Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 7 | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE 087)
CLASS X – SESSION 2019-20
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
i. The question paper has 35 questions in all.
ii. Marks are indicated against each question.
iii. Questions from serial number 1 to 20 are objective type questions. Each question carries one mark. Answer them as instructed.
iv. Questions from serial number 21 to 28 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
v. Questions from serial number 29 to 34 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 120 words each.
vi. Question number 35 is a map question of 6 marks with two parts - 35 a. from History (2 marks) and 35b. from Geography (4 marks).
SECTION – A VERY SHORT ANS. QUESTIONS
Q.1. Association of producers who controlled production and trade of goods in Europe during 17th century were known as ________ . (1 Mark)
Or
Rin derpest was a fast spreading cattle disease that had an impact on the life and economy of the people of ________ .
Ans: Trade Guilds
Or
Africa
Q.2. What is a mineral ? (1 Mark)
Ans: Mineral is a “homogeneous” naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
Q.3. When did Jallianwala Bagh incident take place? (1 Mark)
(a) 13th April 1919
(b) 19th April 1920
(c) 18th April 1919
(d) 15th March 1920
Ans: (a) 13th April 1919
Q.4. In Belgium, how were the tensions between the linguistic communities controlled? (1 Mark)
(a) By an agreement made between the majority and minority groups.
(b) By accepting a federal style of government.
(c) By making amendments to the Constitution of Belgium.
(d) By the minority group accepting the dominance of the majority groups.
Ans: (c) By making amendments to the Constitution of Belgium
Q.5. Match the column: (1 Mark)
Ans: 1.(c), 2.(a), 3.(d), 4.(b)
Q.6. How do we calculate Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country ? (1 Mark)
Ans: The sum of production in the three sectors gives the Gross Domestic Product of a country.
Q.7. Complete the following table with correct information with regard to Iron-Ore : (1 Mark)
Ans: (A) Magnetite (B) Odisha
Q.8. Madhav has no regular work. Sometimes he earns a little with some part-time work. He also has no investment capability to use own skills to earn money. Which sector is Madhav engaged in? (1 Mark)
Ans: Madhav is engaged in the unorganised tertiary sector.
Q.9. Which of the following is a Kharif crop ? (1 Mark)
(i) Cotton
(ii) Paddy
(iii) Jute
(iv) Maize
(a) Only (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (ii) and (Hi)
(c) Only (Hi) and (iv)
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Q.10. Which of the following is the biggest port in India ? (1 Mark)
(a) Chennai
(b) Kolkata
(c) Kochi
(d) Mumbai
Ans: (d) Mumbai
Q.11. 
Which of the following leader is shown in this cartoon? (1 Mark)
(a) Rajiv Gandhi
(b) I. K. Gujaral
(c) H. D. Deve Gowda
(d) A. B. Vajpayee
Ans: (d) A.B. Vajpayee
Q.12. Correct the following statement and rewrite : (1 Mark)
In 1916, Gandhiji travelled to Dandi in Bihar to inspire the peasants to struggle against oppressive Zamindars.
Or
A Khilafat Committee was formed under the leadership of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, Mohammad Ali Jinnah and Hasrat Mohani.
Ans: In 1916, Gandhiji travelled to Champaran in Bihar to inspire the peasant to struggle against oppressive indigo planters.
Or
A Khilafat Committee was formed under the leadership of Maulana Azad, Hakim Ajmal Khan and Hasrat Mohani.
Q.13. Apart from the Central and the State governments, which is the third type of government practised in Belgium ? (1 Mark)
(a) Local government
(b) Municipal government
(c) Community government
(d) Ethnic government
Ans: (c)
Q.14. _______ means when exports are more than imports. (1 Mark)
Ans: Favourable balance of trade
Q.15. Which of the following does not constitute a part of informal credit in India ? (1 Mark)
(a) Commercial Bank
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Friends and relatives
(d) Zamindars
Ans: (a) Commercial Bank
Q.16. Match the following items given in Column I with those in Column II. (1 Mark)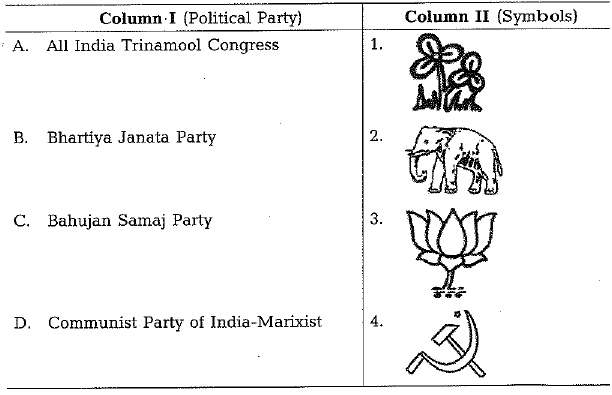
Ans: A - 1, B - 3 , C - 2 , D - 4
Q.17. Assertion (A) : Different people have different developmental goals.
