Geography as a Discipline Class 11 Geography
What is Geography?
Geography is the study of the Earth's physical features, human activities, and the relationships between them. It helps us understand how different places are shaped by their natural environments and how people adapt to and modify these environments.

Why Study Geography?
- Human-Environment Interaction: Geography explores how humans interact with their environment. This includes how we use natural resources, adapt to different climates, and create social and cultural structures.
- Changes Over Time: Geography helps us understand how places and people have changed over time due to various factors, such as technological advancements, environmental changes, and cultural developments.
- Mapping and Visualizing: Geography teaches us how to read and create maps, which are essential for understanding the Earth's surface and the relationship between different places. Modern tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and computer cartography enhance our mapping skills.
- Contribution to Development: Geography equips us with the knowledge and skills to contribute to national development efforts by understanding spatial patterns and planning effectively.
The Earth: Our Home
- The Earth is not just a planet; it's our home and the home to countless other living beings. Its surface is diverse, with various physical features such as mountains, plains, rivers, and oceans.
- Mountains: High, rocky areas that can be challenging to live in but often have valuable resources.
- Plains: Flat, open areas that are usually good for farming and settlements.
- Rivers: Flowing bodies of water that provide water for drinking, farming, and transportation.
- Oceans: Large bodies of saltwater that cover most of the Earth and are crucial for climate regulation and biodiversity.
Physical Features of the Earth
Physical features of the Earth include mountains, hills, valleys, plains, plateaus, oceans, lakes, deserts, and wilderness areas. These features are not uniform and vary from place to place. 
These physical features influence how people live, work, and interact with their environment.
The Concept of Geography
- Home and Habitat: The Earth is not just our planet; it's our home and the habitat for countless other species. The varied physical features like mountains, rivers, and plains create different environments where various plants and animals thrive. For instance, some animals are adapted to live in cold mountainous regions, while others flourish in warm, flat plains.
- Physical Features: The Earth's surface is marked by diverse physical features. These include mountains, hills, valleys, plains, plateaus, oceans, lakes, deserts, and wilderness areas. Each of these features affects how people and animals live. For example, mountains can be barriers to travel but also sources of minerals and fresh water.
- Human Elements: In addition to natural features, the Earth is also shaped by human activities. Over time, people have built cities, roads, railways, ports, markets, and other structures. These human-made elements are vital for trade, transportation, and communication.
- Interaction of Nature and Society: The physical environment provides the setting for human activities. For instance, fertile plains are ideal for agriculture, leading to the development of villages and towns. Similarly, rivers have historically been crucial for transportation and trade, influencing where cities are located.
Geography as an Integrating Discipline
- Geography aims at synthesizing spatial information, analogous to how history synthesizes temporal information.
- It takes a holistic approach, recognizing global interdependencies in a world often likened to a "global village."
- Advancements in transportation have reduced distances, enhancing accessibility.
- Technological advancements, like audio-visual media and information technology, enrich the data available for analysis.
- Technology aids in monitoring natural phenomena, economic trends, and social parameters more effectively.
- Geography interfaces with a variety of natural and social sciences, all aiming to understand reality.
- Geography seeks to grasp associations between various phenomena within different parts of reality.
- Understanding spatial perspectives helps in comprehending reality as a whole.
Geography's Influence on Historical Events:
- Spatial distances have historically influenced significant events.
- Geographical features like mountains, oceans, and coastlines have shaped the course of history.
- Geographical factors in different regions have played crucial roles in altering historical narratives.
- Examples like the Himalayas acting as barriers or sea coasts facilitating trade and contact illustrate geography's impact on history.

Temporal Dimension in Geography:
- Geographical phenomena evolve over time and can be explained temporally.
- Changes in landforms, climate, vegetation, economic activities, and cultures follow historical trajectories.
- Decisions by institutions at certain points in time influence geographical features.
- Converting time into space and vice versa helps understandrelationships between different locations.
- Time is considered the fourth dimension in geography alongside the spatial dimensions.
Branches of Geography
- Geography is an interdisciplinary field of study.
- Two major approaches to studying geography are Systematic and Regional.
- Systematic geography, akin to general geography, focuses on studying phenomena globally and identifying typologies or spatial patterns.
- For instance, when studying natural vegetation, the approach involves examining worldwide patterns such as equatorial rainforests, softwood conical forests, or monsoon forests.
