Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Money and Credit
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What do the banks do with the 'Public Deposits'? Describe their working mechanism.
Ans:
Deposit and Loan System: Banks play a crucial role by accepting deposits from the public. A significant portion of these deposits is strategically utilized by banks to extend loans.
Loan Demand: There is a substantial and consistent demand for loans to fuel various economic activities.
Utilization of Deposits: Banks leverage the collected deposits to meet the diverse loan requirements of individuals and businesses. This practice serves as the primary source of income for banks, as they earn interest on extended loans.
Role as a Mediator: Acting as intermediaries, banks facilitate a financial bridge between those possessing surplus funds (depositors) and those in need of funds (borrowers).
Interest Dynamics: Banks implement a strategic approach by charging a higher interest rate on loans in comparison to the interest rates offered on deposits. This interest differential contributes to the overall financial operations of the bank.
Q2: What are demand deposits? Describe any three salient features of demand deposits.
Ans: People with surplus money or extra amount deposit it in banks. The banks keep the money safe and give interest on it. The deposits can be drawn at any time on demand by the depositors. That is why they are called 'demand deposits'.
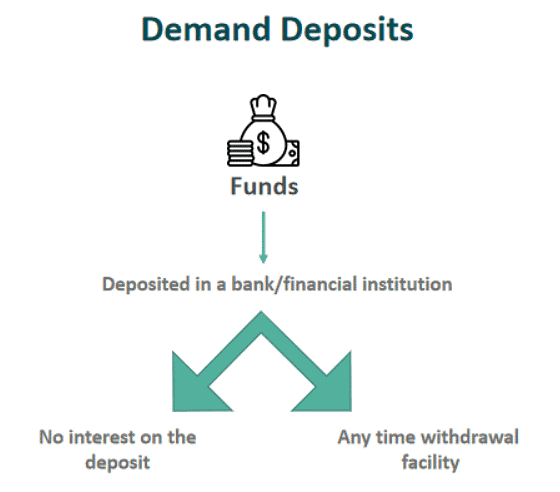
(i) The demand deposits encashable by issuing cheques have the essential features of money.
(ii) They make it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash.
(iii) Since demand drafts/cheques are widely accepted as a means of payment along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Q3: Mention any three points of distinction between formal sector loans and informal sector loans. Ans:
Formal Sources of Credit | Informal Sources of Credit |
Formal sources of credit are generally provided by banks and cooperatives. | Informal sources of credit are generally provided by moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, and friends. |
The interest rate for repaying loans is lower. | The interest rate for repaying loans is costlier. |
RBI supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans and also ensures that these facilities should also be given to small cultivators and small borrowers. | In the informal sector, no such organization is there to supervise the credit activities of lenders that they used to charge a higher rate of interest on loans. |
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain any two features of formal sector loans and informal sector loans.
Ans: Formal Sector Loans:
Formal sector loans include loans from banks and cooperatives. Features of formal sector loans are:
(i) Formal sectors provide cheap and affordable loans and their rate of interest is monitored by RBI.
(ii) The formal sector strictly follows the terms of credit which include interest rate, collateral, documentation, and the mode of repayment.
Informal Sector Loans:
Informal sector loans include loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc. Features for Informal sector loans are:
(i) Their credit activities are not governed by any organization, therefore they charge a higher rate of interest.
(ii) Informal sector loan providers know the borrowers personally, and hence they provide loans on easy terms without collateral and documentation.
Q2: What are the two main reasons for formal credit not being available to the rural poor? Why is there a need to expand rural credit?
Ans: The two main reasons for formal credit not being available to the rural poor are :
(i) The absence of collateral and documentation is the main reason that prevents rural poor from getting bank loans.
(ii) The arrangements of informal sector loans are flexible in terms of timelines, procedural requirements, interest rates, etc. They are adjustable according to the needs and convenience of the borrower.
There is a need to expand rural credit from the side of the formal sector because :
(i) Informal sectors exploit rural the poor by putting them in debt traps.
(ii) Cheap and affordable credit for rural poor is important for the country’s overall development.
Q3: Why do rural borrowers depend on the informal sector for credit? What steps can be taken to encourage them to take loans from formal sources? Explain any two.
Ans: The rural borrowers depend on the informal sector for credit because :
(i) Absence of collateral and documentation with rural borrowers.
(ii) Flexible loans in terms of timelines, interest rates, procedural requirements, etc. are provided to rural borrowers by informal sectors.
Steps that can be adopted to encourage them to take loans from formal sources are :
(i) Awareness among rural borrowers against the exploitation of informal sectors. Need to aware of the rate of interest and debt traps made by such moneylenders.
(ii) Promotion of self-help groups. These groups collect their savings as per their ability to save. Members can take small loans from the groups to meet their requirements. If the group is regular in savings for a year or two, it can avail loan from the bank.
Q4: ‘Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development’. Explain the statement with four points.
