NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physical Chemistry for NEET > Valence Bond Theory
Valence Bond Theory | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
- As we know that Lewis approach helps in writing the structure of molecules but it fails to explain the formation of the chemical bond. It also does not give any reason for the difference in bond dissociation enthalpies and bond lengths in molecules like H2 (435.8 kJ mol-1, 74 pm) and F2 (155 kJ mol-1, 144 pm), although in both cases a single covalent bond is formed by the sharing of an electron pair between the respective atoms. It also gives no idea about the shapes of polyatomic molecules.
- Similarly, the VSEPR theory gives the geometry of simple molecules but theoretically, it does not explain them and also it has limited applications. To overcome these limitations the two important theories based on quantum mechanical principles are introduced. These are the valence bond (VB) theory and molecular orbital (MO) theory.
Valence Bond Theory
- Valence bond theory was introduced by Heitler and London (1927) and developed further by Pauling and others.
 VB Theory for formation of Hydrogen Molecule
VB Theory for formation of Hydrogen Molecule
- A discussion of the valence bond theory is based on the knowledge of atomic orbitals, electronic configurations of elements (Units 2), the overlap criteria of atomic orbitals, the hybridization of atomic orbitals and the principles of variation and superposition.
To start with, let us consider the formation of a hydrogen molecule which is the simplest of all molecules:
- Consider two hydrogen atoms A and B approaching each other having nuclei NA and NB and electrons present in them are represented by eA and eB.
- When the two atoms are at a large distance from each other, there is no interaction between them.
- As these two atoms approach each other, new attractive and repulsive forces begin to operate.
- Attractive forces arise between:
(i) The nucleus of one atom and its own electron, i.e. NA – eA and NB– eB
(ii) The nucleus of one atom and electron of the other atom, i.e. NA– eB and NB– eA - Similarly, repulsive forces arise between:
(i) electrons of two atoms like eA – eB
(ii) nuclei of two atoms NA – NB - Attractive forces tend to bring the two atoms close to each other whereas repulsive forces tend to push them apart.
 Forces of attraction and repulsion during the formation of H2 molecule
Forces of attraction and repulsion during the formation of H2 molecule - Experimentally it has been found that the magnitude of new attractive force is more than the new repulsive forces.
- As a result, two atoms approach each other and potential energy decreases. Ultimately a stage is reached where the net force of attraction balances the force of repulsion and the system acquires minimum energy.
- At this stage, two hydrogen atoms are said to be bonded together to form a stable molecule having a bond length of 74 pm.
- Since the energy gets released when the bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms, the hydrogen molecule is more stable than that of isolated hydrogen atoms. The energy released is known as bond enthalpy, which is corresponding to the minimum in the curve depicted in the graph below.
- Conversely, 435.8 kJ of energy is required to dissociate one mole of H2 molecule.
H2(g) + 435.8 kJ mol–1 → H(g) + H(g)
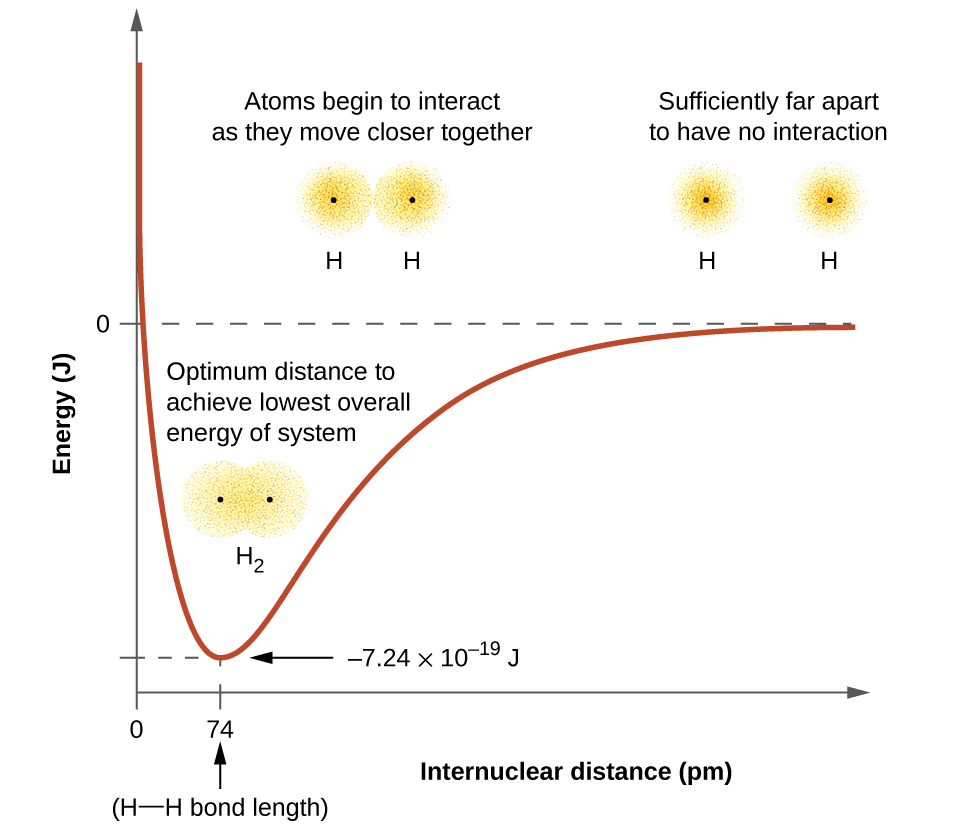 Potential energy curve for the formation of H2 molecule as a function of the internuclear distance of the H atoms
Potential energy curve for the formation of H2 molecule as a function of the internuclear distance of the H atoms
The document Valence Bond Theory | Physical Chemistry for NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physical Chemistry for NEET.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
117 videos|225 docs|239 tests
|
FAQs on Valence Bond Theory - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is valence bond theory? |  |
Ans. Valence bond theory is a model used in chemistry to explain the formation of chemical bonds in molecules. It describes the overlap of atomic orbitals between atoms, resulting in the formation of covalent bonds.
| 2. How does valence bond theory explain the bonding in molecules? |  |
Ans. Valence bond theory explains bonding in molecules by considering the overlap of atomic orbitals. When two atoms approach each other, their atomic orbitals overlap, leading to the formation of a molecular orbital. This overlap allows for the sharing of electrons between the atoms, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond.
| 3. What is hybridization in valence bond theory? |  |
Ans. Hybridization in valence bond theory is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. This mixing occurs when atoms bond, and it helps explain the observed geometry and bonding properties of molecules. Hybrid orbitals are formed by combining different types of atomic orbitals, such as s, p, and d orbitals, to create new orbitals with specific shapes and orientations.
| 4. How does valence bond theory explain the concept of resonance? |  |
Ans. Valence bond theory explains resonance as the delocalization of electrons within a molecule. In molecules with resonance, multiple Lewis structures are used to represent the molecule. Valence bond theory suggests that the true structure of the molecule is a hybrid of these resonance structures, with the electrons being shared or delocalized over multiple atoms.
| 5. What are the limitations of valence bond theory? |  |
Ans. Valence bond theory has some limitations. It cannot fully explain the magnetic properties of molecules, the spectroscopic properties of molecules, and the relative stability of different resonance structures. Additionally, it does not account for the concept of molecular orbitals, which is better explained by molecular orbital theory. However, valence bond theory remains a useful tool for understanding chemical bonding in many molecules.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