- Regional geography divides the world into regions at various hierarchical levels and studies all geographical phenomena within a specific region.
- These regions can be natural, political, or designated areas, and the focus is on understanding the unity in diversity within each region.
- Geography has a dualistic nature, emphasizing either physical geography or human geography.
- Initially, the emphasis was on physical geography, but as humans are integral to the Earth's surface and have influenced it culturally, human geography emerged to highlight human activities.
Branches of Geography: Based on Systematic Approach
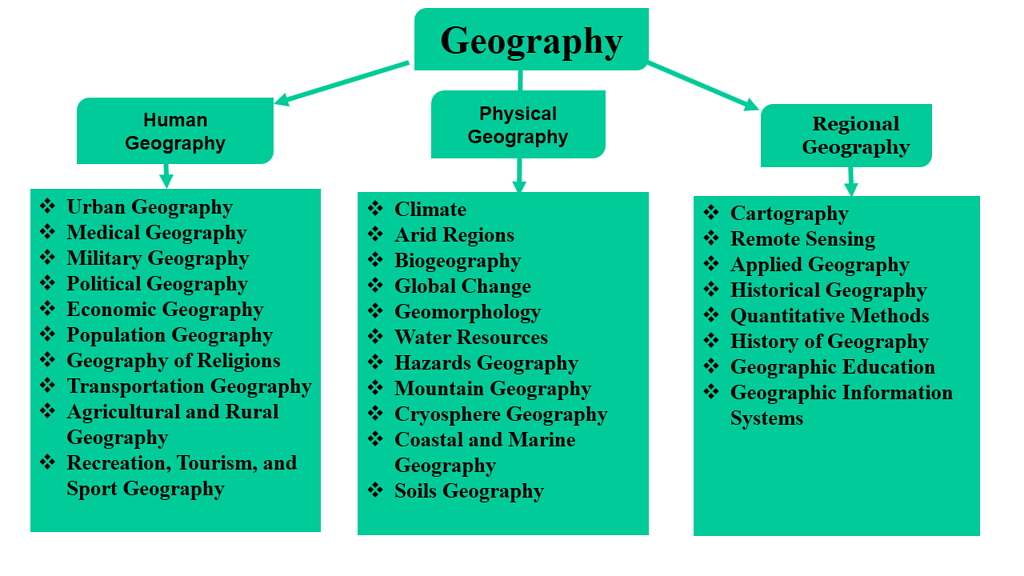
1. Physical Geography
- Geomorphology is devoted to the study of landforms, their evolution and related processes.
- Climatology encompasses the study of the structure of the atmosphere and elements of weather and climates and climatic types and regions.
- Hydrology studies the realm of water over the surface of the earth including oceans, lakes, rivers, and other water bodies, and its effect on different life forms including human life and their activities.
- Soil Geography is devoted to studying the processes of soil formation, soil types, their fertility status, distribution, and use.
2. Human Geography
- Social / Cultural Geography encompasses the study of society and its spatial dynamics as well as the cultural elements contributed by the society.
- Population and Settlement Geography (Rural and Urban). It studies population growth, distribution, density, sex ratio, migration, and occupational structure, etc. Settlement geography studies the characteristics of rural and urban settlements.
- Economic Geography studies the economic activities of the people including agriculture, industry, tourism, trade, and transport, infrastructure, and services, etc.
- Historical Geography studies the historical processes through which space gets organized. Every region has undergone some historical experiences before attaining its present-day status. The geographical features also experience temporal changes and these form the concerns of historical geography.
- Political Geography looks at the space from the angle of political events and studies boundaries, space relations between neighboring political units, delimitation of constituencies, election scenarios and develops a theoretical framework to understand the political behavior of the population.
3. Biogeography
The interface between physical geography and human geography has lead to the development of Biogeography which includes:
- Plant Geography studies the spatial pattern of natural vegetation in their habitats.
- Zoo Geography studies the spatial patterns and geographic characteristics of animals and their habitats.
- Ecology / Ecosystem deals with the scientific study of the habitats characteristic of species.
- Environmental Geography concerns the world over, leading to the realisation of environmental problems such as land gradation, pollution and concerns for conservation.
