Human Neural System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is a Neural Tissue? |

|
| Neuron: The Structural and Functional Unit of the Neural System |

|
| Types of Neurons |

|
Introduction
In all animals, the nervous system consists of specialized cells known as neurons, capable of sensing, receiving, and transmitting various stimuli. The organization of the nervous system is relatively basic in lower invertebrates. For instance, in Hydra, it consists of a network of neurons. Insects exhibit a more advanced neural organization, featuring a brain along with multiple ganglia and neural tissues. Vertebrates possess a highly developed nervous system compared to lower animals.
What is a Neural Tissue?
Neural tissue is also called as the nervous tissue. The neural tissue is the main component of the nervous system – both the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The human nervous system has two main parts:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): This includes the brain and spinal cord, which are responsible for processing information and controlling body functions.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This consists of all the nerves that connect the body to the CNS.
The nerves in the PNS are of two types:
- Afferent Fibers: These carry signals from organs and tissues to the CNS.
- Efferent Fibers: These carry signals from the CNS to the muscles and organs to control their actions.
The PNS is further divided into:
- Somatic Nervous System: This controls voluntary movements by sending signals to the skeletal muscles.
- Autonomic Nervous System: This controls involuntary functions, sending signals to the smooth muscles and organs.
The Autonomic Nervous System has two branches:
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Prepares the body for action (fight or flight).
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Helps the body relax and conserve energy.
Neuron: The Structural and Functional Unit of the Neural System
The neuron is the basic unit of the neural system. Neuron or Nerve cell is made up of cell body & cell process – (Dendron and Axon = Neurites)
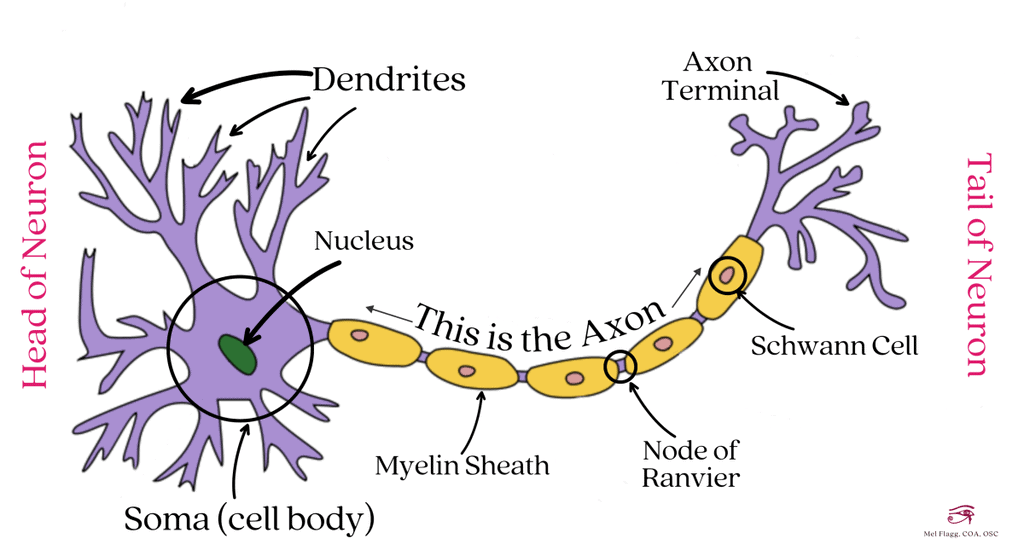 Structure of a Neuron
Structure of a Neuron
- A neuron is a tiny structure made up of three main parts:cell body, dendrites, and axon.
- Cell Body: Contains cytoplasm with cell organelles and Nissl's granules.
- Dendrites: Short, branched fibers that transmit impulses toward the cell body and also contain Nissl's granules.
- Axon: A long fiber that transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body. The distal end branches into bulb-like structures called synaptic knobs, which contain synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters.
Types of Neurons
Neurons are classified into three types based on the number of axons and dendrites:
- Multipolar Neurons: Have one axon and two or more dendrites. Found in the cerebral cortex.
- Bipolar Neurons: Have one axon and one dendrite. Found in the retina of the eye.
- Unipolar Neurons: Have one axon only. Typically found in the embryonic stage.
Types of Axons Axons can be categorized into myelinated and non-myelinated:
- Myelinated Axons: Surrounded by Schwann cells that form a myelin sheath. The gaps between adjacent myelin sheaths are called nodes of Ranvier. Myelinated nerve fibers are found in spinal and cranial nerves.
- Non-myelinated Axons: Enclosed by Schwann cells but lack a myelin sheath. Commonly found in the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Human Neural System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the main function of neurons in the human neural system? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of neurons found in the human body? |  |
| 3. How do neurons communicate with each other? |  |
| 4. What is the role of glial cells in the neural tissue? |  |
| 5. What is myelin, and why is it important for neurons? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|