Reason (R): The capitalist approach to development is detrimental to poor section of the society. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Or
Assertion (A): Non renewable resources are abundant in nature.
Reason (R): Renewable resources can be replenished over a period of time.
(а) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Ans: (b) Or (d)
Q.18. The total geographical area of India is 4.28 million sq. km. [True/False] (1 Mark)
Ans: False.
Q.19. In the question given below, there are two examples - statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option : (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Under MGNREGA 2005, all those who are able to , and are in need of work in rural areas are guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year.
Reason (R): The Central Government in India made a law implementing the Right to work in about 625 districts of India,
Options:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) Both (A) and (B) are wrong.
Ans: Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Q.20. In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
Assertion (A) MNCs are attracted to India for making investments.
Reason (R) India has abundant natural resources, skilled professionals and educated English speaking people.
Options
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is wrong.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Ans: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
SECTION – B SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.21. What were the factors which were responsible for the end of the Bretton Woods system ? (3 Mark)
Or
“The modern industrialisation could not marginalise the traditional industries in England.” Justify the statement with any four suitable arguments.
Ans: (i) The Decline of US Currency : After 1960s, the US was no longer the dominant economic power as it had been for more than two decades. The US dollar now no longer commanded confidence as the world’s principal currency. The dollar could not maintain its value in relation to gold.
(ii) New powers : By the mid-1960s, the E.E.C, and Japan had become international economic powers in their own right.
(iii) Rise of Western Commercial Banks : From the mid 1970’s most of the developing nation were being forced to borrow from Western Commercial Banks instead of international financial institutions. This led to periodic debt crises in the developing world and lower income along with increased poverty, especially in Africa and Latin America.
Or
(i) Expensive new technology : New technologies and machines were expensive, so. the producers and the industrialists were cautious about using them.
(ii) Costlier repair : The machines often broke down and the repair was costly.
(iii) Less effective : The newly invented machines were not as effective as their inventors and manufacturers claimed.
Q.22. Describe the main features of plantation agriculture. (3 Mark)
Ans: (i) It is a single crop farming because a single crop is grown on a large area.
(ii) It is a capital intensive agriculture.
(iii) The produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
(iv) It needs good managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilisers, irrigation, transport facilities and communication network.
(v) Tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana are important plantation crops.
(vi) Some plantations like tea, coffee and rubber have a processing factory within farm itself or close to it.
Q.23. Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follows: (3 Mark)
Source- A The Revolutionaries
During the years following 1815, the fear of repression drove many liberal-nationalists underground. Secret societies sprang up in many European states to train revolutionaries and spread their ideas. To be revolutionary at this time meant a commitment to opposed monarchical forms that had been established after the Vienna Congress, and to fight for liberty and freedom. Most of these revolutionaries also saw the creation of nation-states as a necessary part of this struggle for freedom.
Source- B Italy Unified
Like Germany, Italy too had a long history of political fragmentation. Italians were scattered over several dynastic states as well as the multi-national Habsburg Empire. During the middle of the nineteenth century, Italy was divided into seven states, of which only one, Sardinia-Piedmont, was ruled by an Italian princely house. The north was under Austrian Habsburgs, the centre was ruled by the Pope and the southern regions were under the domination of the Bourbon kings of Spain. Even the Italian language had not acquired one common form and still had many regional and local variations.
Source- C Visualising the Nation
While it is easy enough to represent a ruler through a portrait or a statue, how does one go about giving a face to a nation? Artists in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries found a way out by personifying a nation. In other words they represented a country as if it were a person. Nations were then portrayed as female figures. The female form that was chosen to personify the nation did not stand for any particular woman in real life; rather it sought to give the abstract idea of the nation a concrete form. That is, the female figure became an allegory of the nation.
Source- A The Revolutionaries
(1) Why were the different secret societies founded in Europe during the years following 1815 ?