Branches of Geography: Based on Regional Approach
- Regional Studies/Area Studies Comprising Macro, Meso and Micro Regional Studies
- Regional Planning Comprising Country/Rural and Town/ Urban Planning
- Regional Development
- Regional Analysis
There are two aspects that are common to every discipline, these are:
1. Philosophy
- Geographical Thought
- Land and Human Interaction/Human Ecology
2. Methods and Techniques
- Cartography including Computer
- Quantitative Techniques/Statistical Techniques
- Field Survey Methods
- Geo-informatics comprising techniques such as Remote Sensing, GIS, GPS, etc.
Physical Geography and Its Importance
Physical geography is a branch of geography that focuses on the Earth's lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Soil Formation and Importance
- Soils develop through pedogenesis, influenced by parent rocks, climate, biological activity, and time.
- Time matures soils, aiding in the formation of soil profiles.
- Soils are vital for human activities, providing the foundation for agriculture, forests, minerals, pastures, and water sources.
Climate and Its Impact
- Climate affects human life, influencing housing, clothing, food habits, vegetation, cropping patterns, and industries.
- Technologies like air conditioners modify local climates for comfort.
- Temperature and precipitation affect forest density and grassland quality.
- In India, monsoons drive agricultural cycles and recharge groundwater for farming and domestic use.
Oceans and Soil Resources
- Oceans are rich in resources such as fish, seafood, and minerals, supporting economic activities.
- Soils, renewable resources, impact agriculture and provide a habitat for plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Significance of Physical Geography
- Physical geography aids in evaluating and managing natural resources.
- Understanding the link between the physical environment and humans is crucial for sustainable development.
- Modern technology accelerates resource utilization, leading to ecological imbalances, emphasizing the need for a better understanding of the physical environment.
Some Solved Questions
Q.1. You have already studied geography, history, civics, and economics as parts of social studies. Attempt an integration of these disciplines highlighting their interface.
Ans:
Geography is an integrated discipline.
1. Geography and History: The geographical factors have modified the course of history in different parts of the world. Every geographical phenomenon undergoes change through time and can be explained temporarily. The changes in landforms, climate, vegetation, economic activities, occupations, and cultural developments have followed a definite historical course.
2.Geography and Civics: The core concern of political science is territory, people, and sovereignty while political geography is also interested in the study of the state as a spatial unit as well as people and their political behaviour.
3. Geography and Economics: Economics deals with basic attributes of the economy such as production, distribution, exchange, and consumption. Each of these attributes also has spatial aspects and here comes the role of economic geography to study the spatial aspects of production, distribution, exchange, and consumption.
Q.2. Explain the changes that occurred in the civilization of man over the course of time?
Answer: Many changes have occurred in the civilization of man in course of time.
- Man moved from stage of necessity to stage of freedom.
- Created new possibilities from nature.
- We find now humanized nature and naturalized man.
- Space got organized with the help of transport and communication.
Q.3. Differentiate between Physical geography and Biogeography.
The main differences between Physical geography and Biogeography are given below:
Q.4. As a scientific discipline with how many categories of questions is geography concerned? Explain.
Answer: Geography as a discipline is concerned with three sets of questions
- Some questions are concerned with the identification of the patterns of natural and cultural features as found over the surface of the earth. These are the questions about “what”?
- Second type of questions are related to the distribution of the natural and human/ cultural features over the surface of the earth. These are the questions about where?
- The third question is related to the explanation or the causal relationships between features and the processes and phenomena.
Q.5. Explain different branches of geography under Biogeography.
Answer: Biogeography has emerged as a result of the interface between physical geography and human geography. It has three branches: Plant Geography, Zoo Geography, and Ecology.
Different branches of Biogeography are as follows:
- Plant Geography: It studies the spatial pattern of natural vegetation in their habitats.
- Zoo Geography: It studies the spatial patterns and geographic characteristics of animals and their habitats.
- Ecology: It is concerned with the scientific study of the habitats characteristic of species.
- Environmental Geography: It is concerned with environmental problems such as land gradation, pollution, and environmental conservation.
|
47 videos|183 docs|155 tests
|
FAQs on Geography as a Discipline Class 11 Geography
| 1. What is Geography and why is it considered an integrating discipline? |  |
| 2. What are the main branches of Geography? |  |
| 3. How does the systematic approach differ from the regional approach in Geography? |  |
| 4. Why is Physical Geography important? |  |
| 5. What are some common exam questions related to Geography as a discipline? |  |
|
47 videos|183 docs|155 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|



















