Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts - 3 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page No - 80)
Question 22:
(a) Explain the pH change as the cause of tooth decay. How can tooth decay caused by pH change be
prevented?
(b) Explain how pH change in the lake water can endanger the lives of aquatic animals (like fish). What can be done to lessen the danger to the lives of aquatic animals in the lake?
Solution :
(a) Tooth decay starts when the pH of the acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5 because the acid becomes strong enough to attack the enamel of the teeth and corrode it. (b) The pH of lake water becomes lower because of too much acid rain. The high acidity of lake water can kill aquatic animals like fish since they can survive within a narrow range of pH change.
Calcium carbonate is added to acidic lake water to neutralize the acid and this prevents the fish from being killed.
Question 23:
(a) What happens during a bee sting? What is its remedy?
(b) What happens during a wasp sting? What is its remedy?
Solution :
(a) When a bee stings a person, it injects an acidic liquid into the skin which causes immense pain and irritation. Its remedy is to rub a mild base like baking soda solution on the stung are of the skin.
(b) When a wasp stings, it injects an alkaline liquid into the skin. Rubbing a mild acid like vinegar on the stung area of the skin gives relief.
Question 24:
(a) Why is it wrong to treat a bee sting with vinegar?
(b) Why is it wrong to treat a wasp sting with baking soda solution?
Solution :
(a) Since vinegar is acetic acid so it can’t be used to treat bee sting because bee injects acid into the skin.
(b) Since baking soda is basic in nature so it can’t be used to treat wasp sting because wasp injects alkaline liquid into the skin.
Question 25:
(a) What does the pH of a solution signify ? Three solutions A, B and C have pH values of 6, 4 and 10
respectively. Which of the solutions is highly acidic?
(b) A farmer has found that the pH of the soil in his fields is 4.2. Name any two chemical materials which he can mix with the soil to adjust its pH.
Solution :
(a) The pH of a solution signifies the concentration of hydrogen ions in it. Solution B is highly acidic since it has the lowest pH (pH = 4).
(b) Slaked lime or Chalk can be used to treat acidic soil.
Question 26:
(a) The pH values of six solutions A to F are given below :
A = 0, B = 11, C = 6, D = 3, E = 13, F = 8
Which of the above solutions are (i) acids (ii) alkalis ?
(b) Name the acids or alkalis used to make (i) car batteries (ii) explosives (iii) soaps (iv) fertilizers.
Solution :
(a) (i) Acids; A, C and D.
(ii) Alkalis; B, E and F.
(b) (i)Sulphuric acid.
(ii) Sulphuric acid.
(iii) Sodium hydroxide.
(iv) Nitric acid.
Question 27:
(a) The pH of a cold drink is 5. What will be its action on blue and red litmus solutions?
(b) The pH values of three acids A, B and C having equal molar concentrations are 5.0,2.8 and 3.5 respectively. Arrange these acids in order of the increasing acid strengths.
Solution :
(a) The cold drink turns blue litmus red because of its acidic nature. It will have no action on red litmus.
(b) A < C < B.B will have maximum acid strength because pH is inversely proportional to the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Question 28:
Under what soil conditions do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quicklime (calcium oxide), Or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) ?
Solution :
When the soil is too acidic, it is treated with bases like quicklime or slaked lime or chalk.
Question 29:
Which acid is produced in our stomach? What happens if there is an excess of acid in the stomach? How can its effect be cured?
Solution :
Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid. If there is excess of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, it causes indigestion which produces pain and irritation. Its effect can be cured by taking antacids.
Question 30:
The soil in a field is highly acidic. Name two materials which can be added to this soil to reduce its acidity. Give the reason for your choice.
Solution :
If the soil is too acidic, then it can be treated with materials like quicklime or slaked lime as these materials are bases and hence react with the excess acids present in the soil to reduce its acidity.
Question 31:
What is meant by strong bases and weak bases? Classify the following into strong bases and weak bases :
NH4OH, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2
Solution :
Strong base: A base which completely ionises in water and produces a large amount of hydroxide ions.
Weak base: A base which is partially ionised in water and produces a small amount of hydroxide ions.
Strong bases: NaOH , KOH
Weak bases : NH4OH , Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2
Question 32:
What ions are present in the solutions of the following substances? (write the symbols only)
- Hydrochloric acid
- Nitric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Sodium hydroxide
- Potassium hydroxide
- Magnesium hydroxide
Solution :
- H+, Cl –
- H+, NO32-
- H+, SO42-
- Na+, OH–
- K+, OH–
- Mg2+, OH–
Question 33:
(a) What would you expect the pH of pure water to be ?
(b) What colour would the universal indicator show in an aqueous solution of sugar ? Why?
(c) A sample of rainwater turned universal indicator paper yellow. What would you expect its pH to be? Is it a strong or a weak acid?