Source- B Italy Unified
(2) Which part of Italy was ruled by an Italian Princely house?
Source- C Visualising the Nation
What is an allegorv ?
Ans: (1) Source-A The Revolutionaries
During the years after 1815, different secret societies were founded to train revolutionaries and spread their ideas.
(2) Source-B Italy Unified
Sardinia - Piedmont was ruled by an Italian princely house.
(3) Source-C Visualising the Nation
When an abstract idea is expressed through a female figure, specially for a nation is called an allegory.
Q.24. What is the role of an opposition party in a democracy? (3 Mark)
Or
What efforts have been made to reform political parties in India?
Ans: An opposition party plays a very important role in a democracy as :
(i) It acts as pressure group and mobilises the government into action if the government does not take action on a serious issue.
(ii) It keeps a check on the working of the ruling party so that the ruling party functionaries take their duties seriously.
(iii) It gives its own views in Parliament and criticises the government for its failure or wrong policies.
Or
The following efforts have been made to reform political parties in India :
(i) The Supreme Court has passed an order to reduce the influence of money and criminal activities on political parties.
(ii) The Constitution was amended to prevent MLAs and MPs from changing parties after elections.
(iii) The Election Commission has passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their income tax returns regularly.
Q.25. Distinguish between a regional and a national party. (3 Mark)
Or
Distinguish between a political party and a pressure group.
Ans: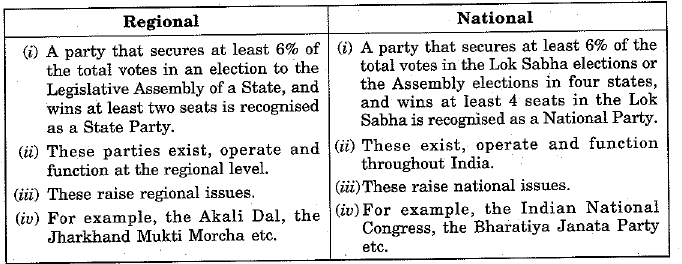

Q.26. “Average income is useful for comparison, but it may bide disparities.” Support the statement with suitable arguments. (3 Mark)
Or
Highlight any three differences between intermediate goods and final goods.
Ans: It is true that while 'averages’ are useful for comparison, they also hide disparities. It is clear from the table given below ;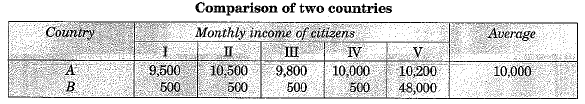
In both the cases in the table, average income in both countries is Rs. 10,000. However, if a choice is given, a person will like to live in country A because in this country people are neither very rich nor extremely poor.
On the other hand, most citizens in country B are poor and one person is extremely rich. Hence, while average income is useful for comparison, it hides disparities and does not show how the income is distributed.
Or
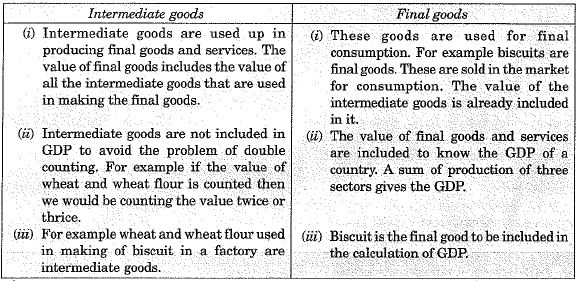
Three differences between the intermediate and final goods are as mentioned below :
Q.27. Explain the role of education and health in the overall development of a country. (3 Mark)
OR
Besides income, what can be the other attributes to compare economic development?
Ans: (i) Role of Education : It plays a vital role ih the overall development of a human being and society, therefore stress on imparting education has been given in our Constitution.
(ii) Role of Health : The general health standard in India is quite low. This is quite inevitable as nearly one-fourth of the population lives below the poverty line.
(iii) A community based programmes on healthcare and medical services in rural areas has been launched. As a result of these efforts, there has been a fall in the incidence of certain diseases like tuberculosis, leprosy and polio.
OR
Income is not only the criterion but it is one of the important indicators of economic development.
Some of the other attributes are:
(i) Infant Mortality Rate : It is an indicator of the availability of doctors and medical facilities in the region as well as the awareness of the people living there in regard to diseases and their prevention. Low infant mortality rate indicates good medical facilities arid all-round development in the society. A high rate will be economic loss for the region as much effort is wasted, which could have been harnessed.
