NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Chemical Kinetics | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: Activation energy of any chemical reaction can be calculated if one knows the value of(a) rate constant at standard temperature
(b) probability of collision
(c) orientation of reactant molecules during collision
(d) rate constant at two different temperatures (NEET 2024)
Ans: (d)
To calculate value of Ea
Equation used is

Hence Ea can be calculated if value of rate constant k is known at two different temperatures T1 and T2.
Q2: Which plot of In k vs 1 / T is consistent with Arrhenius equation?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d)  (NEET 2024)
(NEET 2024)
Ans: (d)
The Arrhenius equation is given as
In k vs 1 / T gives a straight line graph with slope =  and intercept = InA
and intercept = InA
Q3: The rate of a reaction quadruples when temperature changes from 27∘C to 57∘C. Calculate the energy of activation.
Given R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1,log4 = 0.6021
(a) 38.04 kJ/mol
(b) 380.4 kJ/mol
(c) 3.80 kJ/mol
(d) 3804 kJ/mol (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
To solve this problem, we will use the Arrhenius equation, which relates the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction to the temperature (T) and the activation energy (Ea). The equation in its logarithmic form is:
where:
- K is the rate constant,
- A is the pre-exponential factor (frequency factor),
- Ea is the activation energy,
- R is the universal gas constant
- T is the temperature in Kelvin,
According to the problem, the rate of the reaction quadruples (k2

So,
Therefore, the activation energy Ea is 38.07kJ/mol, which best matches Option A:
38.04kJ/mol
2023
Q1: For a certain reaction, the rate = k[A]2[B], when the initial concentration of A is tripled keeping concentration of B constant, the initial rate would (NEET 2023)
(a) Decrease by a factor of nine
(b) Increase by a factor of six
(c) Increase by a factor of nine
(d) Increase by a factor of three
Ans: C

Q2: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R: (NEET 2023)
Assertion (a) A reaction can have zero activation energy.
Reasons R: The minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by reactant molecules so that their energy becomes equal to threshold value, is called activation energy.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: (d)
A reaction cannot have zero activation energy.
Ea is minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by reactant molecules so that their energy becomes equal to threshold value.
2022
Q1: The given graph is a representation of kinetics of a reaction. (NEET 2022 Phase 1) The y and x axes for zero and first order reactions, respectively are (NEET 2022)
The y and x axes for zero and first order reactions, respectively are (NEET 2022)
(a) zero order (y = rate and x = concentration), first order (y = t1/2, and x = concentration)
(b) zero order (y = rate and x = concentration), first order (y = rate and x = t1/2)
(c) zero order (y = concentration and x = time), first order (y = t1/2 and x = concentration)
(d) zero order (y = concentration and x = time), first order (y = rate constant and x = concentration)
Ans: (a)
- For zero order reaction
r = k[A]0
r = k (constant)
hence, 'y' as 'rate' and 'x' as concentration will give desired graph. - For first order reaction

hence, 'y' as 't1/2' and 'x' as concentration will given desired graph.
Q2: For a first order reaction A → Products, initial concentration of A is 0.1 M, which becomes 0.001 M after 5 minutes. Rate constant for the reaction in min–1 is (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) 0.4606
(b) 0.2303
(c) 1.3818
(d) 0.9212
Ans: (d)
A → Product
t = 0 0.1 M
t = 5 min 0.001 M
Q3: For a chemical reaction
4A + 3B
Rate of formation of C is 6
(a) 10
(b) 1
(c) 10
(d) 1
Ans: (b)

2021
Q1: For a reaction A → B, enthalpy of reaction is –4.2 kJ mol–1 and enthalpy of activation is 9.6 kJ mol–1. The correct potential energy profile for the reaction is shown in option. (NEET 2021)
(a) 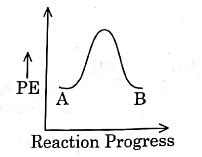
(b) 
(c) 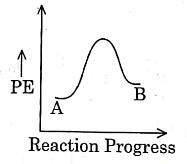
(d) 
Ans: (d)
The enthalpy of reaction is negative, – 4.2 kJ mol−1 . The reaction is an exothermic reaction i.e. the energy of product B, is less than the energy of reactant A. So, the potential energy profile for the reaction is

