NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Plant Life Cycles & Alternation of Generations (Old NCERT)
Plant Life Cycles & Alternation of Generations (Old NCERT) - NEET PDF Download
Alternation of Generation
- Haploid and diploid cells produce haploid and diploid plant bodies, respectively, by mitosis.
- The haploid plant body produces gametes and hence represents gametophytes.
- The zygote divides by mitosis to produce a diploid sporophytic plant body and this plant body produces haploid spores by meiosis, which again divides by mitosis to produce a haploid plant body.
Different plant groups representing gametophytes and sporophytes differ in the following patterns:
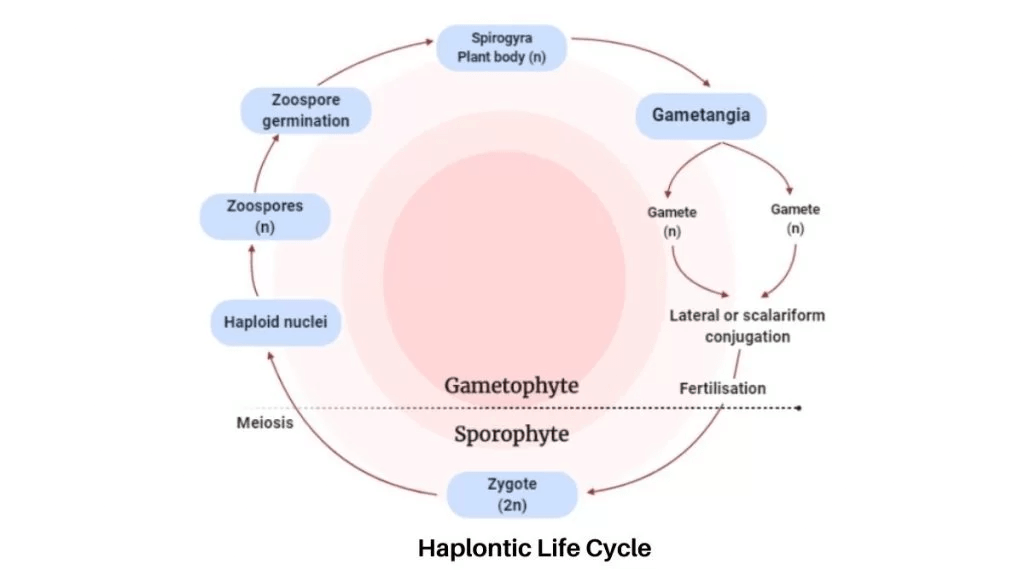
(i) Haplontic
- Sporophytic generation is represented only by the one-celled zygote and free-living sporophytes are absent.
- Haploid spores are formed by meiosis, which divides mitotically to form the gametophyte.
- The dominant, photosynthetic phase in such plants is the free-living gametophyte.
Examples: Volvox, Spirogyra and some species of Chlamydomonas.
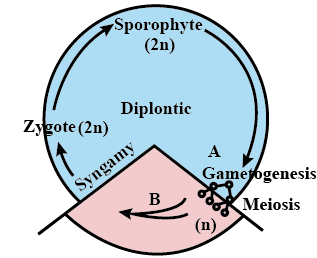
(ii) Diplontic
- Here, the diploid sporophyte is the dominant, photosynthetic, independent phase of the plant.
- The gametophytic phase is represented by the single to the few-celled haploid gametophyte.
Examples: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms. Diplontic Life Cycle
Diplontic Life Cycle
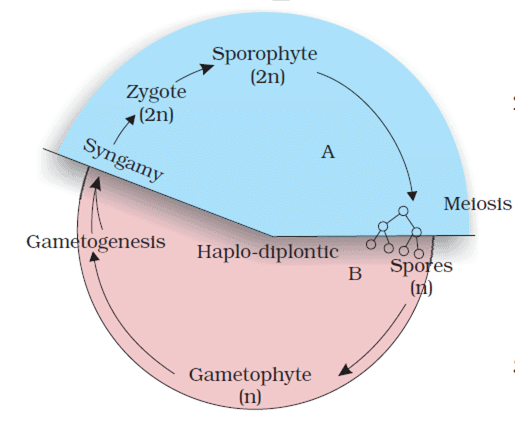
(iii) Haplo-diplontic
- A dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase is represented by a haploid gametophyte and it alternates with the short-lived multicellular sporophyte. Example: Bryophytes
- The diploid sporophyte is represented by a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. It alternates with multicellular, saprophytic/autotrophic, independent but short-lived haploid gametophyte.
Example: Pteridophytes - Some alga genera such as Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, kelps are haplo-diplontic.
 Haplo-diplontic Life Cycle
Haplo-diplontic Life Cycle
FAQs on Plant Life Cycles & Alternation of Generations (Old NCERT) - NEET
| 1. What is alternation of generations in plant life cycles? |  |
Ans. Alternation of generations refers to the life cycle of plants, where they alternate between two distinct phases: the gametophyte phase and the sporophyte phase. In the gametophyte phase, plants produce gametes (reproductive cells) through mitosis. These gametes fuse during fertilization to form a zygote, which develops into the sporophyte phase. The sporophyte phase involves the production of spores through meiosis, which will eventually develop into new gametophytes.
| 2. How do the gametophyte and sporophyte phases differ in plant life cycles? |  |
Ans. The gametophyte phase is the haploid phase of a plant's life cycle, where the cells have only one set of chromosomes. In this phase, plants produce gametes through mitosis. The gametes fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote, which develops into the sporophyte phase. The sporophyte phase is the diploid phase, where the cells have two sets of chromosomes. In this phase, plants produce spores through meiosis, which will eventually develop into new gametophytes.
| 3. What is the significance of alternation of generations in plant life cycles? |  |
Ans. The alternation of generations in plant life cycles allows for genetic variation and adaptation. The gametophyte phase produces gametes through mitosis, which can undergo genetic recombination during fertilization. This genetic recombination creates new combinations of traits, increasing genetic diversity. Additionally, the production of spores through meiosis in the sporophyte phase allows for dispersal and colonization of new habitats, enhancing the survival and success of plants.
| 4. Can you provide an example of a plant that exhibits alternation of generations? |  |
Ans. One example of a plant that exhibits alternation of generations is the fern. Ferns have a distinct gametophyte phase called the prothallus, which is a small, heart-shaped structure that produces gametes. The gametes fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote, which develops into the sporophyte phase. The sporophyte phase is the familiar fern plant that we typically see, with fronds and spore-producing structures on the underside of the fronds.
| 5. How does alternation of generations contribute to the reproductive success of plants? |  |
Ans. Alternation of generations contributes to the reproductive success of plants by facilitating genetic variation and dispersal. The production of gametes through mitosis in the gametophyte phase allows for genetic recombination during fertilization, increasing genetic diversity and potentially enhancing the adaptability of plants to changing environments. The production of spores through meiosis in the sporophyte phase allows for dispersal to new habitats, reducing competition and increasing the chances of successful colonization. Overall, alternation of generations increases the reproductive options and opportunities for plants.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches