Glycolysis & Fermentation | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Glycolysis? |

|
| What is Fermentation? |

|
| Importance of Fermentation |

|
| Advantages of Fermentation |

|
Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It consists of a series of enzymatic reactions that convert one molecule of glucose (a six-carbon sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate (a three-carbon compound). Glycolysis is a critical process in cellular metabolism that also generates small amounts of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH that can be used in other metabolic pathways.
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process.
This process involves a series of enzymatic reactions, including phosphorylation and oxidation, and results in the production of small amounts of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
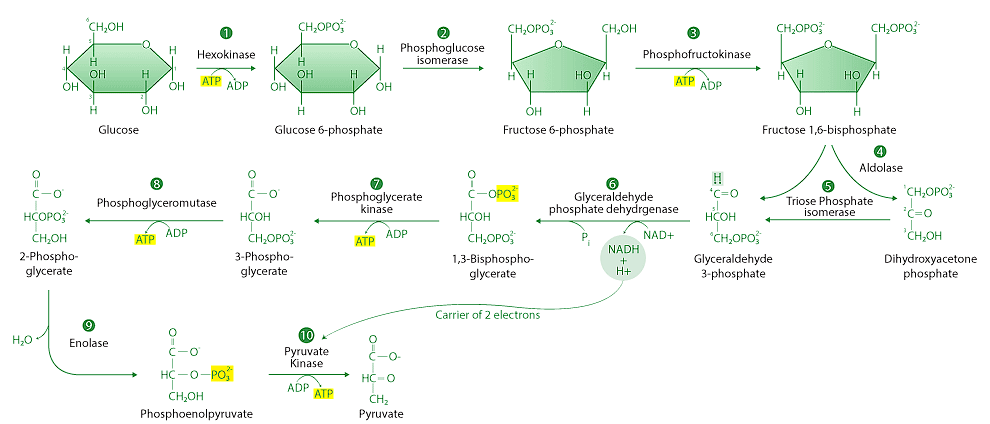
Regulation of Glycolysis
The regulation of the glycolysis occur in the following ways:
Regulation of Hexokinase
The first irreversible stage of glycolysis is the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase.
- Only excess glucose-6 phosphate regulates it. If G6P accumulates in the cell, hexokinase is inhibited by feedback until the G6P is consumed.
- Other mechanisms, such as the pentose phosphate shunt and glycogen production, require glucose-6-phosphate. As a result, unless G-6-P accumulates, the hexokinase process is not blocked.
- In fact, the liver, which is where glycogen is synthesized, has a homologous enzyme called glucokinase. This has a high glucose KM. This permits the brain and muscles to use glucose before it is stored as glycogen.
Regulation of Phosphofructokinase
- The rate-limiting stage in glycolysis is the phosphofructokinase step.
- This enzyme is activated by high AMP/ADP levels, whereas high ATP levels block it (energy charge). Additionally, Citrate, a TCA cycle intermediary, inhibits feed-back.
- Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is a key phosphofructokinase positive effector. The hormone-stimulated phosphorylation of F-6-P results in the formation of F-2,6-BP. Consequently, this is an illustration of allosteric feed-forward activation.
Regulation of Pyruvate Kinase
- Regulation of glycolysis occurs at the pyruvate kinase step if it progresses past the phosphofructokinase step.
- Covalent phosphorylation inhibits pyruvate kinase activity in low-glucose circumstances.
- The pyruvate kinase process is propelled ahead if fructose 1,6 bisphosphate is produced because it functions as an allosteric feedforward activator. AMP and ADP are additional positive effectors, whereas ATP is a negative effector.
- The amino acid alanine, which is produced from pyruvate, is a catabolic inhibitor. A cell’s amount of alanine indicates whether it is anabolic. High levels of alanine suggest that the cell has enough precursors for anabolic processes, allowing catabolism—which supplies the building blocks for anabolism—to be stopped.
What is Fermentation?
Fermentation is the anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates and other organic compounds into alcohols, organic acids, gases, etc. with the help of micro-organisms or their enzymes. It’s an essential process used in industrial processes and in nature for providing energy and metabolic products for organisms in environments with limited or no oxygen.
Examples of Fermentation
The various types of examples of fermentation are:
- Lactic acid bacteria ferment milk sugars (lactose) into lactic acid, curdling the milk and creating yogurt
- Yeast is also used in baking to leaven bread through alcoholic fermentation.
- Lactic acid fermentation, along with other biochemical processes, is involved in the production of various types of cheese.
- Acetic acid fermentation, performed by Acetobacter bacteria, is used to make vinegar.
- Yeast converts sugars in fruits (e.g., grapes for wine, barley for beer) into ethanol and carbon dioxide through alcoholic fermentation. This process is important for making beer, wine, and other spirits.
- Fermentation is used in the production of biofuels, such as ethanol.
Process of Fermentation
Fermentation occurs under anaerobic conditions, it is an alternative pathway for cells to generate energy. The mechanism of fermentation is as follows:

