DC Pandey Solutions: Fluid Mechanics | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 13.1
Ques 1: Two vessels A and B have same base area. Equal volumes of a liquid are poured in the two vessels to different heights hA and hB(> hA). In which vessel, the force on the base of vessel will be more.
Sol: FA = PA A = hA ρgA and FB = hB ρgA
as hA < hB ⇒ FA < FB
Ques 2: A hydraulic automobile lift is designed to lift cars with a maximum mass of 3000 kg. The area of cross section of the piston carrying the load is 425 cm2. What maximum pressure would the smaller piston have to bear?
Sol: 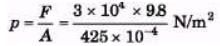
= 6.92 × 105 N/m2
Ques 3: A U tube contains water and methylated spirit seprated by mercury. The mercury columns in the two arms are in level with 10.0 cm of water in one arm and 12.5 cm of spirit in the other. What is the relative density of sprit?
Sol: h1 ρ1 g = h2 ρ2 g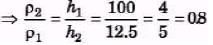
Ques 4: In the above quest ion if 15.0 cm of water and spirit each are further, poured into the respective arms of the tube, what is the difference in the levels of mercury in the two arms? (Relative density of mercury = 13.6)
Sol: (10+15) ρ1g + l1ρg = (125 + 15)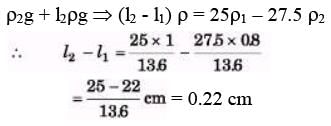
Ques 5: A manometer reads the pressure of a gas in an enclosure as shown in figure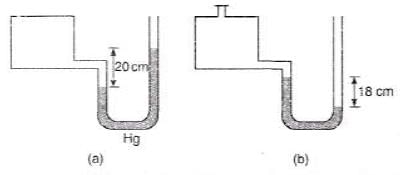
(a) When some of the gas is removed by a pump, the manometer reads as in
(b) The liquid used in the manometers is mercury and the atmospheric pressure is 76 cm of mercury.
(i) Give the absolute and gauge pressure of the gas in the enclosure for cases (a) and (b) in unit s of cm of mercury.
(ii) How would the levels change in case (b) if 13.6 cm of water are poured into the right limb of the manometer?
Sol: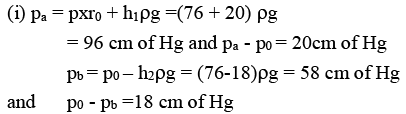
(ii) 13.6 cm of water = 1 cm of Hg,
i.e., Hg in left limb will rise by 0.5 cm and on right limb, it will fall by 0.5 cm. Thus difference in Hg level will become 19 cm.
Introductory Exercise 13.2
Ques 1: A metallic sphere floats in an immissible mixture of water (ρw = 103 kg/m3) and a liquid (ρL = 13.5 × 103 kg/m3) such that its 4/5 th volume is in water and 1/5 th volume in the liquid. Find the density of metal.
Sol: 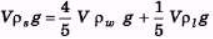
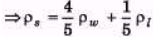
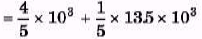
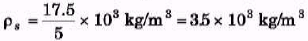
Ques 2: A metallic sphere weighs 210 g in air, 180 g in water and 120 g in an unknown liquid. Find the density of metal and of liquid.
Sol: Vρs = 210 g, V(ρs - ρw) = 180 g and
V(ρs - ρ1) = 120g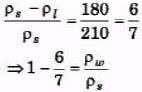
⇒ ρs = 7ρw = 7 × 103 kg/m3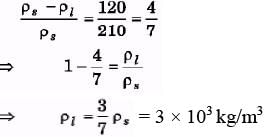
Ques 3: A block of wood floats in a bucket of water placed in a lift. Will the block sink more or less if the lift starts accelerating up?
Sol: As in equilibrium buoyant force and weight balance, so in accelerat ing lift both buoyant force and weight increase such that there is no change in volume of submerged wood.
Ques 4: A weight less balloon is filled with water. What will be its apparent weight when weighed in water?
Sol: As wap =w -B as water is placed in water, so, apparent weight is zero.
Ques 5: A body of weight W1 displaces an amount of water W2. Then W1 < W2, is this statement true or false?
Sol: If a body is placed on water, then it cannot displace water of more weight than its own weight as in such case, buoyant force will be more than weight and the case buoyant jump up the liquid, which is not possible.
Ques 6: A raft of wood (density = 600 kg/m3) of mass 120 kg floats in water. How much weight can be put on the raft to make it just sink?
