Types of Redox Reactions | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Combination Reactions |

|
| Decomposition Reactions |

|
| Displacement Reactions |

|
| Disproportionation Reactions |

|
There are four main types of redox reactions:
- Combination Reactions
- Decomposition Reactions
- Displacement Reactions
- Disproportionation Reactions
Combination Reactions
- Combination Reactions involve the combination of two compounds to form a single compound.
- A combination reaction may be denoted in the manner: A + B → C
- Either A and B or both A and B must be in the elemental form for such a reaction to be a redox reaction.
- All combustion reactions, that make use of elemental dioxygen, as well as other reactions involving elements other than dioxygen, are redox reactions.
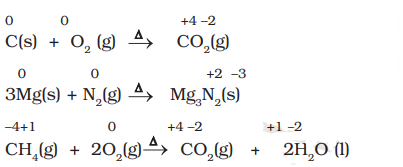 Examples of Combustion Reactions
Examples of Combustion Reactions
Decomposition Reactions
- Decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions.
- Precisely, a decomposition reaction leads to the breakdown of a compound into two or more components, at least one of which must be in the elemental state.
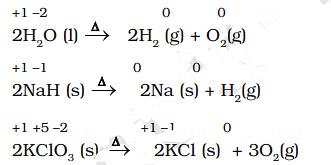 Examples of Decomposition Reactions
Examples of Decomposition Reactions
- It may carefully be noted that there is no change in the oxidation number of hydrogen in methane under combination reactions and that of potassium in potassium chlorate. This may also be noted here that all decomposition reactions are not redox reactions. For example, the decomposition of calcium carbonate is not a redox reaction.

Displacement Reactions
- In a displacement reaction, an ion (or an atom) in a compound is replaced by an ion (or an atom) of another element.
- It may be denoted as: X + YZ → XZ + Y
- Displacement reactions fit into two categories: metal displacement and non-metal displacement.
(a) Metal Displacement:
- A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state.
- Metal displacement reactions find many applications in metallurgical processes, where pure metals are obtained from their compounds in ores.
- A few such examples are:
 Some Examples of Metal Displacement ReactionsIn each case, the reducing metal is a better-reducing agent than the one that is being reduced, demonstrating a greater capability to lose electrons compared to the one that is reduced.
Some Examples of Metal Displacement ReactionsIn each case, the reducing metal is a better-reducing agent than the one that is being reduced, demonstrating a greater capability to lose electrons compared to the one that is reduced.
(b) Non-metal Displacement:
- The non-metal displacement redox reactions include hydrogen displacement and a rarely occurring reaction involving oxygen displacement.
- All alkali metals and some alkaline earth metals (Ca, Sr, and Ba), which are very good reductants, will displace hydrogen from cold water.

- Less active metals such as magnesium and iron react with steam to produce dihydrogen gas.

- Many metals, including those which do not react with cold water, are capable of displacing hydrogen from acids. Dihydrogen from acids may even be produced by metals that do not react with steam, with cadmium and tin being examples of such metals. A few examples for the displacement of hydrogen from acids are:

- Very less active metals, which may occur in the native state such as silver (Ag) and gold (Au), do not react even with hydrochloric acid.
Disproportionation Reactions
Disproportionation reactions are a special type of redox reaction. In such reactions, an element in one oxidation state is simultaneously oxidized and reduced.
Key points about disproportionation reactions include:
- An element in one oxidation state undergoes both oxidation and reduction in a disproportionation reaction.
- At least one of the reacting substances always contains an element that can exist in at least three oxidation states.
- The element in the form of the reacting substance is in the intermediate oxidation state.
- Both higher and lower oxidation states of that element are formed in the reaction.
Example: The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is a familiar example of a disproportionation reaction, where oxygen undergoes disproportionation:

Here, the oxygen of peroxide, initially present in the –1 state, is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 and decreases to –2 oxidation state in H2O.
|
129 videos|244 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Redox Reactions - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is a combination reaction? |  |
| 2. What is a decomposition reaction? |  |
| 3. What is a displacement reaction? |  |
| 4. What is a disproportionation reaction? |  |
| 5. What are the types of redox reactions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|