Solution :
(a) pH of pure water = 7
(b) Aqueous solution of sugar will turn the color of universal indicator green because sugar solution is neutral in nature.
(c) pH of the sample of rain water will be between 5 and 6. It is a weak acid.
Question 34:
(a) What do you think will be the pH in the stomach of a person suffering from indigestion : less than 7 or
more than 7 ?
(b) What do you think will be the pH of an antacid solution : less than 7 or more than 7 ?
(c) How does an antacid work ?
(d) Name two common antacids.
Solution :
(a) The pH in the stomach of a person suffering from indigestion will be l ess than 7 since indigestion is caused due to formation of excess acid in the stomach.
(b) Antacids are a group of mild bases so they have pH more than 7.
(c) Antacids react with excess acid in the stomach and neutralise it.
(d) Antacids: Magnesium hydroxide and Sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Question 35:
Separate the following into substances having pH values above and below 7. How do these influence litmus paper ?
- Lemon juice
- Solution of washing soda
- Toothpaste
- Vinegar
- Stomach juices
Solution :
Substances having pH values above 7: Solution of washing soda and toothpaste; They will turn red litmus paper blue due to their basic nature.
Substances having pH values less than 7: Lemon juice, vinegar and stomach juices; They will turn blue litmus paper red due to their acidic nature.
Question 36:
(a) Do basic solutions also have H+ (aq) ions ? If yes, then why are they basic ?
(b) When a solution becomes more acidic, does the pH get higher or lower ?
Solution :
(a) Yes, all basic solutions have H+ ions. They are basic because the concentration of hydrogen ions is much less than that of hydroxide ions.
(b) When a solution becomes more acidic, pH gets lower.
Question 37:
(a) Define an acid and a base. Give two examples of each.
(b) Give the names and formulae of two strong bases and two weak bases.
(c) What type of ions are formed :
(i) when an acid is dissolved in water ?
(ii) when a base (or alkali) is dissolved in water ?
(d) Write the neutralisation reaction between acids and bases in terms of the ions involved.
(e) Write any two important uses of bases.
Solution :
(a) Acids are those chemical substances which have a sour taste. Example: Acetic acid and citric acid.
Base is a chemical substance which has a bitter taste. Example: Caustic soda and washing soda.
(b) Strong bases – Sodium hydroxide, NaOH , potassium hydroxide (KOH).
Weak bases – Calcium hydroxide, Ca( OH2), ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH.
(c) ( i ) Hydrogen ions.
(ii) Hydroxide ions.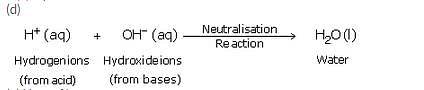
(e) Uses of bases:
(i) Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of soap, paper and rayon.
(ii) Calcium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of bleaching powder.
(Page No - 81)
Question 38:
(a) What happens when zinc granules are heated with sodium hydroxide solution ? Write equation of the
reaction which takes place.
(b) What happens when bases react with non-metal oxides ? Explain with the help of an example. What does this reaction tell us about the nature of non-metal oxides ?
Solution :
(a) When zinc granules are heated with sodium hydroxide solution, then sodium zincate salt and hydrogen gas are formed.

(b) When bases react with non-metal oxides, then salt and water are formed.
Example: Calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate and water.

Question 39:
(a) What effect does the concentration of H+ (aq) ions have on the nature of a solution ?
(b) What effect does the concentration of H– ions have on the nature of a solution ?
(c) Someone put some universal indicator paper into vinegar. The pH is 3. What does this tell you about the vinegar ?
(d) Someone put some universal indicator paper onto wet soap. The pH is 8. What does this tell you about the soap ?
(e) State whether a solution is acidic, alkaline or neutral if its pH is :
(i) 9 (ii) 4 (iii) 7 (iv) 1 (v) 10 (vi) 3
Solution :
(a) As the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, the solution becomes more acidic.
(b) As the concentration of hydroxide ions increases, the solution becomes more basic.
(c) Vinegar is acidic in nature.
(d) Soap is basic in nature.
(e) ( i ) pH = 9 : Alkaline.
(ii) pH = 4 : Acidic.
(iii) pH = 7 : Neutral.
(iv) pH = 1 : Acidic.
(v) pH = 10 : Alkaline.
(vi) pH = 3 : Acidic.
(Page No - 82)
Question 54:
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline ?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd ?
Solution :
(a) Milk is made slightly alkaline so that it may not become sour easily due to the formation of lactic acid in it.
(b) The alkaline milk takes a longer time to set into curd because the lactic acid being formed has to first neutralise the alkali present in it.
Question 55:
Which of the following elements would form oxides which would indicate pH values less than seven, using moist pH paper ?
Magnesium, Carbon, Sulphur, Hydrogen , Copper
Solution :
Carbon and Sulphur being non-metals form acidic oxides.
