Shankar IAS Summary: Biodiversity- 1 | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is defined as the variability among living organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are a part.
- Biodiversity includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems.
- The importance of this definition is that it draws attention to the many dimensions of biodiversity.
- Biodiversity includes all ecosystems—managed or unmanaged.
 Biodiversity provides four main types of benefits to humans: nutritional, cultural, health, and climate-related.
Biodiversity provides four main types of benefits to humans: nutritional, cultural, health, and climate-related.
Levels of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is considered to exist at three levels1. Genetic Diversity
2. Species Diversity
3. Ecosystem/ Community Diversity
1. Genetic Diversity
- Variation in genes within a particular species.
- It is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. Genetic diversity allows species to adapt to changing environments.
- The genetic diversity gives us beautiful butterflies, roses, parakeets, or coral in myriad hues, shapes, and sizes
2. Species Diversity
- It refers to the variety of living organisms on earth.
- Species differ from one another, markedly in their genetic makeup, do not interbreed in nature.
- It is the ratio of one species population over a total number of organisms across all species in the given biome.
- Zero' would be infinite diversity, and ’one’ represents only one species present.
3. Ecosystem/ Community Diversity:
- This refers to the different types of habitats. A habitat is the cumulative factor of the climate, vegetation, and geography of a region. Change in climatic conditions is accompanied by a change in vegetation as well.
- Thus the variety or diversity of species in the ecosystem is influenced by the nature of the ecosystem.
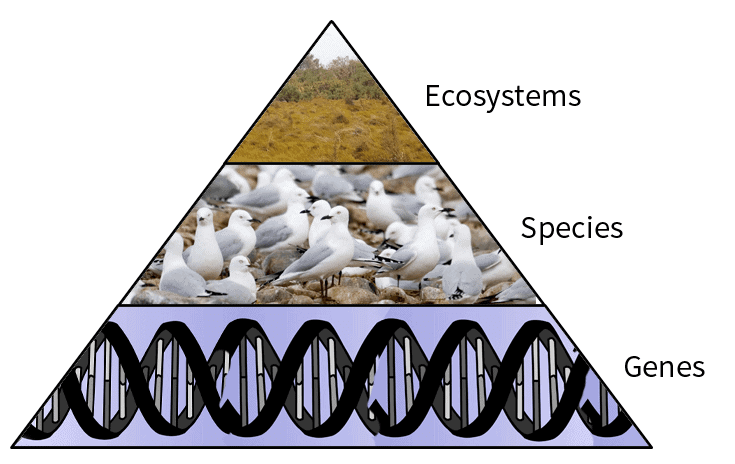 Levels of Biodiversity
Levels of Biodiversity
Major Components of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is measured by two Major Components:
1. Species Richness
2. Species Evenness
1. Species Richness
- It is the measure of the number of species found in a community
- Alpha diversity-It refers to the diversity within a particular area or ecosystem and is usually expressed by the number of species (l.e., species richness) in that ecosystem
- Beta diversity-It is a comparison of diversity between ecosystems, usually measured as the change in the number of species between the ecosystems.
- Gamma diversity-It is a measure of the overall diversity for the different ecosystems Within a region
2. Species Evenness
- It measures the proportion of species at a given site, e.g. low evenness indicates that a few species dominate the site.
- The building blocks of plants, animals, and humans are identical and are made of four elements - carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen
- The chain that links consumers to producers is called the food chain or web of life.
Services Provided by Biodiversity
The key ecosystem services provided by biodiversity are
1. Ecosystem Services
2. Biological Services
3. Social Services
1.
Ecosystem Services
- Protection of water resources, soil formation, and protection, Nutrient storage, and recycling.
- Pollution breakdown and absorption Contribution to climate stability Maintenance of ecosystems.
- Recovery from unpredictable events
2. Biological Services
- Food, Medicinal resources, and pharmaceutical drugs.
- Wood products, Ornamental plants Diversity in genes, species, and ecosystems. Etc.
3. Social Services
- Research, education, and monitoring
- Recreation and tourism Cultural values
Causes for Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity loss is caused by five primary drivers: habitat loss, invasive species, overexploitation (extreme hunting and fishing pressure), pollution, climate change associated with global warming.
- Loss of biodiversity occurs when either a particular species is destroyed or the habitat essential for its survival is damaged. The latter is more common as habitat destruction inevitable fallout of development.
- The extinction of species takes place when they are exploited for economic gain or hunted as a sport or for food. Extinction of species may also occur due to environmental reasons like ecological substitutions, biological factors, and pathological causes which can be caused either by nature or man
- Extinction- end of a species, which is inevitable when the capacity to bread &recovery lost; when they are no longer able to survive in changing environment or against superior Competitor, finally marked by the death of the last individual of that species.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Biodiversity conservation refers to the protection, preservation, and management of ecosystems and natural habitats and ensuring that they are healthy and functional.
- Conservation of biological diversity leads to the conservation of essential ecological diversity to preserve the continuity of food chains.
- Conserving biodiversity outside the areas where they naturally occur is known as ex-situ conservation. For example, the Gangetic gharial has been reintroduced in the rivers of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan where it had become extinct.
- Conserving the animals and plants in their natural habitats is known as in-situ conservation.
- The established natural habitats are: National parks, Sanctuaries, Biosphere Reserves, and Reserved forests, Protected forests, Nature reserves.
Constraints in Biodiversity Conservation:
- Low priority for the conservation of living natural resources. The exploitation of living natural resources for monetary gain.
- Values and knowledge about the species and ecosystem inadequately known.
- Unplanned urbanization and uncontrolled industrialization.
[Question: 890721]
Botanical Garden
A botanical garden refers to the scientifically planned collection of living trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers, and other plants from various parts of the globe.
Zoo
An establishment, whether stationary or mobile, where captive animals are kept for exhibition, to the public and includes a circus and rescue centers but does not include an establishment of a licensed dealer in captive animals -CZA
|
97 videos|188 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Biodiversity- 1 - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is biodiversity? |  |
| 2. What are the major components of biodiversity? |  |
| 3. What are the services provided by biodiversity? |  |
| 4. What are the causes for biodiversity loss? |  |
| 5. How can biodiversity be conserved? |  |




















