Shankar IAS Summary: Indian Biodiversity Diverse Landscape | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Fact
- India is rich in biodiversity and associated traditional knowledge.
- India accounts for nearly 7% of the recorded species even while supporting almost 18% of human population.
INDIA REPRESENTS:
(i) Two 'Realms
- Biogeographic realms are large spatial regions within which ecosystems share a broadly Similar biota. Realm is a continent or sub- continent sized area with unifying features of geography and fauna & flora
- the Himalayan region represented by Palearctic Realm and the rest of the sub-continent represented by Malayan Realm
In world eight terrestrial biogeo graphic realms are typically recognized.
They are
- Nearctic realm, Palaearctic realm,
- africotropical realm,
- indomalayan realm
- Oceania realm
- Australian realm,
- Antarctic realm,
- Neotropical realm
(ii) Biomes of India: The term biome means the main groups of plants and animals living in areas of certain climate patterns.
(iii) The five biomes of India are:
- Tropical Humid Forests
- Tropical Dry or Deciduous Forests (including Monsoon Forests)
- Warm deserts and semi-deserts
- Coniferous forests and
- Alpine meadows.
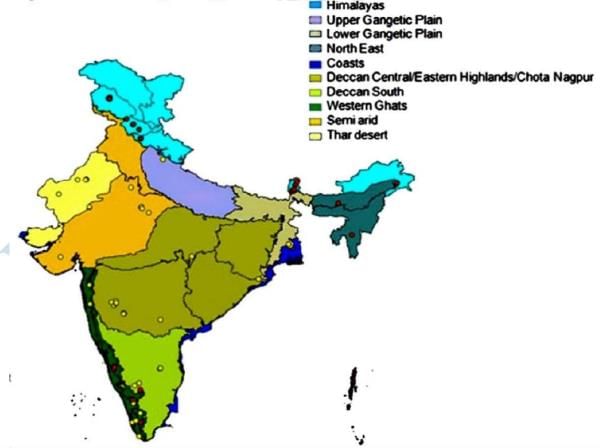
(iv) Bio-geographic Zones
- Trans-Himalayas - An extension of the Tibetan plateau, harboring high-altitude cold desert in Laddakh (J&K) and Lahaul Spiti (H.P) comprising 5.7 % of the country's landmass. East to west parallel to Himalayas
- Himalayas - The entire mountain chain running from north-western to north-eastern India,
- Desert- The extremely arid area west of the Aravalli hill range, comprising both the salty desert of Gujarat and the sand desert of Rajasthan. 6.9% of the country's landmass
- Semi-arid- The zone between the desert and the Deccan plateau, including the Aravalli hill range 15.6 % of the country's landmass. Western ghats-The hill ranges and plains running along the western coastline, south of the Tapti river,
- Deccan peninsula- The largest of the zones, covering much of the southern and south Central plateau with pre-dominantly deciduous vegetation. 4.3 % of the country’s landmass.
- Gangtic plain- Defined by the Ganges river system, these plains are relatively homogenous.
- North-east India- The plains and non-Himalayan hill ranges of northeastern India, with a wide variation of vegetation. 5.2% of the country's landmass.
- Islands- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal, with a highly diverse set of biomes.
- Coasts- A large coastline distributed both to the west and east, with distinct differences between the two;
- India further divided into 25 biogeo graphic provinces.
(v) Vertebrates-
- Vertebrates are animals with backbones and spinal columns. Vertebrates are the most advanced organisms on Earth.
- Although vertebrates represent only a very small percentage of all animals, their size and mobility- often allow them to dominate their environment. Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles, Ayes, Mammals
(vi) Invertebrates
- Do not have backbones.
- More than 98% animal species in the world are invertebrates, don’t have an internal skeleton made of bone.
- Many invertebrates have a fluid-filled, hydrostatic skeleton, like the jelly fish or worm. Others have a hard outer shell, like insects and crustaceans.
(vii) Annelids
- Have bodies that are divided into Segments.