Question 56:
The pH values of five solutions A, B, C, D and E are given below :
A 1
B 5
C 7
D 11
E 13
Which solution is
- weakly alkaline
- neutral
- strongly acidic
- strongly alkaline, and
- weakly acidic ?
Solution :
- Weakly alkaline: D (pH = 11)
- Neutral : C (pH = 7)
- Strongly acidic: A (pH = 1)
- Strongly alkaline: E (pH = 13)
- Weakly acidic : B (pH = 5)
Question 57:
Potatoes grow well on Anhad’s farm which has soil with a pH of 5.5. Anhad decides to add lot of lime to soil so that he can grow broccoli in the same farm :
(a) Do potatoes grow better in acidic or alkaline soil ?
(b) Does broccoli grow better in acidic or alkaline soil ?
Solution :
(a) Potatoes grow better in acidic soil having pH = 5.5
(b) Broccoli grows better in a lkaline soil since adding a lot of lime to acidic soil will make it basic in nature.
Question 58:
Here are some results of solutions tested with universal indicator paper :
Sulphuric acid : Red
Metal polish : Dark blue
Washing-up liquid : Yellow
Milk of magnesia : Light blue
Oven cleaner : Purple
Car battery acid : Pink
Arrange the solutions in order of their increasing pH values (starting with the one with the lowest pH).
Solution :
Sulphuric acid < car battery acid < washing up liquid < milk of magnesia < metal polish < oven cleaner since:
Red : pH = 1
Pink : pH = 3-4
Yellow: pH = 5-6
Light blue : pH = 9
Dark blue : pH = 10
Purple: pH = 11
Question 59:
Solution A turns universal indicator blue to purple whereas solution B turns universal indicator orange to red.
(a) What will be the action of solution A on litmus ?
(b) What will be action of solution B on litmus ?
(c) Name any two substances which can give solutions like A.
(d) Name any two substances which can give solutions like B.
(e) What sort of reaction takes place when solution A reacts with solution B ?
Solution :
(a) Solution A turns universal indicator blue to purple so it is basic in nature and will turn litmus blue.
(b) Solution B turns universal indicator orange to red so it is acidic in nature and will turn litmus red.
(c) Milk of magnesia and sodium hydroxide solution are bases like solution A.
(d) Lemon juice and hydrochloric acid are acids like solution B.
(e) Neutralisation reaction.
Question 60:
A first-aid manual suggests that vinegar should be used to treat wasp stings and baking soda for bee stings. What does this information tell you about the chemical nature of:
(a) wasp stings ?
(b) bee stings ?
Solution :
(a) Wasp stings are alkaline in nature since they are treated using acids like vinegar.
(b) Bee stings are acidic in nature since they are treated using bases like baking soda.
Question 61:
(a) Explain why the pH in a person’s mouth becomes lower after each meal.
(b) What damage could be caused while the pH is low ?
(c) How could the person change his eating habits to lessen chances of suffering from tooth decay ?
Solution :
(a) T he pH in a person’s mouth becomes lower after each meal because bacteria present in the mouth breaks down the sugar to form acids.
(b) If the pH is low, the tooth starts decaying.
(c) A person can lessen the chances of suffering from tooth decay by changing his eating habits such as eating less of sugary foods like ice-creams, candies, sweets etc.
Question 62:
A group of students measured the pH of some substances they found in their homes. Their results are given in the following table :
| Substance | pH | Substance | pH |
| Apples | 3.0 | salt | 7.0 |
| Baking Soda | 8.5 | Sugar | 7.0 |
| Black Coffee | 5.0 | Toothpaste | 9.0 |
| Household Ammonia | 12.0 | Vinegar | 3.0 |
| Milk | 6.5 | Washing Soda | 11.5 |
(a) What would the students have used to measure the pH ?
(b) Which solution is the most acidic
(c) Which solution is the most alkaline ?
(d) Which solutions are neutral ?
(e) Which solution can be used to treat wasp stings ?
(f) Which solution can be used to treat bee stings ?
Solution :
(a) Universal indicator paper is used to measure the pH.
(b) Lemon juice with pH = 2.5 is the most acidic.
(c) Household ammonia with pH = 12 is the most alkaline.
(d) Salt solution and sugar solution with pH = 7 are neutral.
(e) Vinegar (acid) can be used to treat wasp stings since it injects an alkaline liquid into the skin.
(f) Baking soda can be used to treat bee stings since it injects methanoic acid into the skin.
(Page No - 83 )
Question 63:
Hydrochloric acid reacts with a metal X to form a gas Y which bums with a ‘pop’ sound. Sodium hydroxide solution also reacts with the same metal X (on heating) to form the same gas Y.
(a) Name X and Y
(b) Write the chemical equation of the reaction of metal X with (i) hydrochloric acid, and (ii) sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution :


(Page No:96)
Question 1:
What is the chemical formula of (a) baking soda, and (b) washing soda ?
