Isomerism & Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Isomerism? |

|
| Types of IsomerismStructural Isomerism |

|
| Stereo Isomerism |

|
| Why do we need to name the compounds? |

|
What is Isomerism?
It is a phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but possesses different structural formulas and different properties. This is mainly because of different structural or spatial arrangements. Isomers are the compounds exhibiting this phenomenon. Due to this difference in the arrangement of atoms, coordination compounds pre-dominantly exhibit two types of isomerism namely, stereo-isomerism and structural isomerism.
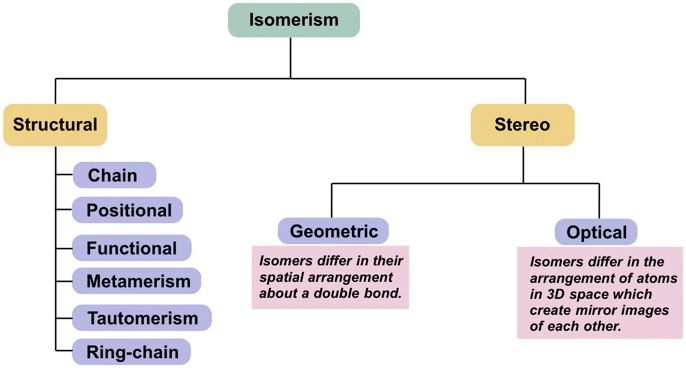
Types of Isomerism
Structural Isomerism
1. Ionisation Isomerism: This type of isomerism is due to the exchange of groups between the complex ion and ions outside it. [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 is red-violet. An aqueous solution of it gives a white precipitate of BaSO4 with BaCl2 solution, thus confirming the presence of free SO42- ions. In contrast [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br is red. A solution of this complex does not give a positive sulphate test with BaCl2. It does give a cream coloured precipitate of AgBr with AgNO3, thus confirming the presence of free Br- ions. Other examples of ionisation isomerism are [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl2 and [Co(en)2NO2.Cl]SCN, [Co(en)2NO2.SCN]Cl and [Co(en)2Cl.SCN]NO2.
2. Hydrate isomerism These isomers arise by the exchange of groups in the complex ion with water. Three isomers of CrCl3.6H2O are known. From conductivity measurements and quantitative precipitation of the ionised Cl-, they have been given the following
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl 3
[Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl 2.H2O
[Cr(H2O)4Cl 2]Cl.2H2O
3. Linkage Isomerism This type of isomerism arises when the ligand attached to the central metal ion of a complex in different ways. Such ligands are called ambidient ligands. Nitrite ion has electron pairs available for coordination both on N and O atoms.
Examples
(a) [Co(NH3)5 ONO]Cl2 pentaamminenitrito-o-cobalt(III) chloride (red)
and
[Co(NH3)5 NO2] Cl2 pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt-(III)-chloride (yellow)
(b) [Mn(CO5).SCN] + pentacarbonylthiocyanto-S-manganese (II) ion
and
[Mn(CO5) (NCS]+ pentacarbonylthiocyanato-N-manganese (II) ion
4. Co-ordination Isomerism When both the cation and anion are complexions, then isomerism may be caused by the interchange of ligands between the anion and cation. For example [Pt(NH3)4], [PtCl4] and [PtCl(NH3)3] [PtCl3(NH3)]. These isomers are called coordination isomers.
5. Co-ordination Position Isomerism In polynuclear complexes, an interchange of ligands between the metal nuclei gives rise to co-ordination position isomerism, for example.
6. Polymerisation Isomerism: This is not true type of isomerism because it occurs among compounds having the same empirical formula, but different molecular formula. Thus, [Pt(NH3)2Cl2], [Pt(NH3)4], [PtCl4], [Pt(NH3)4], [Pt(NH3)Cl 3]2 and [Pt(NH3)3Cl]2,[PtCl 4] all have the same empirical formula.
Stereo Isomerism
These are the isomers in which ligands have different spatial arrangements around central metal atom /ion in 3-D space.
1. Geometrical Isomerism: Geometrical isomers are the isomers in which the atoms are joined to one another in the same way but differ in space because some ligands occupy different relative positions in space.
Geometrical Isomerism in the complex compound having C.N. = 4
Tetrahedron complexes (sp3 hybridization) never exhibit geometry isomerism, however, it is very common in square planer complexes (dsp2 hybridization).
For Example
(a) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] can exist as two geometrical isomers.
(b) [Pt(Gly)2] also exist in two geometrical isomers.
Geometrical Isomerism in Complex compound having co-ordination number 6
(a) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ can exist as
(b) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2Br 2] can exist as
There are many more trans arrangements.
2. Optical Isomerism: If a molecule is asymmetric then it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. These forms are called optical isomers. They are called either Dextro or laevo compounds depending on the direction in which they rotate the plane polarised light in the polarimeter. Optical isomerism is common in octahedral complexes involving bidentate ligand.
