Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur Solutions Class 10 Chemistry - Periodic Classification Of Elements- 3
(Page No - 303)
Question 4:
(a) How does the chemical reactivity of alkali metals vary on going down in group 1 of the periodic table ?
(b) How does the chemical reactivity of the halogens vary on going down in group 17 of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) In group 1 of alkali metals, the chemical reactivity increases from lithium to francium.
(b) In group 17 of halogen elements, the chemical reactivity decreases from fluorine to iodine.
Question 5:
What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as boron have in common ?
Solution :
All elements in the same column of the periodic table as boron have 3 valence electrons.
Question 6:
What property do all the elements in the same group of the periodic table as fluorine have in common ?
Solution :
The element fluorine is in group 17 o f the periodic table and has a valency of 1. So, all the elements in the same group of periodic table as fluorine will have a valency of 1.
Question 7:
(a) What is the number of valence electrons in the atoms of first element in a period ?
(b) What is the usual number of valence electrons in the atoms of the last element in a period ?
Solution :
(a) 1
(b) 8
Question 8:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
On going down in a group of the periodic table, the number of valence electrons increases.
Solution :
False
Question 9:
What is the major characteristic of the first elements in the periods of the periodic table ? What is the general name of such elements ?
Solution :
The first elements in the periods of the periodic table have 1 valence electron. Such elements are called alkali metals.
Question 10:
How do the atomic radii of elements change as we go from left to right in a period of the periodic table ?
Solution :
On moving from left to right in a period, the atomic size decreases.
Question 11:
What happens to the metallic character of the elements as we go down in a group of the periodic table ?
Solution :
On going down in a group of the periodic table, the metallic character of elements increases.
Question 12:
How does the number of valence electrons vary on moving from left to right :
in the first period of the periodic table ? (if) in the second period of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(i) The number of valence electrons increases from 1 to 2 in the 1st period of the periodic table.
(ii) The valence electrons increase from 1 to 8 in the 2nd period of the periodic table.
Question 13:
How does the valency of elements change on moving from left to right in the third period of the periodic table ?
Solution :
The valency of elements increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to zero in the 3rd period.
Question 14:
How does the valency of elements vary in going down a group of the periodic table ?
Solution :
All the elements in a group have the same valency while going down the group.
Question 15:
Name the element which is in :
(a) first group and third period. (b) seventeenth group and second period.
Solution :
(a) Sodium.
(b) Fluorine .
Question 16:
How do electronic configurations of elements change in second period of periodic table with increase in atomic numbers ?
Solution :
2, 1 ; 2, 2 ; 2,3 ; 2,4 ; 2, 5 ; 2, 6 ; 2, 7 ; 2, 8 .
Question 17:
Arrange the following elements in increasing order of their atomic radii :
Li, Be, F, N
Solution :
F < N < Be < Li .
Question 18:
Arrange the following elements in the increasing order of their metallic character :
Mg, Ca, K, Ga
Solution :
Ga < Mg < Ca < K .
Question 19:
Rewrite the following statements after correction, if necessary :
(i) Elements in the same period have equal valency
(ii) The metallic character of elements in a period increases gradually on moving from left to right.
Solution :
(i) Elements in th e same group have equal valency.
(ii) The metallic character of elements in a period decreases gradually on moving from left to right
Question 20:
Fill in the blanks in the following statements :
(a) The horizontal rows in a periodic table are called……….
(b) In going across a period (right to left)in periodic table, the atomic size of the atom………
(c) On moving from right to leftin the second period, the number of valence electrons……….
(d) On going down in a group in the periodic table, the metallic character of elements………..
(e) The tendency to gain an electron…….. on moving down in a group of the periodic table.
Solution :
(a) Periods
(b) Increases
(c) Decreases
(d) Increases
(e) Decreases
Question 21:
Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the periodic table. Write the electronic configurations of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative ? Why ?
Solution :
N (2 ,5 ) ; P (2, 8, 5) ; Nitrogen will be more electronegative because its atom has small size due to which the attraction of its nucleus for the incoming electron is more
Question 22:
An element X belongs to group 2 and another element Y belongs to group 15 of the periodic table :
(a) What is the number of valence electrons in X ? (b) What is the valency of X ?
(c) What is the number of valence electrons in Y ? (d) What is the valency of Y ?
Explain how you have arrived at your answers.
Solution :
(a) 2.
For groups 1 and 2, the number of valence electrons is equal to the group number.
(b) 2 .
Valency is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the atom of the element.
(c) 5 .
For groups 13 to 18, the number of valence electrons is equal to (group no. – 10).
(d) 3 .
The number of electrons lost or gained by one atom of an element to achieve the nearest inert gas configuration, gives us the valency.
Question 23:
(a) What is a period in a periodic table ? How do atomic structures (electron arrangements) change in a
period with increase in atomic numbers from left to right ?