Solution :
(a) NaHCO3.
(b) Na2CO3.
Question 2:
Write the chemical formula of (i) soda ash, and (ii) sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Solution :
(i) Na2CO3.
(ii) Na2CO3.10H2O.
Question 3:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Copper sulphate crystals are always wet due to the presence of water of crystallisation in them.
Solution :
False.
Question 4:
Which of the following salt has a blue colour and why ?
CuSO4.5H2O or CuSO4
Solution :
CuSO4.5H2O
has blue colour due to the presence of water of crystallization.
Question 5:
What would be the colour of litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate ?
Solution :
Blue.
Question 6:
State the common and chemical names of the compound formed when plaster of Paris is mixed with water.
Solution :
The common name is Gypsum and the chemical name is calcium sulphate dihydrate.
Question 7:
With which substance should chlorine be treated to get bleaching powder ?
Solution :
Calcium hydroxide.
Question 8:
What is the commercial name of calcium sulphate hemihydrate ?
Solution :
Plaster of Paris.
(Page No - 97)
Question 9:
Name the product formed when Cl2 and H2 produced during the electrolysis of brine are made to combine.
Solution :
Hydrochloric acid.
Question 10:
Name a calcium compound which hardens on wetting with water.
Solution :
Plaster of Paris
Question 11:
Name a sodium compound which is a constituent of many dry soap powders.
Solution :
Sodium carbonate.
Question 12:
Name a metal carbonate which is soluble in water.
Solution :
Sodium carbonate.
Question 13:
Name an acid which is present in baking powder.
Solution :
Tartaric acid.
Question 14:
Name the metal whose carbonate is known as washing soda.
Solution :
Sodium.
Question 15:
Which compound is used as an antacid in medicine : NaHCO3 or Na2CO3 ?
Solution :
NaHCO3.
Question 16:
What is the common name of (a) NaHCO3 and (b) Na2CO3.10H2O ?
Solution :
(a) Baking soda.
(b) Washing soda.
Question 17:
Write the chemical name and formula of (a) common salt, and (b) caustic soda.
Solution :
(a) Sodium chloride- NaCl.
(b) Sodium hydroxide- NaOH.
Question 18:
What are the two main ways in which common salt (sodium chloride) occurs in nature ?
Solution :
Common salt occurs naturally in sea water and as rock salt.
Question 19:
Name the major salt present in sea-water.
Solution :
Sodium chloride.
Question 20:
How is common salt obtained from sea-water ?
Solution :
Common salt is obtained from sea water by the process of evaporation.
Question 21:
Why is sodium chloride required in our body ?
Solution :
Sodium chloride is required in our body for the working of nervous system, the movement of muscles, and the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Question 22:
Name three chemicals made from common salt (or sodium chloride).
Solution :
Sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Question 23:
Give any two uses of common salt (sodium chloride).
Solution :
(a) It is used in the manufacture of soap.
(b) It is used in cooking food.
Question 24:
What name is given to the common salt which is mined from underground deposits ? How was this salt formed ?
Solution :
Rock salt. It is mined from the underground deposits just like coal.
Question 25:
Name the salt which is used as a preservative in pickles, and in curing meat and fish.
Solution :
Sodium chloride.
Question 26:
Name the raw material used for the production of caustic soda.
Solution :
Sodium chloride.
Question 27:
The electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride gives us three products. Name them.
Solution :
Sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen.
Question 28:
During the electrolysis of a saturated solution of sodium chloride, where is :
(a) chlorine formed ?
(b) hydrogen formed ?
(c) sodium hydroxide formed ?
Solution :
(a) Anode.
(b) Cathode.
(c) Near the
cathode.
Question 29:
Fill in the following blanks :
(a) Common salt is obtained from sea-water by the process of…………..
(b) Rock salt is mined just like……………….
(c) Chemical formula of washing soda is…………
(d) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is……………………. soda whereas sodium carbonate is…………………………………
(e) The chemical formula of plaster of Paris is……………
Solution :
(a) Evaporation.
(b) Coal.
(c) Na2CO3.10H2O.
(d) Baking; washing.
(e) CaSO4. ?H2O
Question 30:
Complete and balance the following chemical equations :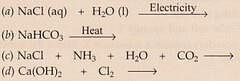
Solution :
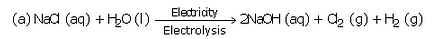
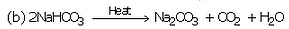
(c) Nacl+ NH3 +H2O+CO2 --> NaHCO3 +NH4Cl
(d) Ca(Oh)2 + Cl2 --> CaCCl2 + H2O
Question 31:
What is washing soda ? State two properties and two uses of washing soda.
Solution :
Washing soda is
sodium carbonate decahydrate. Properties:
(i) It is transparent crystalline solid.