OR
Why do we need to expand the formal sources of credit in India? Explain any four reasons.
Ans: If the loans are cheap and affordable, this can lead to countries development in the following ways :
(i) Cheap loans result in higher incomes and higher profits which can help in the expansion of business.
(ii) More and more people can be benefited from the loans in their businesses.
(iii) This can help in making more and more agricultural activities, small-scale industries, etc. Credit can be distributed more equally which helps in benefiting the poor by the help of cheaper loans.
Q5: Answers the following questions :
(a) Why are banks unwilling to lend loans to small farmers?
(b) Besides banks, what are the other sources of credit from which the small farmers can borrow.
(c) Explain how terms of credit can be unfavorable for small farmers.
(d) From where can small farmers get cheap loans?
Ans:
(a) Banks provide loans after collateral and documentation securities, which generally the small farmers failed to comply with. Therefore, banks are unwilling to lend loans to small farmers.
(b) There are several informal sources of credit like landlords, moneylenders, traders, relatives, and friends, etc.
(c) Terms of informal credit can put small farmers into debt traps. Higher rates of interest and unfavorable conditions exploit farmers through the situation of multiple loans.
(d) Farmers can get cheap and safe loans from formal credit providers i.e., banks and cooperative societies.
Q6: Which are the two major sources of formal sector credit in India? Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit?
Ans: The two major sources of formal sector credit in India are — commercial banks and cooperative societies.
We need to expand formal sources of credit for to following reasons :
(a) Informal sources of credit exploit the poor resulting in putting them into debt traps.
(b) Formal sources of credit are cheaper and thus they help in the country’s development.
Q7: What is meant by the term of credit? What does it include?
Ans: Terms of credit are the requirements that need to be satisfied for any credit arrangements. It includes the interest rate, collateral, documentation, and mode of repayment. However, the terms of credit vary depending upon the nature of the lender, borrower, and loan.
Q8: How does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks? Why is this necessary?
Ans: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervised the banks in the following ways :
(i) It monitors the balance kept by banks for day-to-day transactions.
(ii) It checks that the banks give loans to profit-making businesses and traders and small borrowers.
(iii) Periodically banks have to give details about lending, borrowers, and interest rate to RBI. It is necessary for securing public welfare. It avoids the bank running the business with a profit motive only. It also keeps a check on the interest rate of credit facilities provided by the bank. RBI makes sure that the loans from the banks are affordable and cheap.
Q9: Describe four features of the Self-Help Group (SHG).
Ans: The features of Self-Help Group (SHG) are :
(i) People form their groups for savings and also lend money to themselves.
(ii) The rate of interest is lower than informal service providers.
(iii) They can also avail of loans from banks if their savings are regular.
(iv) Decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by group members. Self-Help Group
Self-Help Group
Q11: What is a double coincidence of wants? How has money solved this problem?
Ans: Barter System: In a barter system, goods are exchanged without the involvement of money.This system confines trade to local transactions within villages or towns.
- Double Coincidence of Wants:
- The double coincidence of wants is a crucial aspect of the barter system.
- It necessitates both parties to mutually agree to exchange specific commodities.
- Successful exchange depends on a perfect match of desired goods between the parties involved.

Role of Money:
- Money plays a pivotal role in simplifying trade by eliminating the need for a double coincidence of wants.
- Serving as an intermediary in the exchange process, money is commonly referred to as a medium of exchange.
- It enables a smooth exchange of goods for money, and subsequently, money can be used to acquire desired items.
Q12: How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Ans: People keep their surplus money in banks for safety and interest which is provided by banks to them. Banks again keep only a small proportion of their cash with themselves. These days banks keep only 15% of the total deposits with them. The rest of the money banks keep extending loans. Banks charge interest on loans which is higher than the interest on deposits. This surplus interest becomes the source of income for the banks. The 15% of cash deposits that banks keep with themselves help to carry on with, day-to-day transactions. Like every day, depositors come to withdraw some of their cash.
Q13: Differentiate between formal and informal sources of credit.
Ans:
Formal Sources | Informal Sources |
1. Formal sources of credit are loans from banks and cooperative societies. | 1. Informal sources of credit are money- lenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc. |
2. The functioning of formal sources of credit is governed by the Reserve Bank of India. RBI periodically checks their interest rate and money lending details. | 2. No organization manages or checks the credit activities performed by informal sources. |
3. The rate of interest is common and fixed for all formal sources and borrowers. | 3. The rate of interest depends upon the choice of moneylenders. |
4. Formal sources of credit need to satisfy all the terms of credit before credit activities. | 4. Informal sources of credit are flexible in terms of credit. |
5. They provide cheap and affordable credit for both urban and rural borrowers. | 5. They generally charge a higher rate of interest. |
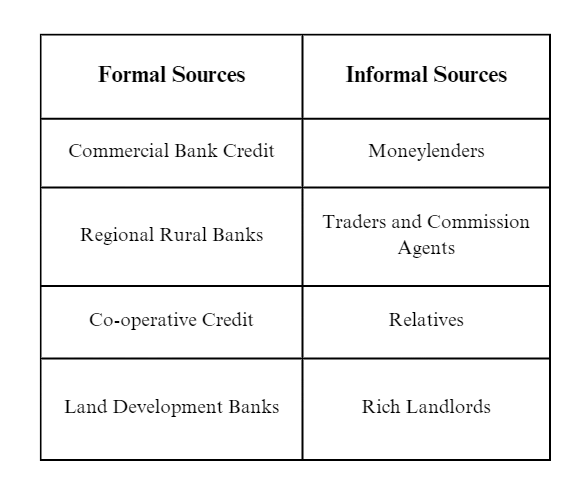
Q14: Mention four characteristics of each of the formal and informal sources of credit in India.