Q2: The slope of Arrhenius Plot (ln k v/s 1/T) of the first-order reaction is –5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1] (NEET 2021)
(a) 166 kJ mol-1
(b) -83 kJ mol-1
(c) 41.5 kJ mol-1
(d) 83.0 kJ mol-1
Ans: (c)
Arrhenius equation

2020
Q1: An increase in the concentration of the reactants of a reaction leads to change in :
(a) heat of reaction
(b) threshold energy
(c) collision frequency
(d) activation energy (NEET 2020)
Ans: (c)
The correct answer to this question is collision frequency. Here's an explanation for each option to understand why:
- Option A - Heat of Reaction: The heat of reaction, also known as the enthalpy change (ΔH), is determined by the difference in the energy levels of the reactants and products. It is a characteristic feature of a particular chemical reaction and is not typically affected by the concentration of reactants except in cases of extremely high or non-ideal concentrations where volume changes might somewhat influence pressure and therefore the heat of reaction in gases. Under normal conditions, however, changing the concentration of reactants does not alter the heat of reaction.
- Option B - Threshold Energy: Threshold energy is the minimum energy that reactant molecules must possess in order to undergo a successful collision, leading to a chemical reaction. This value is inherent to the specific reaction and is related to the strength of the bonds in the reactants as well as the energy required to form the activated complex during the reaction. The threshold energy does not change simply because the concentration of reactants is altered.
- Option C - Collision Frequency: Collision frequency corresponds to how often reacting particles collide in a given time interval. When the concentration of reactants is increased, there are more reactant particles per unit volume. This statistically leads to an increased number of collisions per unit time, thereby raising the collision frequency. This is in accordance with the collision theory of chemical kinetics.
- Option D - Activation Energy: Activation energy is the minimum energy barrier that must be overcome for reactants to be converted into products. It is a property of a particular reaction and is related to the nature of the reactants and the reaction pathway. Altering the concentration of reactants does not change the activation energy for that reaction.
Thus, the only factor among the provided options that changes with an increase in the concentration of reactants is indeed the collision frequency.
Q2: The rate constant for a first-order reaction is 4.606 × 10-3 s-1. The time required to reduce 2.0 g of the reactant to 0.2 g is:
(a) 500 s
(b) 1000 s
(c) 100 s
(d) 200 s (NEET 2020)
Ans: (a)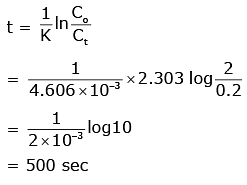
2019
Q1: If the rate constant for a first-order reaction is k, the time (t) required for the completion of 99% of the reaction is given by: (NEET 2019)
(a) t = 0.693/k
(b) t = 6.909/k
(c) t = 4.606/k
(d) t = 2.303/k
Ans: (c)
The first-order rate constant is given as,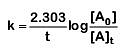
99% completed reaction,
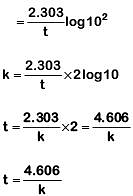
Q2: For the chemical reaction 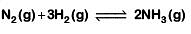 The correct option is: (NEET 2019)
The correct option is: (NEET 2019)
(a)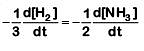
(b)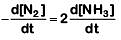
(c)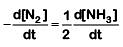
(d)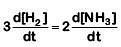
Ans: (c)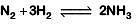
The rate of reaction is given as
2018
Q1: The correct difference between first- and second-order reaction is that (NEET 2018)
(a) the rate of a first-order reaction does not depend on reactant concentration; the rate of a second-order reaction does depend on reactant concentrations.
(b) the half-life of a first-order reaction does not depend on [A]0; the half-life of a second-order reaction does depend on [A]0
(c) a first-order reaction can be catalyzed; a second-order reaction cannot be catalyzed.
(d) the rate of a first-order reaction does depend on reactant concentrations; the rate of a second-order reaction does not depend on reactant concentrations
Ans: (b)
For the first order reaction, t1/2 =
which is independent of initial concentration [A]0.
For second order reaction, t1/2 = 
which depends on initial concentration [A]0.
Q2: When the initial concentration of the reactant is doubled, the half-life period of a zero-order reaction (NEET 2018)
(a) is halved
(b) is doubled
(c) is tripled
(d) remains unchanged
Ans: (b)
Half life of zero order