- In the initial step glucose is breaks down into pyruvate molecules in the cytoplasm of cells and generates a small amount of ATP and NADH.
- In the absence of oxygen, cells can’t undergo the complete oxidation of pyruvate as in aerobic respiration. NADH produced during glycolysis is to be converted back to NAD+ to keep glycolysis running. In fermentation electrons is transfered from NADH to the organic molecules derived from the original sugar.
- End products depend on the type of fermentation and the microorganisms involved. For example, in alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide, while in lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid.
Types of Fermentation
Fermentation are of various types depending upon the specific microorganism involved in the reaction and on the resulting product. Different types of fermentation are as follows:
1. Lactic Acid Fermentation
It is a metabolic process by which starch or sugar is converted into metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid by yeast strains and bacteria. It is an anaerobic fermentation process that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells when energy spend is more than the supplied oxygen. In this process, one glucose molecule is converted into pyruvate and then into lactic acid.
2. Alcohol Fermentation
Ethanol Fermentation or Alcohol Fermentation is a biological process where pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is broken down into Ethanol (alcohol) and carbon dioxide. Yeast performs this process in the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation is an anaerobic process. Ethanol Fermentation is mainly used for the preparation of Alcoholic beverages like beer and the production of ethanol fuel.
3. Acetic acid Fermentation
Acetic acid is also known as vinegar. The production of acetic acid generally involves two processes, the first is using yeast alcohol produced from sugar and the second is utilizing acetic acid bacteria to oxidize ethyl alcohol to acetic acid through acetaldehyde. Fermentation of acetic acid is done by two methods, surface fermentation and submerged fermentation.
Importance of Fermentation
- Fermentation have importance across various sectors due to its diverse applications and contributions to numerous processes. Some of the importance of fermentation are as follows:
- Fermentation has many uses in various fields ranging from the food industry to the manufacturing industry.
- Food products can be preserved and stored using the fermentation process, which increases the shelf life of food.
- Various flavors and tastes can be added to food items through this process.
Advantages of Fermentation
Fermentation provides a variety of advantages across various industries and applications, making it an important process for numerous purposes. Some of the advantages of fermentation are as follows:
- Fermentation preserves food by creating an environment conducive to the growth of beneficial microorganisms while inhibiting harmful ones, thereby increasing the shelf life of food products.
- Fermentation is important for making biofuels like ethanol, which can replace fossil fuels. This helps reduce pollution and our reliance on limited natural resources.
- Fermentation processes, like anaerobic digestion, convert organic waste into useful products such as biogas and compost.
- Fermentation is used in the synthesis of various chemicals, like organic acids, enzymes, and amino acids, which have applications in industries such as food, agriculture, and textiles.
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Glycolysis & Fermentation - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is fermentation? |  |
| 2. How does fermentation produce alcohol? |  |
| 3. What is lactic acid fermentation? |  |
| 4. Which microorganisms are involved in alcohol fermentation? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of fermentation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















