Relative Velocity in a Plane | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
What is Relative Motion Velocity?
The relative motion velocity refers to an object which is relative to some other object that might be stationary, moving with the same velocity, or moving slowly, moving with higher velocity or moving in the opposite direction. The wide concept of relative velocity can be very easily extended for motion along a straight line, to include motion in a plane or either in three dimensions.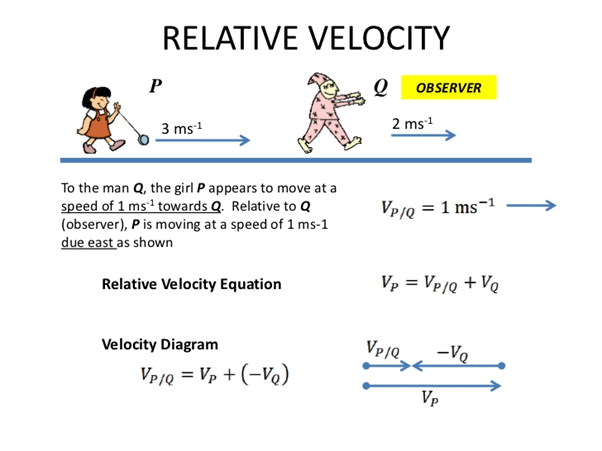
Velocity
Velocity refers to a physical vector quantity which is described by both magnitude and direction. The magnitude or scalar absolute value of velocity is referred to as speed. As stated by the Pythagorean Theorem, the magnitude of the velocity vector is given by –
| v | = v = √ ( vx ²+ vy ² )
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. Numerically or in terms of components, it can be presented as –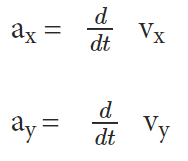
Relative Motion Velocity in Two Dimensions
Let us consider two objects A and B who are moving with the velocity at Va and Vb with respect to some common frame of reference, for example, may be the ground or the earth. In this case, the velocity of object A relative to that of B will be –
Vab= Va – Vb
Similarly, the velocity of object B relative to that of A will be :
Vba = Vb– Va
Therefore,
Vba= – Vba
And | Vab | = | Vba |
When two objects seem to be stationary for one another, in that case –
Vb = Va
Vba = Vab = 0
The magnitude of Vba and Vab will be lower than the magnitude of Va and Vb if Va and Vb are of same sign. Object A appears faster to B and B appears slower to A if Va > Vb.
The magnitude of Vba and Vab will be higher than the magnitude of Va and Vb if Va and Vb are of opposite sign. In this case, both objects will appear moving faster to one another.
Solved Questions
Q.1. If rain is falling vertically at a speed of 35 m/s and a person is riding a bicycle at 12 m/s ( east to west ) then the relative motion velocity of rain will be Vrb
Solution: Vrb = Vr – Vb = ( 35 – 12 ) m/s = 23 m/s
Tan θ = Vw / Vr = 12 / 35 = 0.343
θ = 19 degree
The person must hold an umbrella at an angle of 19 degrees with vertical towards the west to avoid the rain.
Q.2. A plane is traveling at velocity 100 km/hr, in the southward direction. It encounters wind traveling in the west direction at a rate of 25 km/hr. Calculate the resultant velocity of the plane.
Solution: Given, the velocity of the wind = Vw = 25km / hr
The velocity of the plane = Va = 100 km / hr
The relative motion velocity of the plane with respect to the ground can be given as the angle between the velocity of the wind and that of the plane is 90°. Using the Pythagorean theorem, the resultant velocity can be calculated as,
R2= (100 km/hr)² + (25 km/hr)²
R2 = 10 000 km² / hr² + 625 km² / hr²
= 10 625 km² / hr²
Hence, R = 103.077 km/hr
Using trigonometry, the angle made by the resultant velocity with respect to the horizontal plane can be given as,
Tan θ = ( window velocity / airplane velocity )
Tan θ =( 25/100 )
θ = tan −1(1/4)
θ =1/4 radians
|
95 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Relative Velocity in a Plane - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is relative motion velocity? |  |
| 2. How is relative velocity calculated in a plane? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of relative velocity in a plane? |  |
| 4. Can relative velocity in a plane be negative? |  |
| 5. How does relative velocity in a plane affect the trajectory of objects? |  |





















