Potentiometer & Its Applications | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is Potentiometer?
Potentiometer working can be explained when the potentiometer is understood. It is defined as a three-terminal resistor having either sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. In order to use the potentiometer as a rheostat or variable resistor, it should have only two terminals with one end and the wiper.
Following are the terms used to describe types of potentiometers:
1. Slider pot or slide pot: This can be adjusted by sliding the wiper right or left with a finger or thumb.
2. Thumb wheel pot or thumb pot: This can be adjusted infrequently with the help of small thumb wheel which is a small rotating potentiometer.
3. Trimmer pot or trim pot: This can be adjusted once for fine-tuning of an electric signal.
Necessity of Potentiometer
- Practically voltmeter has a finite resistance (ideally it should be ∞). In other words, it draws certain current from the circuit. To overcome this problem a potentiometer is employed because at the instant of measurment , it draws no current from the circuit.
Working Principle of Potentiometer
- Any unknown potential difference is balanced on a known potential difference which is uniformly distributed over the entire length of a potentiometer wire.
This process is termed as zero deflection or null deflection method.
Note :
(i) Potentiometer wire : Made up of alloys of manganin, constantan, eureka.
(ii) Special properties of these alloys are high specific resistance, negligible temperature co-efficient of resistance (α). This results in invariability of resistance of potentiometer wire over a long period.
Circuits of Potentiometer

- Primary circuit contains source of constant voltage & rheostat or Resistance Box.
- Secondary circuit contains battery & galvanometer.
➢ Potential gradient (x) (V/m)
- Potential difference corresponding to unit length of potentiometer wire is called potential gradient.
- Rate of growth/fall of potential per unit length of potentiometer wire is equal to potential gradient.
- Let r = 0 and R1 = 0 then VAB = E (max. in the ideal case) then x = E/L
Unit and dimensions : (V/m ; MLT-3A-1) - Always VAB < E ; (∵ r + R1 ≠ 0)
x = VAB/L - Now VAB = I RP (RP = resistance of potentiometer wire)
- Let ρ = Resistance per unit length of potentiometer wire

current in primary circuit I
- If cross-sectional radius is uniform ⇒ x is uniform over the entire length of potentiometer wire.
- If I constant, then

- 'x' depends on → ρ, r , σ etc.
➢ Factors affecting 'x'
- If VAB = constant and L = constant then for any change → x remains unchanged.
- If there is no information about VAB then always take VAB as constant so (x ∝ 1/L)
- If VAB and L are constant :
- For any change like radius of wire, substance of wire (σ) there is no change in x.
- Any change in the secondary circuit results in no change in x because x is an element of primary circuit.
Note:
xmax or xmin on the basis of range of rheostat or resistance box (R.B.)
Applications of Potentiometer
Comparison of EMF's of two cells using potentiometer
- Consider the circuit arrangement of potentiometer given below used for comparison of emfs of two cells

- Positive terminals of two cells of emfs E1 and E2 (whose emf are to be compared) are connected to the terminals A and negative terminals are connected to jockey through a two way key K2 and a galvanometer
- Now first key K1 is closed to establish a potential difference between the terminals A and B then by closing key K2 introduce cell of EMF E1 in the circuit and null point junction J1 is determined with the help of jockey.If the null point on wire is at length
l1 from A then
E1 = Kl1
Where K → Potential gradient along the length of wire Similarly cell having emf E2 is introduced in the circuit and again null point J2 is determined. If length of this null point from
A is l2 then
E2 = Kl2
Therefore
E1/E2 = l1/l2
This simple relation allows us to find the ratio of E1/E2if the EMF of one cell is known then the EMF of other cell can be known easily
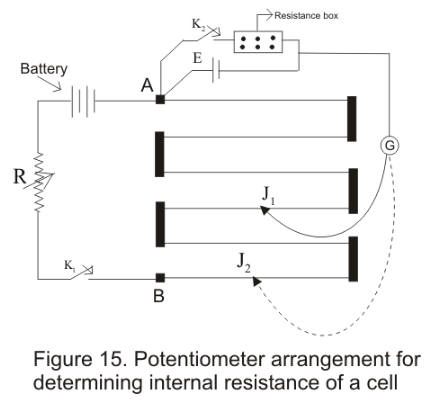
Determination of internal resistance of the cell
- Potentiometer can also be used to determine the internal resistance of a cell

- For this a cell whose internal resistance is to be determined is connected to terminal A of the potentiometer across a resistance box through a key K2
- First close the key K1 and obtain the null point. Let l1 be the length of this null point from terminal A then
E = Kl1 - When key K2 is closed ,the cell sends current through resistance Box (R). If E2 is the terminal
Potential difference and null point is obtained at length l2(AJ2) then
V = Kl2
Thus
E/V=l1/l2
But E = I(R+ r) and V = IR
This gives
E/V = (r+R)/R
So (r + R)/R = l1/l2
giving
r = R(l1/l2-1) - Using above equation we can find internal resistance of any given cell
|
97 videos|336 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Potentiometer & Its Applications - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is a potentiometer? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of a potentiometer? |  |
| 3. How does a potentiometer work? |  |
| 4. Can a potentiometer be used as a voltage divider? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using a potentiometer? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|