2017
Q1: Mechanism of a hypothetical reaction (NEET 2017)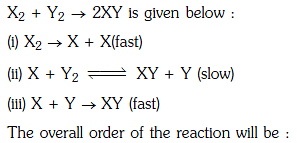
(a) 2
(b) 0
(c) 1.5
(d) 1
Ans: (c)

Q2: A first-order reaction has a specific reaction rate of 10–2 sec–1. How much time will it take for 20g of the reactant to reduce to 5 g ? (NEET 2017)
(a) 138.6 sec
(b) 346.5 sec
(c) 693.0 sec
(d) 238.6 sec
Ans: (a)
2016
Q1: The rate of a first-order reaction is 0.04 mol ℓ-1 s-1 at 10 seconds and 0.03 mol ℓ-1 s-1 at 20 seconds after initiation of the reaction. The half-life period of the reaction is : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) 54.1 s
(b) 24.4 s
(c) 34.1 s
(d) 44.1 s
Ans: (b)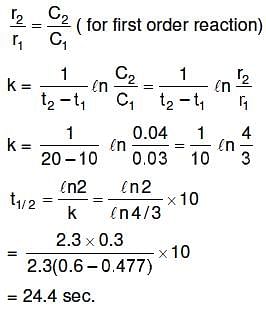
Q2: The addition of a catalyst during a chemical reaction alters which of the following quantities? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Enthalpy
(b) Activation energy
(c) Entropy
(d) Internal energy
Ans: (b)
A catalyst provides an alternate path to the reaction which has lower activation energy.
Q3: The decomposition of phosphine (PH3) on tungsten at low pressure is a first-order reaction. It is because the
(a) rate is proportional to the surface coverage
(b) rate is inversely proportional to the surface coverage
(c) rate is independent of the surface coverage
(d) rate of decomposition is very slow. (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
At low pressure, rate is proportional to the surface coverage and is of first order while at high pressure it follows zero order kinetic due to complete coverage of surface area.
2015
Q1: The rate constant of the reaction A
(a) 3.60 M
(b) 0.36 M
(c) 0.72 M
(d) 1.08 M
Ans: (c)
For zero order reaction unit of rate constant is mole per second.
For zero order
x = kt
x = 0.6 × 10–3 × 20 × 60 = 0.72 M
Q2: The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope of which of the following graphs? )
(a)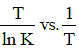
(b) ln K vs. T
(c)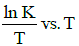
(d)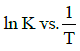 (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
Ans: (d)
According to Arrhenius equation,
Taking natural log on both the sides we get,
Comparing (1) with standard form of equation of line
y = mx + C
We get Slope, 
Hence, if ln k is plotted against 1/T, slope of the line will be  .
.
Q3: When the initial concentration of a reactant is doubled in a reaction, its half-life period is not affected. The order of the reaction is : (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) More than zero but less than first
(b) Zero
(c) First
(d) Second
Ans: (c)
Half-life period of a first order reaction is independent of initial concentration,
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What is chemical kinetics and why is it important in the field of chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 3. How can reaction mechanisms be determined in chemical kinetics? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between rate constant and rate of reaction in chemical kinetics? |  |
| 5. How can chemical kinetics be applied in real-life scenarios? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|



















