develops a reddish color due to a wide diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks. It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form. The fine-grained red and yellow soils are normally fertile, whereas coarse-grained soils found in dry upland areas are of poor infertility. They are generally poor in nitrogen, phosphorous, and humus.
Laterite Soil
- Laterite has been derived from the Latin word ‘Later’ which means brick. The laterite soils develop in areas with high temperatures and high rainfall. These are the result of intense leaching due to tropical rains. With rain, lime and silica are leached away, and soils rich in iron oxide and aluminum compounds are left behind. Humus content of the soil is removed fast by bacteria that thrive well in high temperatures. These soils are poor in organic matter, nitrogen, phosphate, and calcium, while iron oxide and potash are in excess. Hence, laterites are not suitable for cultivation; however, the application of manures and fertilizers are required for making the soils fertile for cultivation.
- Red laterite soils in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Kerala are more suitable for tree crops like cashew nuts. Laterite soils are widely cut as bricks for use in house construction. These soils have mainly developed in the higher areas of the Peninsular plateau. The laterite soils are commonly found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
Arid Soil
Arid soils range from red to brown in colour. They are generally sandy in structure and saline in nature. In some areas, the salt content is so high that common salt is obtained by evaporating the saline water. Due to the dry climate, high temperature, and accelerated evaporation, they lack moisture and humus. Nitrogen is insufficient, and the phosphate content is normal. Lower horizons of the soil are occupied by ‘kankar’ layers because of the increasing calcium content downwards.
The ‘Kankar’ layer formation in the bottom horizons restricts the infiltration of water, and as such, when irrigation is made available, the soil moisture is readily available for sustainable plant growth. Arid soils are characteristically developed in western Rajasthan, which exhibits characteristics and topography. These soils are poor and contain little humus and organic matter.
Saline Soils
- They are also known as Usara soils. Saline soils contain a larger proportion of sodium, potassium, and magnesium, and thus, they are infertile and do not support any vegetative growth. They have more salts, largely because of the dry climate and poor drainage. They occur in arid and semi-arid regions, and in waterlogged and swampy areas. Their structure ranges from sandy to loamy.
- They lack nitrogen and calcium. Saline soils are more widespread in western Gujarat, deltas of the eastern coast, and in Sundarbans areas of West Bengal. In the Rann of Kuchchh, the Southwest Monsoon brings salt particles and deposits there as a crust. Seawater intrusions in the deltas promote the occurrence of saline soils.
- In the areas of intensive cultivation with excessive use of irrigation, especially in areas of the green revolution, the fertile alluvial soils are becoming saline. Excessive irrigation with dry climatic conditions promotes capillary action, which results in the deposition of salt on the top layer of the soil. In such areas, especially in Punjab and Haryana, farmers are advised to add gypsum to solve the problem of salinity in the soil.
Peaty Soils
- They are found in areas of heavy rainfall and high humidity, where there is a good growth of vegetation.
- Thus, a large quantity of dead organic matter accumulates in these areas, and this gives rich humus and organic content to the soil. Organic matter in these soils may go even up to 40-50 percent.
- These soils are normally heavy and black in color. In many places, they are alkaline also.
- It occurs widely in the northern part of Bihar, the southern part of Uttaranchal, and the coastal areas of West Bengal, Orissa, and Tamil Nadu.
Forest Soils
Soil Degradation
In a broad sense, soil degradation can be defined as the decline in soil fertility, when the nutritional status declines and the depth of the soil goes down the erosion and misuse.
 Soil degradation is the main factor leading to the depleting soil resource base in India.
Soil degradation is the main factor leading to the depleting soil resource base in India.- The degree of soil degradation varies from place to place according to the topography, wind velocity, and amount of rainfall.
Soil Erosion
Soil Erosion refers to the wearing away of a field's topsoil by the natural physical forces of water and wind.
- The destruction of the soil cover is described as soil erosion.
- The soil-forming processes and the erosional processes of running water and wind go on simultaneously.
- But generally, there is a balance between these two processes. The rate of removal of fine particles from the surface is the same as the rate of addition of particles to the soil layer.
- Sometimes, such a balance is disturbed by natural or human factors, leading to a greater rate of removal of soil. Human activities too are responsible for soil erosion to a great extent.
- As the human population increases, the demand for land also increases. Forest and other natural vegetation are removed for human settlement, for cultivation, for grazing animals, and for various other needs.
- Wind and water are powerful agents of soil erosion because of their ability to remove soil and transport it.
