Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Reaching the Age of Adolescence Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 7
Adolescence
- The stage of life when the body undergoes changes to become capable of reproduction is known as adolescence.
- This phase starts around the age of 11 and continues until about 18 or 19 years old.
- As this time covers the 'teen' years (13 to 18 or 19), adolescents are often referred to as ‘teenagers’. Girls may start this stage a year or two earlier than boys, and the timing can vary for each individual.
Puberty
- During adolescence, the body experiences numerous changes, signalling the onset of puberty.
- The key change is that both boys and girls become capable of reproduction.
- Puberty concludes when an adolescent reaches reproductive maturity.
Increase in height
- It is caused by the growth in long bones of the arms and legs.
- Girls grow faster than boys initially but both reach their maximum height by the age of 18 years.
Change in body shape
- Boys develop broader shoulders, wider chests, and prominent muscles.
- In girls the region below the waist becomes wider.
Change in the voice pattern
- Voice box or larynx starts growing during puberty.
- It protrudes in males in the neck region and is called Adam’s apple.
- Boys develop deep low-pitched voice.
- Girls develop high-pitched voice.
Change in activity of sweat and sebaceous glands
- The activity of sweat glands increases during puberty, resulting in production of more sweat.
- The oily secretions from sebaceous glands increase. The accumulation of oil and bacterial action leads to acne problems in teenagers.
Changes in sex organs
- Boys’ testes and penis fully develop.
- Testes start producing sperm.
- In girls, ovaries develop completely and begin to release eggs. Breast development also starts during puberty.
Change in intellectual level
- The brain’s capacity for learning improves.
- Intellectual growth occurs throughout adolescence.
- Body hair grows in various places. Girls develop breasts, while boys grow facial hair, like moustaches and beards.
Secondary sexual characteristics in boys
- Development of moustaches and beard.
- Growth of hair on the chest.
- Hair appears under the arms and in the pubic area.
Secondary sexual characteristics in girls
- Increase in breast size
- Growth of hair in the pubic region.
Hormones
- Hormones are chemical secretions that bring about various changes in the body.
- They are produced by endocrine glands.
- These glands release hormones into blood to reach specific target site.
- Production of hormones is under the control of hormones produced from pituitary gland.
Characteristics of hormones
- Hormones act as chemical messengers.
- They are secreted by living cells/tissues or organs called glands.
- They are secreted in very small quantities by glands.
- They act upon specific cells, tissues, or organs called the target sites.
- They are generally slow in action, but have long lasting effects.
- They either accelerate or inhibit a reaction.
Note: The male hormone, or testosterone, is released by the testes at puberty, leading to changes such as facial hair growth. In girls, the female hormone, or oestrogen, promotes breast development.
Endocrine glands
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas etc.
- Major endocrine glands in humans are
(i) Pituitary
(ii) Hypothalamus
(iii) Pineal
(iv) Thyroid
(v) Parathyroid
(vi) Thymus
(vii) Pancreas
(viii) Adrenal
(ix) Testis in men /ovary in women - A feedback mechanism (positive and negative) regulates the action of the hormones.
Pituitary gland
- It is a small gland the size of a pea, located at the bottom of the brain. It releases various hormones, including growth hormone (GH).
- This hormone is essential for normal body growth.
- A lack of growth hormone can lead to a condition known as dwarfism.
- Excess growth hormone can cause gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults.
- The pituitary gland also releases hormones that prompt other glands, such as the thyroid and adrenal glands, to produce their own hormones.
Thyroid gland
- It is situated near the trachea in the neck and produces a hormone called thyroxine.
- This hormone is crucial for controlling the body's metabolism.
- A deficiency in thyroxine leads to hypothyroidism.
- This condition can result in issues like simple goitre and myxoedema.
- Adequate levels of iodine are necessary for thyroxine production; a lack of iodine causes a deficiency, leading to goitre.
- Excess thyroxine results in hyperthyroidism, causing symptoms like increased metabolism, protruding eyeballs, high blood pressure, nervousness, and weight loss.
Parathyroid Gland
- There are four parathyroid glands found at the back of the thyroid glands, which produce parathyroid hormone, or PTH.
- This hormone controls the amount of calcium in the blood.
- Too much parathyroid hormone can cause a condition known as hyperparathyroidism, leading to the loss of calcium from bones, making them weaker.
- PTH also helps increase calcium absorption in the intestines and its reabsorption in the kidneys.
Pancreas
- It produces two hormones- Insulin and Glucagon.
- These hormones maintain blood sugar level.
- Deficiency of insulin results in diabetes.
Adrenal Gland
- There are two adrenal glands situated on top of each kidney.
- The glands consist of two parts: the cortex and the medulla.
- The cortex produces hormones like cortisol, which helps regulate metabolism.
- The medulla produces hormones such as adrenaline, which prepares the body for stressful situations.
- The adrenal glands also release hormones that help keep the correct salt levels in the blood.
Gonads
- It consists of testes in males and ovaries in females.
- The male sex hormone is testosterone, made by the testes at the start of puberty.
- Ovaries produce female hormones such as oestrogen and progesterone.
- While oestrogen is important for fertility, infertility can result from many factors, not just low oestrogen.
- Hormones from the pituitary gland encourage the testes and ovaries to release testosterone and oestrogen.
- During puberty, girls begin to develop breasts, while boys start growing facial hair, including moustaches and beards.