(ii) Literacy Rate: This is an indicator of the number of schools and teachers available in a region and it also indicates whether the facilities are being used or not due to societal pressures. Low literacy rate exhibits backwardness and slow economic development.
(iii) Life Expectancy: This is also an indicator of available health facilities. Low life expectancy will be a hindrance to economic development.
Q.28. Why is there overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world? Explain. (3 Mark)
Ans: There is overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world because we generally think that democracy can address all socio-economic and political problems. However, our expectations from democracy are not always fulfilled. Sometimes it may work slowly, less efficiently, having a poor response or not working cleanly. But, in democracy, regular and free elections are held. Also, there is always scope for open public debate. The government is the people's own government as it has been elected by them. People wish to be ruled by the people they have elected. They also feel that this form of government is best for their country, thus, giving it overwhelming support.
SECTION – C LONG ANS. QUESTIONS
Q.29. How does foreign trade play ara important role in integrating the markets across the countries ? Explain. (5 Mark)
Or
What is liberalisation ? What steps were taken by the government to liberate the Indian economy ?
Ans: (i) Main channel for connecting countries: Since time immemorial foreign trade has been the main channel connecting countries and the markets.
(ii) Expansion of local market : To put it simply, foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world.
(iii) Better choice for the buyers : With the expansion of trade, the choice of goods in the market rises. Consumers get more variety and quality goods at cheaper rates. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
(iv) Impact on prices : With the expansion of market the prices of similar goods in the two markets tend to become equal.
(v) Competition : Trade promotes competition both within as well as outside the nation. Producers of different countries now closely compete against each other even though they are separated by thousands of miles.
(vi) Trade and globalisation : Trade is the most important component of globalisation. Trade has played a very important role in stimulating the process of globalisation. .
Or
“Liberalisation of the economy means to free it from direct or physical controls imposed by the government.” For this, the following steps were taken :
(i) All industries except three industries were exempted from any kind of industrial licensing. ‘
(ii) Under the policy of liberalisation, industries are free to expand and produce according to the need of the market.
(iii) Now producers are free to import the machinery and raw material from abroad.
(iv) Now the industry is also free to import modem technology from other countries.
Q.30. Why did Mahatma Gandhi give the call for ‘Civil Disobedience Movement’ ? (5 Mark)
How did this movement unite the country ? Explain.
Or
How did non-cooperation movement spread in cities ? Why did it gradually slow down ?
Ans: (a) Gandhiji started the Civil Diobedience Movement due to the events as mentioned below :
(i) Boycott of Simon Commission.
(ii) Announcement of Lord Irwin in October 1929.
(1) In October 1929 in order to win over Congress and the Muslim League, Lord Irwin Viceroy made an offer of ‘dominion status’ for In d ia in an unspecified future.
(2) He also stated that a Round Table Conference would be held to discuss a future constitution for India. These actions of Lord Irwin could not satisfy the radicals within the Congress.
(iii) Subhash Chandra Bose and Jawaharlal Nehru became more assertive.
(iv) Under these conditions at Lahore Congress session resolution for complete independence was passed in Dec. 1929.
(b) Gandhiji found in salt a powerful symbol that could unite the nation. Salt was something consumed by the rich and the poor a like, and it was one of the most essential items of food. Besides salt law, Gandhiji made his demands wide ranging so that everyone could be brought together in a united campaign.
Or
(a) In the towns, middle classes participated in the movement in the following ways :
(i) Students left the schools and colleges. Headmasters and teachers resigned. Lawyers gave up their practice.
(ii) Elections were boycotted except in Madras, where Justice Party, took part in elections because it was a party of non-Brahmans and felt that entering the Council was one way of gaining some power - something that usually only Brahmans had access to.
(iii) Foreign goods were boycotted.
(iv) Liquor shops were picketed.
(v) Foreign clothes were burnt in huge bonfires.
(vi) Many traders refused to import foreign cloth or trade in foreign goods.
(vii) The movement in the cities gradually slowed down for the reasons as given below :
(b) (i) Khadi was often more expensive than mass produced mill cloth and poor people could not afford to buy it.
(ii) Similarly the boycott of British institutions failed because to be successful alternative Indian institutions could not be set up in place of the British ones.
(iii) The lawyers too joined back work in government courts.