(b) How do the following change on going from left to right in a period of the periodic table ?
(i) Chemical reactivity of elements (ii) Nature of oxides of elements
Give examples in support of your answer.
Solution :
(a) The horizontal rows of elements in a periodic table are called periods. As we move from left to right in a period, the atomic number of elements increases which means that the no. of protons and electrons in the atom increases. Due to large positive charge on the nucleus, the electrons are pulled in more close to the nucleus and the size of the atom decreases.
(b) (i) On moving from left to right in a period, the chemical reactivity of elements first decreases and then increases.
Example: In the 3rd period of elements, sodium is a very reactive element, magnesium is less reactive whereas aluminium is still less reactive. Silicon is the least reactive in the third period. Now, phosphorus is quite reactive, sulphur is still more reactive whereas chlorine is very reactive.
(ii) On moving from left to right in a period, the basic nature of oxides decreases and the acidic nature of oxides increases.
Example: In the 3rd period of the periodic table, sodium oxide is highly basic in nature and magnesium oxide is comparatively less basic. The aluminium and silicon oxides are amphoteric in nature. Phosphorus oxides are acidic, sulphur oxides are more acidic whereas chlorine oxides are highly acidic in nature.
Question 24:
(a) How does the size of atoms (atomic size) generally vary in going from left to right in a period of the
periodic table ? Why does it vary this way ?
(b) What happens to the metallic character of the elements as we move from left to right in a period of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) On moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table, the atomic size decreases. As we move from left to right in a period, the atomic number of elements increases which means that the no. of protons and electrons in the atoms increases. Due to large positive charge on the nucleus, the electrons are pulled in more close to the nucleus and the size of atom decreases.
(b) On moving from left to right in a period, the metallic character of elements decreases.
(Page No - 304)
Question 25:
(a) Explain why :
All the elements of a group have similar chemical properties.
All the elements of a period have different chemical properties.
The atomic radii of three elements X, Y and Z of a period of the periodic table are 186 pm; 104 pm and 143 pm respectively. Giving a reason, arrange these elements in the increasing order of atomic numbers in the period.
Solution :
(a) (i) All the elements of a group have similar chemical properties because they have same no. of valence electrons in their outermost shell.
(ii) All the elements of a period have different chemical properties because they have different no. of valence electrons in their atoms.
(b) Order of atomic numbers of elements: X < Z < Y. Because as the atomic number increases in a period from left to right, the size of atoms goes on decreasing
Question 26:
(a) How does the electropositive character of elements change on going down in a group of the periodic table ?
State how the valency of elements varies (i)in a group, and (ii)in a period, of the periodic table.
Solution :
(a) On going down in a group of the periodic table, the electropositive character of elements increases.
(b) (i) In a group, all the elements have the same valency.
(ii) In a period, on moving from left to right, the valency of elements first increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to zero.
Question 27:
(a) What is the fundamental difference in the electronic configurations between the group 1 and group 2 elements ?
(b) On the basis of electronic configuration, how will you identify :
(i) chemically similar elements ?
(ii) the first element of a period ?
Solution :
(a) The fundamental difference between the electronic configuration of group 1 and group 2 elements is that group 1 elements have 1 valence electron in their atoms whereas group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons in their atoms.
(b) ( i ) All the chemically similar elements will have same valence electrons.
(ii) The 1st element in a period is determined by the no. of valence electrons in its atoms. The 1st element of every period has 1 valence electron.
Question 28:
(a) What is the usual number of valence electrons and valency of group 18 elements of the periodic table ?
(b) What happens to the number of valence electrons in the atoms of elements as we go down in a group of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) Usual number of valence elec trons is 8; Valency is 0 (zero).
(b) The number of valence electrons remains the same .
Question 29:
(a) What is the main characteristic of the last elements in the periods of the periodic table ? What is the general name of such elements ?
(b) What is the number of elements in : (a) 1st period, and (b) 3rd period, of the modern periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) The main characteristic of last elements in a period is that they all have 8 valence electrons in their atoms except helium. Such elements are called noble elements.
(b) (i) 2
(ii) 8.
Question 30:
(a) How does the atomic size vary on going down from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table ? Why does it vary this way ?
(b) Lithium, sodium and potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements ? Explain your answer.
Solution :
(a) On going down in a group of the periodic table, the atomic size increases. When we move from top to bottom in a group, a new shell of electrons is added to the atoms at every step due to which the size of atom increases.
(b) The similarity in the atoms of lithium, sodium and potassium is that all of them have 1 valence electron each.
Question 31:
(a) How does the tendency to lose electrons change as we go down in group 1 of the periodic table ? Why does it change this way ?
(b) How does the tendency to gain electrons change as we go down in group 17 of the periodic table ? Why does it change this way ?