- Very well-developed internal organs.
- Found almost anywhere in the world, don't have any limbs. E.g-earthworms, leeches, roundworms.
(viii) Molusks
- Have a soft, skin-like organ covered with a hard outside shell.
- Some mollusks live on land, such as the snail and slug.
- Other mollusks live in water, such as the oyster, mussel, clam, squid and octopus.
(ix) Echinoderms
- Are marine animals.
- Most echinoderms have arms or spines that radiate from the center of their body. Common echinoderms include the sea star, sea urchin, sand dollar and sea cucumber.
- Protozoa, Arthropods, Crustaceans, Insects, Arachnids are the other Invertebrates.
FLORAL DIVERSITTY
(i) Algae
- The green non differentiated plants (non -differentiated into organs like root, stem and leaf.) possessing chlorophyll is known as Algae.
- The fresh-water algae are generally green or blue-green in colour, whereas the marine ones are red or brown. These are autotrophic plants, as they can manufacture their own food.
(ii) Fungi:
- Non-green non differentiated plants characterized by total absence of chlorophyll are called Fungi.
- Moulds and mushrooms are the familiar examples of saprophytic fungi.
- The maximum diversity of fungi is in the Western Ghats followed by the eastern Himalaya and the western Himalaya.
(iii) Bacteria
- Non-chlorophyllous micro-organisms which lead saprophytic or parasitic existence. Many of them are pathogenic;
- Saprophytic bacteria are rather beneficial. They are soil borne and many of them are used in industries.
(iv) Lichens
- A peculiar combination of an alga and a fungus -the two live deriving mutual benefit. They are group of greyish green plants which grow on rocks, three-trunks, dead wood, etc.
- The algae manufactures carbohydrate food which becomes available to the fungus, and the latter absorbs and retains water and -thus keeps the algal cells moist. So it is a nice example of symbiosis.
(v) Bryophvtes
- The plant body is differentiated into a small stem and simple leaves, but true roots are absent They usually grow in moist places. E.g. Liverworts, mosses
- They are the second largest group of green plants in India distributed largely in Eastern Himalaya, North-eastern India, Western Himalaya and the Western Ghats.
- Mosses constitute the major component of Indian bryo flora followed by liverworts and bornworts
(vi) Pteridophvtes
Have well-differentiated plant bodies, consisting of roots, stems and leaves. Moreover, they possess vascular bundles.
(vii) Gymnosperms
- Gymnosperms (gymnos-naked, sperma-seed) are the naked-seeded plants
- They have very simple flowers without accessory whorls and the microsporophylls (stamens) and megas porophylls (carpels) remain aggregated in cones.
(viii) Angiosperms:
- Angiosperms (angeion=a case) are the closed seeded plants.
- These are the most highly developed plants which bear flowers having conspicuous accessory and essential whorls.
- Carpels have the ovary, style and stigma
(ix) Crop genetic diversity
The national gene bank at National Bureau Of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR), Delhi is primarily responsible for conservation of unique accessions on long-term basis, as base collections for posterity, predominantly in the form of seeds
(x) Livestock genetic diversity
India ranks first in buffaloes, second in cattle and goats, third in sheep, fourth in ducks, fifth in chicken and sixth in camels in the world.
WILDLIFE OF INDIA
(i) Himalayan foothills
- Flora: Natural monsoon evergreen and semi-evergreen forests; donminant species are Sal, silk-cotton trees, giant bamboos; tall grassy meadow with savannahs in tarai.
- Fauna: Includes big mammals of like elephant, sambar, swamp deer, cheetal, hog deer, barking deer, wild boar tiger, panther, wild dogs, hyena, black bear, sloth bear, porcupine, Great Indian one-horned rhinoceros, wild buffalo, gangetic gharial, golden langur.
(ii) Western Himalayas (High altitude region)
- Flora: Natural monsoon evergreen and semi-evergreen forests; rhododendrons; dwarf hill bamboo and birch forests mixed with alpine pastures.