- Maintaining a balanced diet and good personal hygiene is crucial during adolescence.
- Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream to target specific body parts.
- These hormones induce necessary changes to ensure the body functions properly.

Historical background and Discovery of HIV
- The first cases of AIDS were identified in the U.S.A in 1981.
- The virus responsible for AIDS, called HIV, was first isolated in 1983 by a team led by Luc Montagnier.
- In 1984, American virologist Robert Charles Gallo reported on the virus that causes AIDS.
- The name HIV was proposed by the International Committee on the Nomenclature of Viruses.
- In India, the first case of AIDS was reported in 1986.
- HIV is a retrovirus that targets the immune system, especially the CD4 cells (also known as T cells).
- AIDS, or Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, is a viral disease caused by HIV.
- HIV/AIDS has resulted in millions of deaths globally and continues to be a major public health concern.
Structure of HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is spherical in shape and contains RNA as its genetic material.
- Externally, the virus is covered by the double layered membrane made up of fatty substances.
- Inside the fatty membrane a core of proteins is found that surrounds the viral RNA along with the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
Transmission of HIV
- Sharing syringes during drug use.
- Engaging in unprotected sexual activities.
- Receiving blood transfusions with infected blood.
- Transmission from an infected mother to her baby through breast milk.
- The virus can also spread through sexual contact with someone who is HIV positive.
Prevention of HIV
- Avoid sexual relations with infected individuals.
- Use disposable syringes only.
- Ensure blood from blood banks is screened properly.
Tests for detection of HIV
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- ELISA (Enzyme linked Immuno Sorbent Assay)
- Western Blot
Personal health and hygiene in adolescents
- The physical and mental well-being of a person is known as their health.
- Adolescence is a time of quick growth, so it’s important to plan a proper diet.
- A balanced diet includes the right amounts of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins.
- Adolescents should maintain cleanliness to avoid bacterial infections.
- Girls need to pay special attention to cleanliness during their menstrual cycle. They should track their cycle and be ready for menstruation, using sanitary napkins or clean homemade pads, and change them every 4-5 hours as needed.
- To stay healthy, everyone, regardless of age, must have a balanced diet, practice personal hygiene, and engage in physical activity.
- Incorporating physical exercises is crucial for maintaining fitness and hygiene during adolescence.
Sex determination in humans
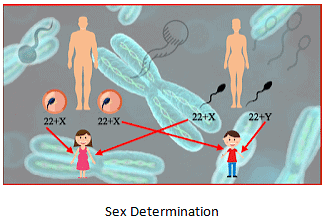
- Autosomes: First 22 pairs of chromosomes that do not determine the sex of an individual.
- Sex chromosomes: Last pair of chromosomes, represented as X and Y.
- Females have two X chromosomes, so can be represented as 44+XX.
- Males have one X and one Y chromosome, so can be represented as 44+XY.
- Each gamete receives half of the chromosomes i.e. 22+X or 22+Y.
- Male gametes have 22 autosomes and either X or Y sex chromosome.
- Male gametes can be of two types, 22+X or 22+Y.
- Female gametes can be of only one type, 22+X.
- Sex of a baby is determined by the type of the male gamete (X or Y) that fuses with the female gamete.
The document Reaching the Age of Adolescence Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 7 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Reaching the Age of Adolescence Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 7
| 1. Adolescence क्या है और यह किस आयु वर्ग में आती है ? |  |
Ans.Adolescence वह अवधि है जब व्यक्ति शारीरिक, मानसिक और भावनात्मक विकास के महत्वपूर्ण चरण से गुजरता है। यह आमतौर पर 10 से 19 वर्ष की आयु के बीच होती है।
| 2. adolescence के दौरान शारीरिक परिवर्तन क्या होते हैं ? |  |
Ans.Adolescence के दौरान विभिन्न शारीरिक परिवर्तन होते हैं, जैसे कि शरीर की ऊँचाई में वृद्धि, यौन अंगों का विकास, और हार्मोनल परिवर्तन। लड़कों में मांसपेशियों का विकास और लड़कियों में ब्रेस्ट का विकास देखा जाता है।
| 3. adolescence में मानसिक विकास कैसे होता है ? |  |
Ans.Adolescence में मानसिक विकास में सोचने की क्षमता, निर्णय लेने की क्षमता, और सामाजिक कौशल में वृद्धि होती है। इस दौरान व्यक्तियों में आत्म-सम्मान और पहचान बनाने की प्रक्रिया भी शुरू होती है।
| 4. adolescence के दौरान सामाजिक संबंधों में क्या परिवर्तन आते हैं ? |  |
Ans.Adolescence के दौरान सामाजिक संबंध अधिक महत्वपूर्ण हो जाते हैं। किशोर अपने दोस्तों और समूहों के प्रति अधिक आकर्षित होते हैं, और परिवार के साथ संबंधों में भी कुछ बदलाव देख सकते हैं।
| 5. adolescence के दौरान भावनात्मक बदलाव क्या होते हैं ? |  |
Ans.Adolescence के दौरान भावनात्मक बदलावों में मूड स्विंग्स, आत्म-विश्वास में परिवर्तन, और भावनाओं की गहराई में वृद्धि शामिल होती है। किशोर अक्सर अपनी भावनाओं को समझने और व्यक्त करने की कोशिश करते हैं।
Related Searches
