(ii) It is soluble in water.
Uses:
(i) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap and paper.
Question 32:
Write the formulae of sodium chloride and sodium carbonate. Explain why an aqueous solution of sodium chloride is neutral but an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is basic (or alkaline). Write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Solution :
Sodium chloride – NaCl.
Sodium carbonate – Na2CO3.
The aqueous solution of sodium chloride is neutral because it is formed from a strong acid and a strong base. The aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is basic because it gets hydrolysed to some extent and forms sodium hydroxide which is a strong base and carbonic acid which is a weak acid.
Question 33:
Write the chemical formula of ammonium chloride. Explain why an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is acidic in nature ? Illustrate your answer with the help of a chemical equation.
Solution :
The chemical formula of ammonium chloride is NH4Cl. Since, ammonium chloride is the salt of a strong acid HCl and a weak base NH4OH, so an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is acidic in nature.
When dissolved in water, it gets hydrolysed to some extent to form HCl and NH4OH. HCl being a strong acid is fully ionised and gives a large amount of hydrogen ions whereas NH4OH is only slightly ionised. So, NH4Cl contains more of hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions and is hence acidic in nature.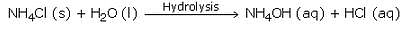
Question 34:
What is baking soda ? Write the chemical name of baking soda. Give the important uses of baking soda. How does baking soda differ chemically from washing soda ?
Solution :
Baking soda is a substance added to food for its faster cooking. Its chemical name is sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Uses: (i) It is used as an antacid to remove acidity of stomach.
(ii) It is used in fire extinguishers.
Baking soda is sodium hydrogencarbonate whereas washing soda is sodium carbonate decahydrate.
Question 35:
Describe how sodium hydrogencarbonate (baking soda) is produced on a large scale. Write equation of the reaction involved.
Solution :
Sodium hydrogencarbonate is produced on large scale by reacting a cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride with ammonia and carbon dioxide.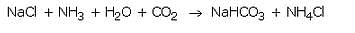
Question 36:
What happens when a cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride reacts with ammonia and carbon dioxide ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place.
Solution :
When a cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride reacts with ammonia and carbon dioxide, sodium hydrogencarbonate and ammonium chloride are formed.
(Page No - 98)
Question 37:
(a) What is meant by “water of crystallisation” in a substance ? Explain with an example.
(b) How would you show that blue copper sulphate crystals contain water of crystallisation ?
(c) Explain how anhydrous copper sulphate can be used to detect the presence of moisture (water) in a liquid.
Solution :
(a) The water molecules which form part of the structure of a crystal are called water of crystallization.
Example: CuSO4.5H2O
(b) The blue copper sulphate crystals contain water of crystallization as it is blue in colour.
(c) Anhydrous copper sulphate turns blue on adding water. This property of anhydrous copper sulphate is used to detect the presence of moisture in a liquid.
Question 38:
(a) What is the common name of sodium hydrogencarbonate ?
(b) What happens when a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate is heated ? Write equation of the reaction involved.
(c) Explain why, sodium hydrogencarbonate is used as an antacid.
Solution :
(a) Baking soda.
(b) When a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate is heated, then it decomposes to give sodium carbonate with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
(c) Sodium hydrogencarbonate is used as an antacid because it neutralises the excess acid present in the stomach and relieves indigestion.
Question 39:
(a) What will happen if heating is not controlled while preparing plaster of Paris ?
(b) Write an equation to show the reaction between plaster of Paris and water.
Solution :
(a) If heating is not controlled while preparing POP, then all the water of crystallisation of gypsum is eliminated and it turns into a dead burnt plaster.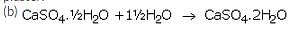
Question 40:
(a) What happens when copper sulphate crystals are heated strongly ? Explain with the help of an equation.
(b) What happens when a few drops of water are added to anhydrous copper sulphate ? Explain with the
help of an equation.
Solution :
(a) On strong heating, blue copper sulphate crystals turn white.

(b) When water is added to anhydrous copper sulphate, it gets hydrated and turns blue. CuS04 + 5H2O → CuS04.5H20
Question 41:
(a) Name two constituents of baking powder.
(b) How does baking powder differ from baking soda ?
(c) Explain the action of baking powder in the making of cake (or bread). Write equation of the reaction involved.
Solution :
(a)Sodium hydrogencarbonate and tartaric acid.
(b)Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid whereas baking soda is only sodium hydrogencarbonate.
(c)When baking powder mixes with water, then sodium hydrogencarbonate reacts with tartaric acid to evolve carbon dioxide gas which gets trapped in the wet dough and bubbles out slowly making the cake soft and spongy.
Question 42:
(a) What is the chemical name of bleaching powder ?
(b) What is the chemical formula of bleaching powder ?
