Fertilisation in Flowering Plants & Double Fertilisation | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Fertilisation
The fusion of male gamete with female gamete is called fertilisation. First of all, fertilisation was discovered by Strasburger (1884) in the Monotrapa plant.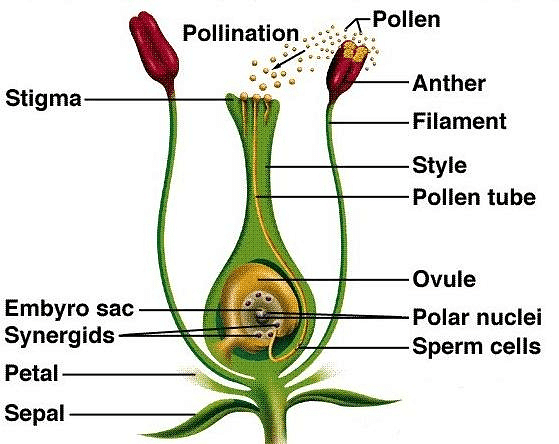 Fertilisation in Flowering Plant
Fertilisation in Flowering Plant
This process is completed in the following steps:
1. Germination of Pollen Grains
- After pollination, pollen grains germinate on the stigma. They absorb moisture and sugar contents from stigma and swell up.
 Sunflower seedling, three days after germination
Sunflower seedling, three days after germination - The intine of pollen grain grows out through any one germinal pore of exine, in the form of tube-like outgrowth is called pollen tube. When one pollen tube develops in Capsella and most of Angiosperms, it is called monosiphonous condition.
- When more than one pollen tube develops in Malvaceae and Cucurbitaceae family, it is called polysiphonous.
- When the pollen tube comes down from the stigma into the style, first of all, the vegetative nucleus enters into the pollen tube then it is followed by generative cell. The tube nucleus always occupies in terminal position in the pollen tube. The vegetative nucleus controls the growth of the pollen tube.
- Meanwhile, the generative cell divides mitotically to form two male gametes. Both of the male gametes are non-motile.
- Boron and calcium ions (mainly Boron) are essential for the growth of pollen tube and the best temperature for the growth of pollen tubs is 20-30º C. Pollen tube shows apical growth and chemotropic movement.
2. Entry of Pollen Tube into Ovule
- Finally, the pollen tube enters the ovary at that time, the ovule becomes mature. Inside the ovary, obturators guide the passage of the pollen tube towards the micropyle. A mature ovule in which the embryo sac also matured, has three paths for the entry of pollen tube.
(i) Porogamy: In this, pollen tube enters into the ovule through the micropyle. It is known as porogamy. It is found in most of the Angiosperms (Capsella).
(ii) Chalazogamy: In this method, the pollen tube enters into the ovule through the chalaza. This method is discovered in Casuarina by Treub (1891).
Examples: Betula and Juglans (walnut).
(iii) Mesogamy: In this method, pollen tube enters into the ovule either through integuments - Cucurbita or through the funiculus - Pistacia and Populus.
3. Entry of Pollen Tube into Embryo Sac
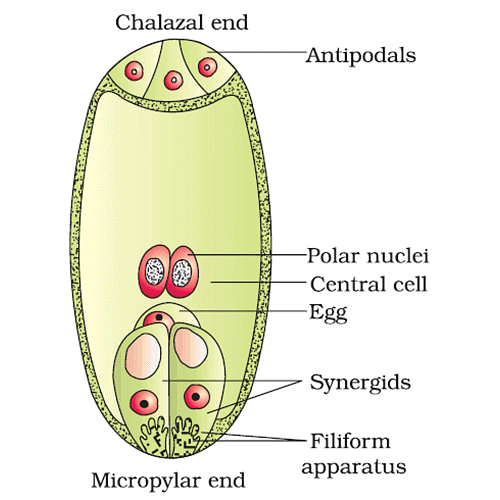
- Pollen tube can enter into the ovule through any passage but inside the embryo sac, it enter only through the egg apparatus.
 Embryo sac
Embryo sac
- After the entrance inside the ovule, it grows towards the egg apparatus because synergids cells secrete the chemical (hormones) which attracts the growth of the pollen tube. It means the pollen tube shows chemotropic movement in the ovule.
- Any one synergid starts degenerating when the pollen tube comes near the egg apparatus. The pollen tube enter into the embryo sac through the degenerating synergids.
- When the tip of the pollen tube enters into the embryo sac, the vegetative nucleus degenerates. The tip of the pollen tube swells and burst (Endosmosis) after reaching inside the embryo sac. The pollen tube released all contents including both male gametes inside the degenerating synergids of the embryo sac.
- Two dark granules appear in the region of degenerating synergids. These are known as X-bodies. They are two in number and both X-bodies are formed by the degenerating nucleus of tube cell and synergids.