Solution :
(a) The tendency of an atom to lose electrons increases on moving down in a group of the periodic table. As we go down in group 1, one more electron shell is added at every stage and the size of the atom increases. The valence electrons become more and more away from the nucleus and hold of the nucleus on valence electrons decreases. Due to this, the atoms can lose valence electrons more easily to form positive ions and hence electropositive character increases.
(b) The tendency of an atom to gain electrons decreases on going down in a group of the periodic table. When we move from top to bottom in group 17, a new shell of electrons is added to the atoms at every step, due to which the size of atom increases. The nucleus goes more deep inside the atom due to which the attraction of nucleus for the incoming electron decreases due to which the atom cannot form negative ions easily and hence the electronegative character decreases.
Question 32:
(a) Why does the size of the atoms progressively become smaller when we move from sodium (Na) to chlorine (Cl) in the third period of the periodic table ?
(b) Helium and neon are unreactive gases. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common ?
Solution :
(a) As we move from Na to Cl in the 3rd period, the size of the atoms of the elements decreases. Na atom is the biggest whereas Cl atom is the smallest in size. As we move from left to right in a period, the atomic no. of elements increases i.e. the number of protons and electrons in the atoms increases. Due to large positive charge on nucleus, the electrons are pulled in more close to the nucleus and thus the size of the atom decreases from Na to Cl.
(b) Helium and neon atoms have completely filled outermost electron shells (containing the maximum number of electrons which can be accommodated in them) .
Question 33:
(a) In the modern Periodic Table, why does cobalt with higher atomic mass of 58.93 appear before nickel having lower atomic mass of 58.71 ?
(b) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) Modern periodic table arranges the elements according to increasing atomic numbers. So, the atomic number of cobalt (27) comes first whereas the atomic number of nickel (28) comes later.
(b) In Mendeleev’s periodic table, hydrogen has been placed in group I since like alkali metals, hydrogen also combines with halogens, oxygen and sulphur to form compounds having similar formulae. This means that hydrogen resembles alkali metals in some of the properties.
Hydrogen also resembles halogens in some of the properties. So, hydrogen could also be placed in group VII of halogen elements.
Thus, Mendeleev’s periodic law could not assign a correct position to hydrogen in the periodic table.
Question 34:
(a) What are the periods and groups in a periodic table ? Give two characteristics of each.
(b) In terms of electronic configurations, explain the variation in the size of the atoms of the elements belonging to the same period and same group.
(c) Given alongside is a part of the periodic table. As we move vertically downward from Li to Fr :
(i) What happens to the size of atoms ?
What happens to their metallic character ?
(d) Name two properties of elements whose magnitudes change when going from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table. In what manner do they change ?
(e) Rewrite the following statement after correction, if necessary :
Groups have elements with consecutive atomic numbers.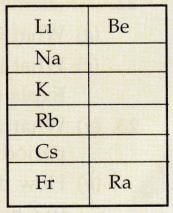
Solution :
(a) The horizontal rows of elements in a periodic table are called periods.
Characteristics:
(i) The elements in a period have consecutive atomic numbers.
(ii) The no. of elements in period is fixed by the maximum no. of electrons which can be accommodated in various shells.
The vertical columns in a periodic table are called groups.
Characteristics:
(i) The elements in a group do not have consecutive atomic numbers.
(ii) All the elements in a group have similar electronic configurations and show similar properties.
(b) The size of atom decreases on moving from left to right in a period. As we move from left to right in a period, the atomic number of elements increases which means that the no. of protons and electrons in the atom increases. The electronic configuration of the atoms increases in the same shell. Due to large positive charge on the nucleus, the electrons are pulled in more close to the nucleus and the size of the atom decreases.
On going down in a group of the periodic table, the atomic size increases. The no. of electron shells in the atoms gradually increases and the electronic configuration also increases due to which the atomic size increases.
(c)(i) The atomic size increases gradually from lithium to francium.
(ii) The metallic character increases from lithium to francium.
(d) On going down in a group of the periodic table, the atomic size and metallic character increases. When we move down from top to bottom in group 1 of alkali metals, the size of atoms increases gradually from lithium to francium.
In group 1 of alkali metals, lithium is the least metallic element whereas francium is the most metallic element.
(e) Periods have elements with consecutive atomic numbers .
(Page No - 305)
Question 35:
(a) Explain why, the first period of the modern periodic table has only two elements whereas second period has eight elements
(b) Why do elements in the same group show similar properties but the elements in different groups show different properties ?
(c) For each of the following triads, name the element with the characteristics specified below :
(d) State one reason for keeping fluorine and chlorine in the same group of the periodic table.
(e) What are the merits of the modern periodic table of elements ?
Solution :
(a) The 1st period has two elements because the 1st electron shell of an atom c a n take a maximum of two electrons only. The 2nd period of the periodic table has 8 electrons because the maximum no. of electrons which can be put in the 2nd shell of an atom is 8.