(c) What are the materials used for the preparation of bleaching powder ?
(d) State one use of bleaching powder (other than bleaching).
Solution :
(a) Calcium oxychloride.
(b) CaOCl2
(c) Calcium hydroxide and chlorine.
(d) It is used for disinfecting drinking water supply.
Question 43:
What does a soda-acid type fire extinguisher contain ? How does it work ? Explain the working of a soda- acid fire extinguisher with the help of a labelled diagram.
Solution :
Working:
A soda-acid type fire extinguisher contains a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate and sulphuric acid in separate containers in separate containers inside them. When the knob of the fire extinguisher is pressed, then sulphuric acid mixes with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to produce carbon dioxide gas which forms a blanket around the burning substance and cuts off the supply of air to burning substance; this stops the process of burning and fire gets extinguished.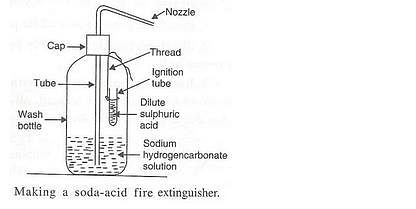
Question 44:
(a) Name a sodium compound used for softening hard water.
(b) Which compound of calcium is used for disinfecting drinking water supply ?
(c) Name a metal compound which has detergent properties (cleansing properties).
(d) Name one compound of calcium which is used for removing the colour of a coloured cloth.
(e) State a peculiar (or remarkable) property of plaster of Paris.
(f) Name the substance obtained by the action of chlorine on solid (dry) slaked lime.
Solution :
(a) Sodium
carbonate.
(b) Bleaching
powder.
(c) Sodium carbonate.
(d) Bleaching
powder.
(e) It sets into a
hard mass on mixing with proper quantity of water.
(f) Bleaching
powder.
Question 45:
(a) What is gypsum ? What happens when gypsum is heated to 100°C (373 K) ?
(b) Name a sodium compound which is used for making borax and glass.
(c) Name the compound which is used in hospitals for setting fractured bones.
(d) Which is the real bleaching agent present in bleaching powder ?
Solution :
(a) Gypsum is calcium sulphate dihydrate, CaSO4.2H2O. When gypsum is heated to a temperature of 100?C, it loses 3/4th of its water of crystallisation and forms plaster of Paris.
(b) Sodium carbonate.
(c) Plaster of Paris.
(d) Chlorine.
Question 46:
(a) What is “baking powder”? How does it make the cake soft and spongy ?
(b) In addition to sodium hydrogencarbonate, baking powders contain a substance X. Name the substance X. What is the role of substance X in the baking powder ?
Solution :
(a) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid. When baking powder mixes with water, then sodium hydrogencarbonate reacts with tartaric acid to evolve carbon dioxide gas which gets trapped in the wet dough and bubbles out slowly making the cake soft and spongy.
(b) Substance X is tartaric acid. It can react with any sodium carbonate formed and neutralise it otherwise cakes and bread will taste bitter.
Question 47:
State two uses each of the following compounds :
(a) Sodium hydroxide
(b) Chlorine
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Solution :
(a) Sodium hydroxide:
(i) It is used for making soaps and detergents.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of paper.
(b) Chlorine:
(i) It is used in the production of bleaching powder.
(ii) It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
(c) Hydrogen:
(i) It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
(ii) It is used in the hydrogenation of oils.
(d) Hydrochloric acid:
(i) It is used in medicines and cosmetics.
(ii) It is used in textile/dyeing and tanning industries.
Question 48:
(a) What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2 ?
(b) Name the raw material used for the preparation of plaster of Paris.
(c) Which property of plaster of Paris is utilised in making casts for broken limbs in hospitals ?
(d) Explain why chlorine is used for sterilising drinking water supply.
Solution :
(a) Bleaching powder.
(b) Gypsum.
(c) It sets into a hard mass in about 30 mins.
(d) Chlorine is used for sterilising drinking water supply because it is a disinfectant which kills germs or bacteria.
Question 49:
(a) What happens when a concentrated solution of sodium chloride (brine) is electrolysed ? Write the equation
of the reaction involved.
(b) Why is the electrolysis of a concentrated solution of sodium chloride known as chlor-alkali process ?
(c) Name three products of the chlor-alkali process. State two uses of each of these products.
Solution :
(a) When a concentrated solution of sodium chloride is electrolysed, it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen.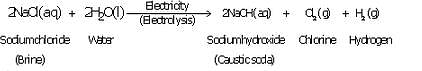
(b) Because of the products formed: Chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
(c) Sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen.
Uses of Sodium hydroxide:
(i) It is used for making soaps and detergents.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of paper.
Uses of chlorine:
(i) It is used in the production of bleaching powder.
(ii) It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
Uses of hydrogen:
(i) It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
(ii) It is used in the hydrogenation of oils.
Question 50:
(a) Describe how washing soda is produced starting from sodium chloride (common salt). Write equations
of all the reactions involved.
(b) State whether an aqueous solution of washing soda is acidic or alkaline ? Give reason for your answer.
(c) What is meant by saying that washing soda has detergent properties ?
(d) Give two important uses of washing soda (or sodium carbonate).
Solution :
(a) Production of washing soda: Washing soda is produced from sodium chloride (or common salt) in the following three steps:
(i) A cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride (called brine) is reacted with ammonia and carbon dioxide to obtain sodium hydrogen carbonate :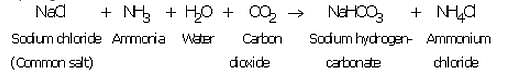
Sodium hydrogen carbonate formed is only slightly soluble in water, so it precipitates out as a solid.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is separated by filtration, dried and heated. On heating, sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes to form sodium carbonate: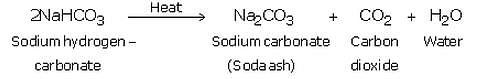
The anhydrous sodium carbonate obtained here is called soda ash.
(iii) Anhydrous sodium carbonate (soda ash) is dissolved in water and recrystallised to get washing soda crystals containing 10 molecules of water of crystallisation :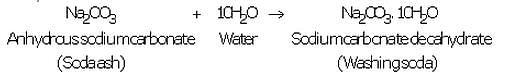
(b) An aqueous solution of washing soda is alkaline because it turns red litmus to blue.
(c) Washing soda has detergent properties because it can remove dirt and grease from dirty clothes.
(d) (i) It is used as cleansing agent for domestic purposes.
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
(Page No - 99)
Question 51:
(a) What is bleaching powder ? How is bleaching powder prepared ? Write chemical equation of the reaction
involved in the preparation of bleaching powder.
(b) What happens when bleaching powder reacts with dilute sulphuric acid ? Give equation of the reaction involved.
(c) State two important uses of bleaching powder.
Solution :
(a) Bleaching powder is Calcium oxychloride (CaOCl2). It is prepared by passing chlorine gas over dry slaked lime.
CaOCl)2 Cl2 → Ca0Cl2 + H20
(b) When bleaching pow&r reacts with dilute sulphuric acid it produces chlorine gas. CaOCl2 + H2S04 → CaS04 + Cl2 + H20
(c) (i) It is used for disinfecting drinking water supply.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of chloroform.
Question 52:
(a) What is plaster of Paris ? Write the chemical formula of plaster of Paris.
(b) How is plaster of Paris prepared ? Write chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(c) Explain why plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container.
(d) State two important uses of plaster of Paris.
Solution :
(a) Plaster of paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate. Its chemical formula is: CaSO4.1/2H2O.
(b) It is prepared by heating gypsum to a temperature of 100oC in a kiln; it loses 3/4th of its water of crystallisation and forms plaster of paris.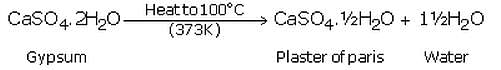
(c) This is because the presence of moisture can cause the slow setting of plaster of Paris by bringing about its hydration.
(d) Uses of plaster of Paris:
(i) It is used as a fire proofing material.
(ii) it is used in hospitals for setting fractured bones in the right position to ensure correct healing.
Question 53:
(a) What is a salt ? Give the names and formulae of any two salts. Also name the acids and bases from which these salts may be obtained.
(b) What is meant by ‘a family of salts’ ? Explain with examples.
(c) What is meant by ‘hydrated’ and ‘anhydrous’ salts ? Explain with examples.
(d) Write the names, formulae and colours of any two hydrated salts.
(e) What will be the colour of litmus in an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride salt ?
Solution :
(a) A salt is a compound formed from an acid by the replacement of the hydrogen in the acid by a metal.
Example: Sodium chloride – NaCl; It is obtained from hydrochloric acid and sodium metal.
Ammonium chloride – NH4Cl; It is obtained from ammonia and hydrochloric acid.
(b) The salts having the same positive ions are said to belong to a family of salts.
Example: Sodium chloride and sodium sulphate belong to the same family of salts called sodium salts.
(c) The salts which contain water of crystallisation are called hydrated salts.
Example: Copper sulphate crystals contain 5 molecules of water of crystallisation.
The salts which have lost their water of crystallisation are called anhydrous salts.
Example: On strong heating, copper sulphate crystals lose all the water of crystallisation and form anhydrous copper sulphate.
(d) Copper sulphate pentahydrate salt – Its chemical formula is CuSO4.5H2O. It is blue in colour.
Iron sulphate heptahydrate salt – Its chemical formula is FeSO4.7H2O. It is green in colour.
(e) The aqueous solution of ammonium chloride salt turns blue litmus red.