4. Fusion of Gametes
- Before or after the entrance of the pollen tube into the embryo sac, both polar nuclei of the central cell fused together to form a diploid nucleus. It is known as the secondary nucleus or definitive nucleus.
- Out of two, one male gamete fertilised with the egg cell and to form a diploid zygote. This fusion is known as syngamy. This is the true mechanism of the fertilisation process.
- The second male gamete fused with a diploid secondary nucleus which is formed by the fusion of two polar nuclei. This fusion is known as triple fusion resulting, a triploid (3n) structure is formed. It is called the primary endosperm nucleus.
- Fertilization takes place twice at a time in Angiosperm is called double fertilisation.
- Double fertilisation was discovered by "Nawaschin" in Lilium and Fritillaria plants.
- Double fertilisation and triple fusion is the specific or universal characteristic of Angiosperm. There are five nuclei and three gametes that participate in double fertilization.
- A zygote is formed by true fertilisation (syngamy) develops into an embryo. Triploid primary endosperm nucleus is formed by triple fusion develops into the endosperm which is used as nutrition for growing embryo.
- All the remaining cells of the embryo sac like antipodal cells, synergids degenerate excluding the zygote and primary endosperm nucleus after the fertilisation. At this time, the zygote obtains food from degenerating synergids and antipodal cells.
- The fertilisation in which non-motile gametes are carried to female gamete through pollen tube is known as "Siphonogamy".
- The entry of more than one pollen tube into the ovule leading to the occurrence of supernumerary male gametes is called "Polyspermy".
Table: Differences between Pollination and Fertilisation

Double Fertilisation
“Double fertilisation is a complex process which involves the fusion of one female gametophyte with two male gametes”
What is Double Fertilisation?
Double fertilisation is a chief trait of flowering plants. In the phenomena, one female gamete unites with two male gametes. One of the male gametes fertilizes the egg resulting in the formation of a zygote and the other unites with 2 polar nuclei for the formation of an endosperm.
Double fertilisation provides stimulus to the plant resulting in the ovarian development to fruits and development of ovules into the seed. When the haploid male gametes and female gametes fuse, the diploid state of the plant is restored.
Double Fertilisation Process
The process of double fertilisation is explained below:
Double Fertilisation in Angiosperms
Angiosperms are flower-bearing plants and are the most diverse group of terrestrial plants. The flowers form the reproductive part of angiosperms with separate male and female reproductive organs. Each contains gametes – sperm and egg cells, respectively.
Pollination helps the pollen grains to reach stigma via style. The two sperm cells enter the ovule-synergid cell. This proceeds to fertilisation.
In angiosperms, fertilisation results in two structures, namely, zygote and endosperm, hence the name “double fertilisation.”
Double fertilisation is a complex process where out of two sperm cells, one fuses with the egg cell and the other fuses with two polar nuclei which result in a diploid (2n) zygote and a triploid (3n) primary endosperm nucleus (PEN) respectively.
Since endosperm is a product of the fusion of three haploid nuclei, it is called triple fusion. Eventually, the primary endosperm nucleus develops into the primary endosperm cell (PEC) and then into the endosperm.
The zygote becomes an embryo after numerous cell divisions.
Development of Embryo in Angiosperms
Once fertilisation is completed, embryonic development starts and no more sperms can enter the ovary. The fertilized ovule develops into a seed, and ovary tissues develop a fleshy fruit which encloses the seed.
After fertilisation, the zygote divides into the upper terminal cell and lower basal cell. The basal cell develops into suspensor, which helps in the transport of nutrients to the growing embryo. The terminal cell develops into pro-embryo.
Following are the different stages involved in the development of an embryo.
Stages of Embryonic Development In Angiosperms
- In the first stage of development, the terminal cell divides forming a globular pro-embryo. The basal cell also divides, into a suspensor.
- The developing embryo attains a heart shape due to the presence of cotyledons.
- The growing embryo gets crowded and begins to bend.
- The embryo fills the seed completely.
Significance of Double Fertilisation
The significance of double fertilisation is as follows:
- Two products are obtained as a result of double fertilisation.
- There are chances of polyembryony, and the plant has better chances of survival.
- Double fertilisation gives rise to an endosperm that provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
- It increases the viability of the seeds of angiosperms.
- It utilizes both the male gametes produced by the pollen grains.
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on Fertilisation in Flowering Plants & Double Fertilisation - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is fertilisation in flowering plants? |  |
| 2. How does double fertilisation occur in flowering plants? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of double fertilisation in flowering plants? |  |
| 4. Are there any variations in the process of fertilisation among different types of flowering plants? |  |
| 5. What happens after fertilisation in flowering plants? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|