(b) The elements in the same group show similar properties because they have similar electronic configuration (having the same number of valence electrons) whereas the elements of different groups have different electronic configurations (different number of valence electrons) due to which they show different properties.
(c) (i) F; Br
(ii) Li; Li
(d) Fluorine and chlorine have been placed in the same group because both of them have 7 valence electrons.
(e) Merits of modern periodic table:
(i) The modern periodic table is based on the atomic numbers of elements which is the most fundamental property of elements.
(ii) It helps us to understand why elements in a group show similar properties but elements in different groups show different properties.
(iii) It explains the reasons for the periodicity in properties of elements.
(iv) It tells us why the properties of elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18 and 32 elements.
Question 36:
(a) What is a group in the periodic table ? In which part of a group would you separately expect the elements to have (i) the greatest metallic character (ii) the largest atomic size ?
(b) In what respects do the properties of group 1 elements differ from those of group 17 elements ? Explain with examples by taking one element from each group.
(c) From the standpoint of atomic structure, what determines which element will be the first and which the last in a period of the periodic table ?
(d) Explain why, the properties of elements are repeated after 2, 8,18 and 32 elements in the periodic table.
(e) What are the advantages of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(a) The vertical columns in a periodic table are called groups.
(i) The greatest metallic character is found in the elements in the lowest part of the group.
(ii) The largest atomic size is found in the lowest part of the group.
(b) Group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and are ionic in chemical reactions. Their chemical reactivity increases down the group. They are electropositive in nature and it increases down the group.
Whereas, the elements of group 17 have 7 valence electrons. They all are non-metals. Their chemical reactivity decreases down the group. They are electronegative in nature and it decreases down the group.
(c) The no. of valence electrons in the atoms of elements decides which element will be the 1st element in a period and which will be the last in a period.
(d) The properties of elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18 and 32 elements in the periodic table because the electronic configurations of the elements are repeated in this manner.
(e) Advantages of the periodic table:
(i) It has made the study of chemistry systematic and easy.
(ii) It is easier to remember the properties of an element if its position in the periodic table is known.
(iii) The type of compounds formed by an element can be predicted by knowing its position in the periodic table.
(iv) It is used as a teaching aid in chemistry in schools and colleges.
(Page No - 306)
Question 57:
The atomic numbers of the three elements X, Y and Z are 2, 6 and 10 respectively.
Which two elements belong to the same group ?
Which two elements belong to the same period ?
Give reasons for your choice.
Solution :
(i) X and Z.
X and Z have zero valency hence they belong to same group: noble gases.
(ii) Y and Z.
Y: 2,4 and Z: 2,8 so, both of them belong to second period with two shells filled.
Question 58:
An atom has the electron structure of 2, 7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this atom ?
(b) To which of the following would it be chemically similar ?
7N, 15P, 17CI, isAr
(c) Why would you expect it to be similar ?
Solution :
(a) 9.
(b) 17 Cl.
(c) Both have the same number of valence electrons (7 electrons each) in their atoms.
Question 59:
Consider the following elements :
20Ca, gO, isAr, 16S, 4Be, 2He Which of the above elements would you expect to be :
(i) very stable ? (ii) in group 2 of the periodic table ?
(iii) in group 16 of the periodic table ?
Solution :
(i) 18 Ar and 2 He (Noble gases) .
(ii) 20 Ca and 4 Be (no. of valence electrons in each = 2).
(iii) 8 O and 16 S (no. of valence electrons in each = 6).
Question 60:
In each of the following pairs, choose the atom having the bigger size :
(a) Mg (At. No.12) or Cl (At. No. 17)
(b) Na (At. No. 11) or K (At. No. 19)
Solution :
(a) Mg since atomic size decreases from left to right in a period.
(b) K since atomic size increases on going down a group .
Question 61:
The atomic numbers of three elements A, B and C are given below :
(i) Which element belongs to group 18 ? (ii) Which element belongs to group 15 ?
(iii) Which element belongs to group 13 ? (iv) To which period/periods do these elements belong ?
Solution :
(i) C (2, 8).
(ii) B (2, 5).
(iii) A (2, 3).
(iv) 2nd period (2 shells are filled).
Question 62:
An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 2 of the periodic table. State :
(a) number of valence electrons (b) valency (c) metal or non-metal (d) name of the element
Solution :
(a) 2.
(b) 2 .
(c) Metal .
(d) Magnesium .
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur Solutions Class 10 Chemistry - Periodic Classification Of Elements- 3
| 1. What is the periodic classification of elements? |  |
| 2. How are elements classified in the periodic table? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry? |  |
| 4. How does the periodic table help in predicting the properties of elements? |  |
| 5. What are the main trends observed in the periodic table? |  |
