Sol: w + Vρg + Vσg
m = V(σ - ρ)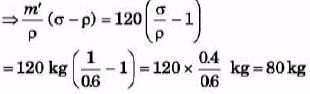
Ques 7: A man is sitting in a boat which is floating in a pond. If the man drinks some water from the pond, how will the level of water in the pond change?
Sol: The amount of water drink and the volume of water displaced due to weight of drank water remains same such that water level do not change.
Vρg + mg = Vσg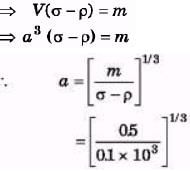
= 10-1 × 51/3 = 10 × 51/3 cm = 17 cm
Ques 8: A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. What can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9. 9. When a cube of wood floats in water, 60% of its volume is submerged. When the same cube floats in an unknown fluid 85% of its volume is submerged. Find the densities of wood and the unknown fluid.
Sol: V ρg = 0.6 V σ1g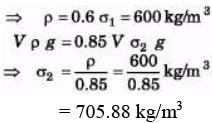
Ques 9: A glass tube of radius 0.8 cm floats vertical in water, as shown in figure. What mass of lead pellets would cause the tube to sink a further 3 cm?
Sol: Vσg = mg
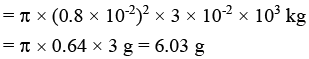
Introductory Exercise 13.3
Ques 1. A water film is made between two straight parallel wires of length 10 cm each, and at a distance of 0.5 cm from each other. If the distance between the wires is increased by 1 mm, how much work will be done? Surface tension of water = 7.2 x 10-2 N/m.
Sol:
ΔW =F × s = 2 Tl × 0.5
= 2 × 7.2 × 10-2 × 10-1 × 10-3
= 1.44 × 10-5 J
Ques 2. A soap bubble of radius R has been formed at normal temperature and pressure under isothermal conditions. Compute the work done. The surface tension of soap solution is T,
Sol:
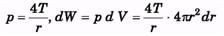
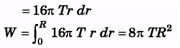
Ques 3. If a drop of radius r breaks up into 27 small drops then how much will be the change in the surface energy. The surface tension of liquid is T.
Sol: 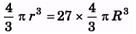
⇒ r =3R
⇒ R = r/3 ΔS = 27 × 4pR2 - 4πr2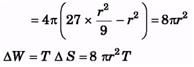
Ques 4. When wax is rubbed on cloth, the cloth becomes water proof why?
Sol: As wax seals thread capillaries which sucks water, that's why water cannot spread over cloth and cloth becomes waterproof.
Ques 5. Water at 20°C is flowing in a pipe of radius 20.0 cm. The viscosity of water at 20°C is 1.005 centipoise. If the water's speed in the centre of the pipe is 3.00 m/s, what is water's speed:
(a) 10.0 cm from the centre of the pipe (half way between the centre and the walls)
(b) at the walls of the pipe?
Sol:
(a) 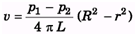
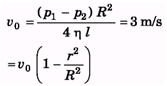
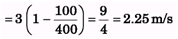
(b) At r = R ⇒ v = 0
Ques 6. Water at 20°C is flowing in a horizontal pipe that is 20.0 m long. The flow is laminar and the water completely fills the pipe. A pump maintains a gauge pressure of 1400 Pa, at a large tank at one end of the pipe. The other end of the pipe is open to the air, The viscosity of water at 20°C is 1.005 poise.
(a) If the pipe has diameter 8.0 cm, what is the volume flow rate?
(b) What gauge pressure must the pump provide to achieve the same volume flow rate for a pipe with a diameter of 4.0 cm?
(c) For pipe in part (a) and the same gauge pressure maintained by the pump, what does the volume flow rate become if the water is at a temperature of 60°C (the viscosity of water at 60°C is 0.469 poise)
Sol:
(a) 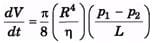
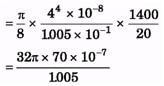
= 7.005 × 10-4 m3/s
(b) 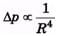
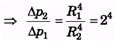
= 16
⇒ Δp2 = 16Δp1 = 224 × 104Pa
(c) 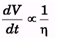
∴ For new value of h.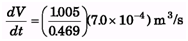
= 1.5 × 10-3 m3/s
|
97 videos|378 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Fluid Mechanics - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is fluid mechanics? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of fluid mechanics? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of fluids in fluid mechanics? |  |
| 4. What is Bernoulli's principle in fluid mechanics? |  |
| 5. How is fluid mechanics related to everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