[Co(en)2Cl2+] exist as cis-and trans-isomers. But only cis-isomer can have d and l optical isomers.
Optical isomers of [Co(en)3]3+ are
Why do we need to name the compounds?
How would your teacher call you and your best friend if you both didn’t have any names? Similarly, the naming of coordination compounds(complex nomenclature) is important to provide an unambiguous method to represent and describe formulas and names of coordination compounds systematically.
Also, it becomes very important while you deal with isomers. We follow a few rules of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) system while naming these compounds. In a nutshell, the rules are as follows:
In Coordination Compounds,
- within the coordination entities, we list down the central atom/ion first followed by the ligands.
- After this, we list down the ligands in alphabetical order.
- We write the formula of coordination entity in square brackets.
- Ligand abbreviations are to be enclosed in parentheses.
- We must not keep any space between the ligands and the metal within a coordination sphere.
- The charge on the cation(s) should be equal to the charge of the anion(s).
Now, let us look at these rules of complex nomenclature in greater details, along with suitable examples:
- Rule 1: While naming a coordination compound, we always name the cation before the anion. This rule does not count the fact of whether the complexion is cation or anion.
Example:
Na[Co(NH)4(Cl)2]: Na is to be named first followed by [Co(NH)4 (Cl)2], i.e. Sodium tetramminedichlorocoblatate(I)
[Co(NH)4(Cl)2]SO4: [Co(NH)4(Cl)2] is to be named first followed by SO4, i.e Tetraamminedichlorocobalt(0) sulphate. - Rule 2: When we see that there are multiple types of ligands present in any coordination compound, we name the ligands in alphabetic order after by the name of central metal atom/ion.
- Name of the anionic ligands ends with ‘o’.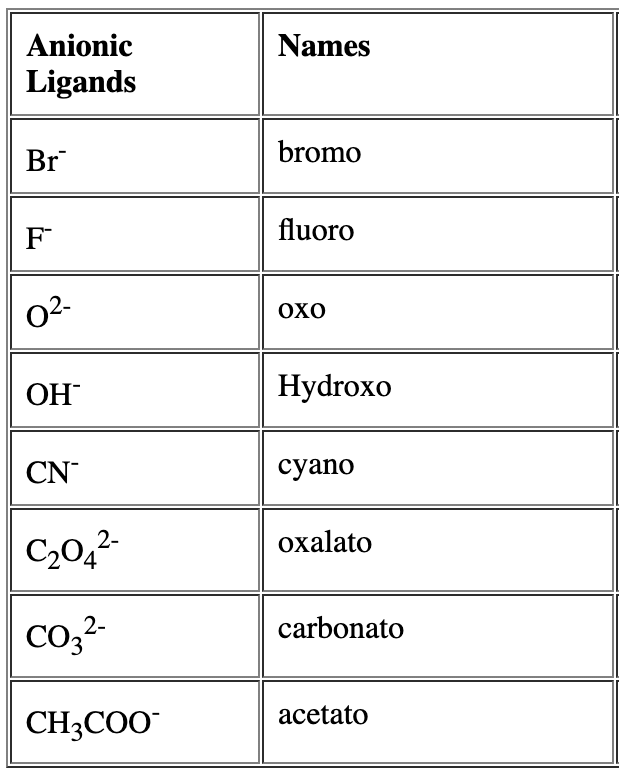 - For neutral ligands, their common name is used as such e.g.
- For neutral ligands, their common name is used as such e.g.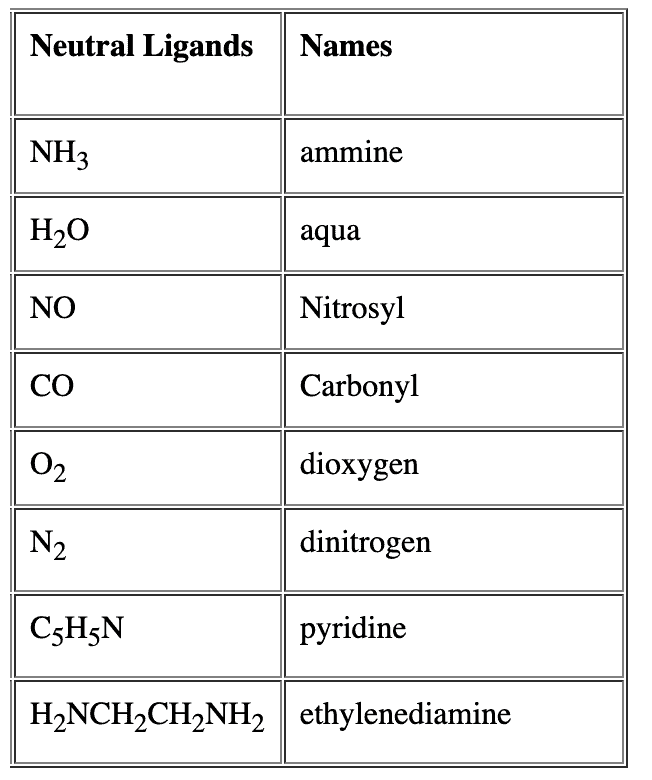
- Rule 3: If the names of the ligands have a numerical prefix, then we use the terms bis, tris, tetrakis. This will represent the ligand to which they refer is placed in parentheses.