(Page No - 100)
Question 69:
P and Q are aqueous solutions of sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide, respectively. Which of these will turn :
(a) blue litmus red ?
(b) red litmus blue ?
Solution :
(a) No solution will turn blue litmus to red.
(b) Solution Q (sodium hydroxide) will turn red litmus blue.
Question 70:
The metal salt A is blue in colour. When salt A is heated strongly over a burner, then a substance B is eliminated and a white powder C is left behind. When a few drops of a liquid D are added to powder C, it becomes blue again. What could be A, B, C and D ?
Solution :
A is copper sulphate pentahydrate, CuSO4.5H2O
B is water, H2O
C is anhydrous copper sulphate, CuSO4
D is water, H2O
Question 71:
When the concentrated aqueous solution of substance X is electrolysed, then NaOH, Cl2 and H2 are produced. Name the substance X. What is the special name of this process ?
Solution :
X is Sodium chloride. The process is called Chlor-alkali process.
Question 72:
Consider the following substances :
NaCl, Ca(OH)2, NaHCO3, NH3, Na2CO3, H2O, Cl2, CO2, CaSO4.2H2O, 2CaSO4.H2O, CaOCl2
(a) Which two substances combine to form bleaching powder ?
(b) Which four substances are utilised in the production of washing soda ?
(c) Which compound represents plaster of Paris ?
(d) Which compound is a part of baking powder ?
(e) Which compound is used as an antacid ?
Solution :
(a) Ca(OH)2 and Cl2
(b) NaCl, NH3, H2O and CO2
(c) 2CaSO4.H2O
(d) NaHCO3
(e) NaHCO3
Question 73:
Give one example each of a salt which gives an aqueous solution having :
(a) pH less than 7
(b) pH equal to 7
(c) pH more than 7
Solution :
(a) Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl
(b) Sodium chloride, NaCl
(c) Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3
Question 74:
A compound X which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with a proper quantity of water.
(a) Identify the compound X ,
(b) Write the chemical equation for its preparation
(c) For what purpose is it used in hospitals ?
Solution :
(a) Plaster of Paris.
(c) POP is used in hospitals for setting fractured bones in the right position to ensure correct healing.
Question 75:
Consider the following salts :
Na2CO3, NaCl, NH4Cl, CH3COONa, K2SO4, (NH4)2SO4 Which of these salts will give :
(a) acidic solutions ?
(b) neutral solutions ?
(c) basic solutions (or alkaline solutions) ?
Solution :
(b) NaCl, K2SO4
(c) N02C03, CH3COONa
Question 76:
A white powdery substance having strong smell of chlorine is used for disinfecting drinking water supply at waterworks. Identify the substance. Give its chemical name and write the chemical reaction for its preparation.
Solution :
Bleaching powder, CaOCl2.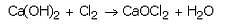
Question 77:
A salt X when dissolved in distilled water gives a clear solution which turns red litmus blue. Explain the phenomenon.
Solution :
Salt X is like sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, which is made from
a strong base and a weak acid. On dissolving in water, salt X gets hydrolysed
to form some strong base and some weak acid. The strong base thus formed
makes the solution alkaline which turns red litmus blue.
Question 78:
A person found that the cake prepared by him is hard and small in size. Which ingredient has he forgotten to add that would have caused the cake to rise and become light ? Explain your answer.
Solution :
Baking
powder; When baking powder mixes with water, then sodium hydrogen carbonate
reacts with tartaric acid to evolve carbon dioxide gas which gets trapped in
the wet dough and bubbles out slowly making the cake soft and spongy.
Question 79:
A white chemical compound becomes hard on mixing with proper quantity of water. It is also used in surgery to maintain joints in a fixed position. Name the chemical compound.
Solution :
Plaster of Paris.
Question 80:
When chlorine and sodium hydroxide being produced during the electrolysis of brine are allowed to mix, a new chemical is formed. Name this chemical and write its uses.
Solution :
Sodium hypochlorite, NaClO; used in making household bleaches and for bleaching fabrics.
Question 81:
Write the name and formula of one salt each which contains :
(a) two molecules of water of crystallisation
(b) five molecules of water of crystallisation
(c) ten molecules of water of crystallisation
Solution :
(a) Gypsum – CaSO4.2H2O
(b) Copper sulphate crystals – CuSO4.5H2O
(c) Sodium carbonate crystals – Na2CO3.10H2O
Question 82:
How many molecules of water of crystallisation (per formula unit) are present in :
(a) copper sulphate crystals ?
(b) washing soda ?
(c) gypsum ?
Solution :
(a) 5.
(b) 10.
(c) 2.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Acids, Bases & Salts - 3 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are acids and bases? |  |
| 2. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |
| 3. What is the pH scale? |  |
| 4. How can we test whether a substance is an acid or a base? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of acids, bases, and salts? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