Ans: Features of formal sources of credit are :
(a) Formal sources of credit are provided by banks and cooperative societies to the borrowers.
(b) The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governs the functioning of the formal sources of credit. RBI periodically checks the interest rate and other details of these sources.
(c) They follow proper terms of credit which include collateral, documentation, rate of interest, and mode of repayment.
(d) They provide cheap and affordable credits with common terms of credit for all.
Features of informal sources of credit are :
(a) Informal sources of credit are moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc.
(b) No government or private organization manages or checks the credit activities performed by informal sources.
(c) Their terms of credit are flexible for the personal benefit of the lenders and the condition of borrowers.
(d) They generally charge higher rates of interest and exploit the borrowers for their benefits.
Q15: Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow :
PEOPLE DEPENDING ON FORMAL SECTOR CREDIT IN URBAN AREAS(i) Poor household's share of formal credit in the urban areas is low as compared to that of rich households. Why is it so?
(ii) Mention two difficulties poor households face in taking loans from a formal sector.
Ans:
(i) Poor households' share of formal credit in urban areas is low as compared to that of rich households due to the following reasons :
(a) Poor generally lack collateral guarantees and do not have a proper mode of repayment.
(b) Informal sources of credit are generally flexible in timings, rate of interest, repayment schedule, etc.
Therefore, it is easier for the poor to approach moneylenders as they know them personally.
(ii)
(a) Poor are not able to satisfy general terms of credit mostly collateral guarantees.
(b) Informal moneylenders know the poor borrowers personally and are therefore flexible in terms of the repayment schedule, amount and interest, etc.
Q16: What are the modern forms of money currency in India? Why is it accepted as a medium of exchange? How is it executed?
Ans: Modern forms of money include currency (paper notes) and coins. It is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorized by the government of India. No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupee. Any person holding money can easily exchange it with any commodity or service that he desires. It acts as an intermediate in the exchange process of different countries.
Q17: Why are transactions made in money? Explain with suitable examples.
Ans: Money is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorized by the government of India. In money transactions, money can be paid for any goods or services one desires. For example: the producer of shoes may want wheat in exchange for his shoes. But he may find it difficult to find a person who is also willing to exchange his wheat for shoes. So simultaneous fulfillment of mutual wants is the first and foremost condition to buy and sell the commodity. In money transactions, one can buy a commodity whenever one wants it. One does not have to wait for another person to agree to an exchange of goods.
Q18: Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow :
(a) Which are the two major sources of credit for rural households in India?
(b) Which one of them is the most dominant source of credit for rural households?
(c) What is the most dominant source of credit? Give two reasons.
Ans:
(a) Moneylenders and cooperative societies.
(b) Moneylenders
(c) (i) Moneylenders do not ask for collateral.
(ii) Complicated paperwork or documentation is not involved.
Q19: What are the various sources of credit in rural areas? Which one of them is the most convenient source of credit? Why is it most convenient? Give two reasons.
Ans: Various sources of credit in rural areas are :
(i) Agricultural traders,
(ii) Moneylenders,
(iii) Commercial banks,
(iv) Cooperative societies and
(v) Relatives and friends.
The most convenient source of credit is a moneylender. It is most convenient because of the following two reasons :
(i) There is no need for a documentation process while taking loans from informal sources (moneylenders).
(ii) No collateral is required. Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, livestock, etc.) and is used as a guarantee to the lender until the loan is repaid.
Q20: Differentiate between the Reserve Bank of India RBI and Commercial Bank.
Ans.
Reserve Bank of India | Commercial Bank |
It has the sole monopoly right to issue currency notes. | No such thing is done by a commercial bank. |
It is the apex bank in the money market of a country. | It is a unit in the banking structure of the country. |
It does not deal with the public. | It directly deals with the public and business firms. |
It acts as a banker to the government. | It has no such responsibility towards the state. |
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Money and Credit
| 1. What is the importance of money in our daily lives? |  |
| 2. How does credit work? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using credit cards? |  |
| 4. How does the banking system create money? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in the Indian financial system? |  |






