For example, we name [NiCl2(PPh3)2] as dichloridobis(triphenylphosphine)nickel(II)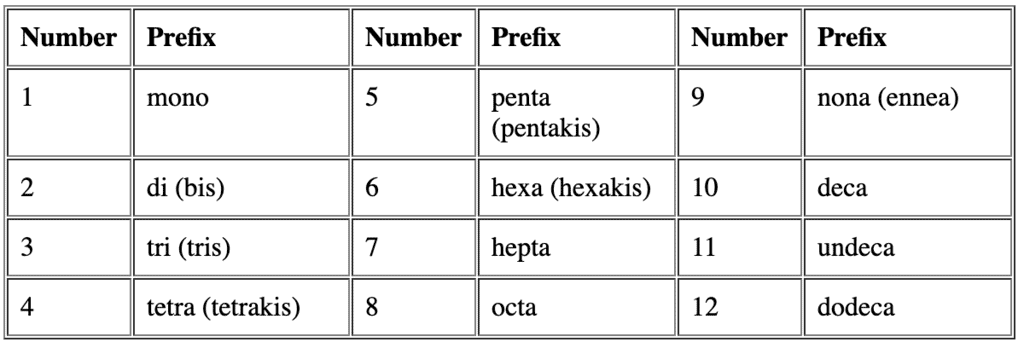
- Rule 4: After naming the ligand in alphabetic order, we name the central metal atom/ion.
- If the complex ion is a cation, we name the metal the same as the element.
- If the complex is an anion, the name of metal ends with the suffix -ate for Latin name.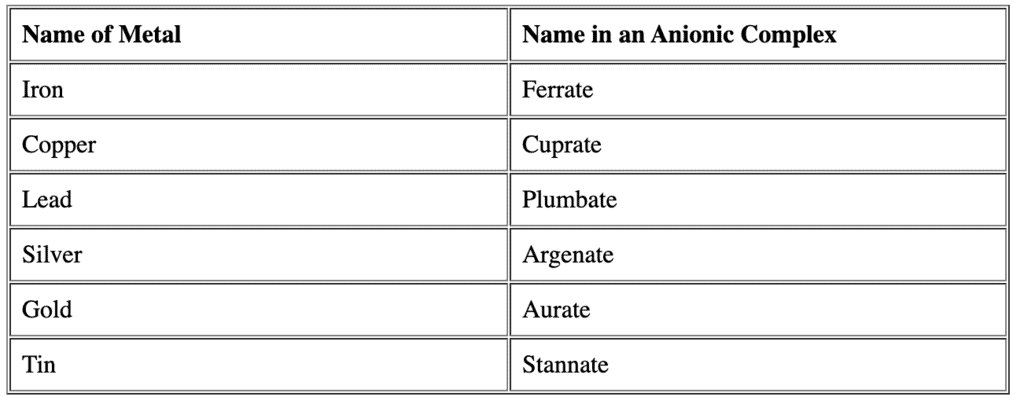
- Rule 5: We give the oxidation state of the metal in the complex as a roman numeral in parentheses.
- Rule 6: We name the neutral complex molecule similar to that of the complex cation.
- Rule 7: There are some ligands like NO2, CN that are attached to the central metal atom/ion through different atoms. We name them as follows:
M-NO2 → nitro
M-ONO → nitrito
M-SCN → thiocyanato
M-NCS → isothiocyanato
Rule 8: If any lattice component such as water or solvent of crystallisation is present, these follow their name, and are preceded by the number of these groups in Arabic numericals. These rules are illustrated by the following examples.
(a) Complex cations
IUPAC name
(b) Complex anions
(c) Organic groups
(d) Bridging groups
(e) Hydrates
AlK(SO4)2. 12H2O
Aluminium potassium sulphate 12-water Writing the formula of a coordination compound:
- When writing the formula of complexes, the complex ion should be enclosed by square brackets. The metal is named first, then the coordinated groups are listed in the order: negative ligands, neutral ligands, positive ligands (and alphabetically according to the first symbol within each group).
- [M negative ligands, Neutral ligands, positive ligands]
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Isomerism & Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is isomerism? |  |
| 2. What are the types of isomerism? |  |
| 3. Why do we need to name compounds? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between isomerism and the nomenclature of coordination compounds? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions about isomerism and nomenclature of coordination compounds? |  |