- Fauna: Wild ass, wild goats (thar, markhor, ibex) and sheep (Nayan, Marcopolo’s sheep, bharal or blue sheep) ; antelopes (Chiru and Tibetan gazelle), deers (hangul of Kashmir stag and shou or Sikkim stag, musk deer); marmots and pikas or mouse hares; golden eagle, snow partridges; snow leopard, wolf, fox, cats, black and brown bears; birds like Himalayan monal pheasant, western trogopan, Koklass, whitecrested khalij cheer pleasant; Griffon vultures, lammergiers, choughs, ravens.
(iii) Eastern Himalayas
- Flora- Oaks, magnolias, laurels and birches covered with moss and ferns; coniferous forests of pine, fir, yew and junipers with undergrowth of scrubby rhododendrons and dwarf bamboos; lichens, moses, orchids, and other epiphytes dominant (due to high humid and high rainfall).
- Fauna- Red panda, hog badgers forest badgers, crestless porcupines, goat antelopes (Scrow, Goral, Takins).
(iv) Peninsular India
- It is home to tropical moist deciduous to tropical dry deciduous and scrub vegetation depending upon the variation in rainfall and humidity.
- Flora: Sal in north and east extensions (higher rainfall) and teak in southern plateau are dominant trees
- West Ghats have evergreen vegetation (flora and fauna similar to evergreen rainforests of north eastern of India
- In dry areas of Rajasthan and Aravalli hills, trees are scattered and thorny serub species predominate. The forests give way to more open savannah habit.
- Fauna: Elephant, wild hoar, deers (cheetal or axis deer), hog deer swamp deer or barasinga, Sambar, muntjak or barking deer, antelopes (four- hourned antelope, nilgai, blackbuck, chinkara gazelle), wild dog or dhole, tiger, leopard, cheetah, lion, wild pig, monkey, striped hyena, jackal, gaur
(v) Indian desert
- Flora: Thorny trees with reduced leaves; cacti, other succulents are the main plants.
- Fauna: Animals are mostly burrowing ones. Among mammals rodents are the largest group. The Indian desert gerbils are mouse like, rodents, other animals are, wild ass, black buck, desert cat, caracal, red fox; reptiles (snakes, lizards and tortoise) well represented. Desert lizards include agamids, lacertids and geckos.
- Among birds the most discussed is Great Indian bustard.
(vi) Tropical rain forest region
- Distributed in areas of western ghats and north east India.
- Flora: Extensive grass lands interspersed with densely forested gorges of evergreen vegetation known as sholas occur in the Nilgiris (an offshoot of western ghats) The rain forests of the Western ghats have dense and lofty trees with much species-diversity. Mosses, ferns, epiphytes, orchids, lianas and vines, herbs, shrubs make diverse habitat.
- Ebony trees predominate in these forests. A variety of tropical orchids are found. Stratification in rain forests is very distinct-three horizontal layers are distinguished.
- Fauna- There are wild elephants, gaur and other larger animals. Most species are tree dwellers.
- The most prominent are hoolock gibbon (only ape found in India), golden langur, capped langur or leaf monkey, Assam macaque and the pig-tailed macaque, lion-tailed macaque, Nilgiri langur slender loris, bats, gaint squirrel, civets, flying squirrels, Nilgiri mongoose, spiny mouse
(vii) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Flora. These are home for tropical rain forests among marine mammals there are dugong false killer whale, dolphin. Among birds are rare one is Narcondum hornbill.
- Nicobar pigeon and megapode. There are also other birds like white-bellied sea-eagle, white breasted swift let and several fruit pigeons
|
98 videos|188 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Indian Biodiversity Diverse Landscape - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the floral diversity of India? |  |
| 2. What are the key factors contributing to India's floral diversity? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of India's wildlife? |  |
| 4. How does India's diverse landscape contribute to its wildlife? |  |
| 5. What are some conservation measures taken to protect India's biodiversity? |  |



