Q.31. Why is energy needed? How can we conserve energy resources? Explain. (5 Mark)
Ans: Energy is required for all activities. It is needed to cook, to provide light and heat, to propel vehicles and to drive machinery in industries.
We can conserve energy resources by:
(i) Developing a sustainable path of energy development, i.e. energy development but not at the cost of environment or needs of future generation.
(ii) Judicious use of limited energy resources.
(iii) Wastage of minerals should be minimised.
(iv) Modern technology should be used for the exploitation of energy resources,
(v) Export of energy resources should be minimised.
Q.32. "At first the rich peasants of Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat were enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement, but later they refused to participate." Analyse the statement. (5 Mark)
Ans: The rich peasant communities such as the Patidars from Gujarat and Jats from Uttar Pradesh were active in the Civil Disobedience Movement. As they were producers of commercial crops, they were hit hard by the trade depression and falling prices. As their cash income disappeared, they found it impossible to pay the government’s revenue demand. These rich peasants became enthusiastic supporters of the movement and also forced other people to join the movement. For them, the fight for Swaraj was a struggle against the payment of high revenues. They were highly disappointed when the movement was called off in 1931 without the revenue rates being revised. When the movement restarted in 1932 many of them refused to participate.
Q.33. How are deposits with the hanks beneficial for individual as well as for the nation ? Explain with examples. (5 Mark)
Ans: (i) It is a safer place to keep money as compared to the house or a working place.
(ii) People can earn interest on the deposited money.
(iii) People have the provisions to withdraw the money as and when they require.
(iv) People can also make payments through cheques.
(v) Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits with themselves and rest is extended as loan which is used for the overall development of nation.
Q.34. Highlight the contribution of public sector in the economic development of a country.
Or
Using examples from your area compare and contrast the activities and functions of private and public sectors. (5 Mark)
Ans: (i) In the public sector, the government owns most of the assets and provides all the services. Railways or post office is an example of the public sector.
(ii) The services which the private sector do not provide are provided by the public sector for the welfare of the public.
(iii) The public sector provides roads, bridges, railways, electricity. The government undertakes heavy spendings and ensure these facilities are available for everyone.
(iv) The government buys wheat etc. and sells at a lower price to consumers through ration shops in the interest of the poor people.
(v) The govt, takes responsibility of large number of activities such as running of schools and educational institutions. Similarly the government pays attention to aspects of human development such as safe drinking water, housing facilities etc. All the above activities help in the economic development of the country.
Or
The activities and functions of private and public sectors in our area may be compared as mentioned below: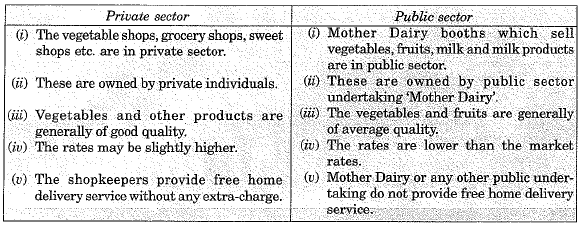
MAP SKILL BASED QUESTION
Q.35. Three features (a), (b) and (c) are marked on the given political outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked near them :
(a) The place where the Indian National Congress session was held in 1919. (2 Mark)
(b) The place from where Gandhiji organised Satyagraha in favour of Indigo planters, (2 Mark)
(c) The place where peasant satyagraha was held in Gujarat. (2 Mark) 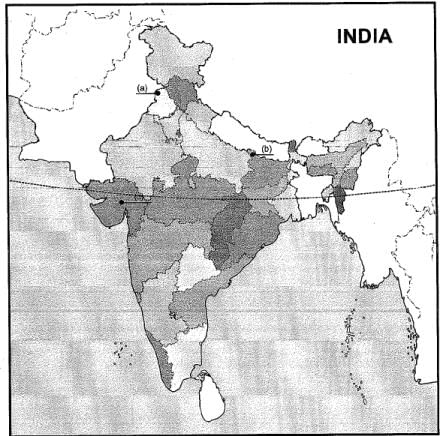
Ans: (a) Amritsar
(b) Charnparan
(c) Kheda
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2019-20) - 7 - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science? |  |
| 2. How can CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Social Science help students? |  |
| 3. Are the CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Social Science available online? |  |
| 4. Are the CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Social Science the same as the actual exam paper? |  |
| 5. Can solving CBSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10 Social Science guarantee good marks in the exam? |  |
