Causes of Soil Erosion
Wind Erosion
Wind erosion is a natural process that moves soil from one location to another by wind power
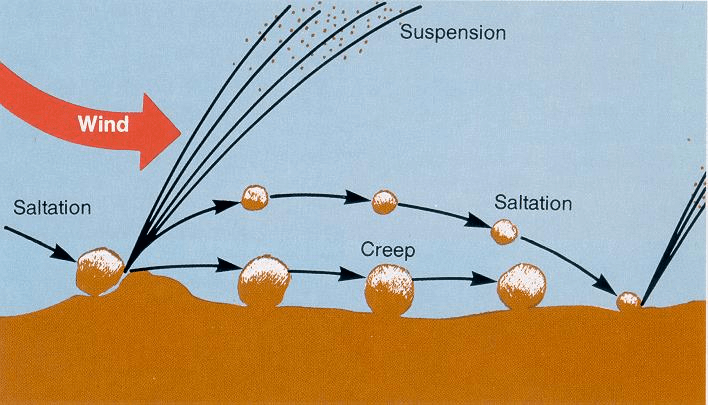
- Wind erosion is significant in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Wind erosion can be caused by a light wind that rolls soil particles along the surface through to a strong wind that lifts a large volume of soil particles into the air to create dust storms
- In regions with heavy rainfall and steep slopes, erosion by running water is more significant.
Water Erosion
Water erosion is the removal of soil by water and transportation of the eroded materials away from the point of removal.
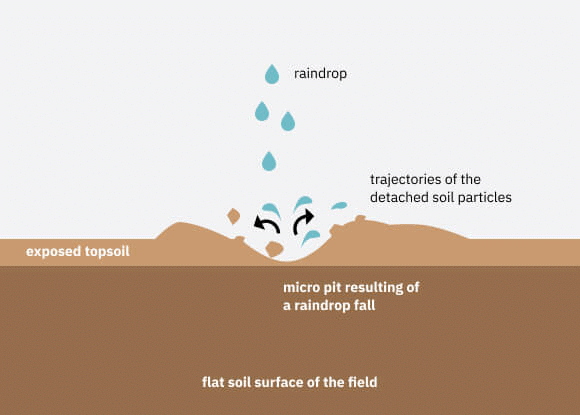
- Water erosion which is more serious and occurs extensively in different parts of India takes place mainly in the form of sheet and gully erosion.
- Sheet erosion takes place on level lands after a heavy shower and the soil removal is not easily noticeable.
- But it is harmful since it removes the finer and more fertile topsoil.
- Gully erosion is common to steep slopes.
- Gullies deepen with rainfall, cut the agricultural lands into small fragments, and make them unfit for cultivation.
- A region with a large number of deep gullies or ravines is called a badland topography.
- Ravines are widespread, in the Chambal basin. Besides this, they are also found in Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. The country is losing about 8,000 hectares of land to ravines every year.
Deforestation
Deforestation, clearance, clearcutting, or clearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use.
- Deforestation is one of the major causes of soil erosion. Plants keep soils bound in locks of roots, and thus, prevent erosion.
- They also add humus to the soil by shedding leaves and twigs. Forests have been denuded practically in most parts of India but their effect on soil erosion is more in hilly parts of the country.
- A fairly large area of arable land in the irrigated zones of India is becoming saline because of over-irrigation.
- The salt lodged in the lower profiles of the soil comes up to the surface and destroys its fertility.
- Chemical fertilizers in the absence of organic manures are also harmful to the soil. Unless the soil gets enough humus, chemicals harden it and reduce its fertility in the long run.
- This problem is common in all the command areas of the river valley projects, which were the first beneficiaries of the Green Revolution. According to estimates, about half of the total land of India is under some degree of degradation.
- Every year, India loses millions of tonnes of soil and its nutrients to the agents of its degradation, which adversely affects our national productivity. So, it is imperative to initiate immediate steps to reclaim and conserve soils.
Measures Adopted to Reduce Soil Erosion
Contour binding, Contour terracing, regulated forestry, controlled grazing, cover cropping, mixed farming, and crop rotation are some of the remedial measures which are often adopted to reduce soil erosion.
|
180 videos|475 docs|198 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Soils- 1 - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the factors affecting the formation of soil? |  |
| 2. What is soil erosion and what causes it? |  |
| 3. What are black soils and where are they found? |  |
| 4. How does deforestation contribute to soil erosion? |  |
| 5. How can soil degradation be prevented? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
 Soil degradation is the main factor leading to the depleting soil resource base in India.
Soil degradation is the main factor leading to the depleting soil resource base in India.

















