Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Nutrition in Animals
Short Answer Question
Q1: What do you mean by animal nutrition?
Ans: Animal nutrition refers to the study of the nutritional needs of animals, which includes:
- The requirement for nutrients essential for growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
- The mode of food intake, which varies among different species.
- The utilisation of food within the body for various physiological processes.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for improving animal health and productivity.
Q2: What is digestion?
Ans: Digestion is the process of breaking down complex components of food, such as carbohydrates, into simpler substances. These simpler substances are then absorbed and assimilated by the body.
Q3: Name different modes of feeding in animals?
Ans: Scraping, chewing, brewing, capturing and swallowing, sucking etc. are the different mode of feeding in animals.
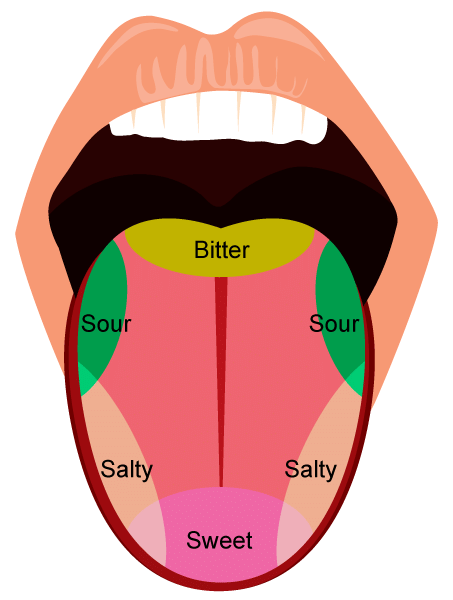
Q4: What are the functions of the tongue in human body?
Ans: The functions of the tongue are as follows:
- Speech: It is essential for talking; it is not possible to articulate words without it.
- Mixing: The tongue mixes saliva with food during chewing, aiding in the swallowing process.
- Taste: Thanks to the presence of taste buds, it identifies various flavours such as sweet and salty.
 Taste Buds
Taste Buds
Q5: What are Milk teeth and permanent teeth?
Ans: The first set of teeth, known as milk teeth, develops during infancy and typically falls out between the ages of six and eight years. These are replaced by the permanent teeth, which are designed to last throughout most of a person's life. However, some permanent teeth may be lost during old age.
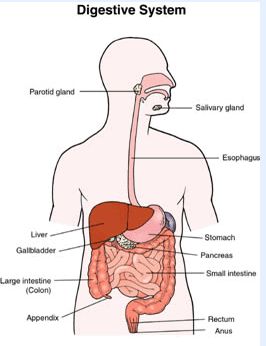
Q6: Name the main organs of digestive system.
Ans: The main organs of digestive system are liver, Gall bladder Stomach, Pancreas, Small intestine, Large intestine, Rectum, Anus. The digestive tract and the associated glands together constitute the digestive system.
Q7: Explain tooth decay?
Ans: Our mouth contains some useful bacteria, but if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, harmful bacteria can also begin to thrive. These harmful bacteria break down the sugars from leftover food and release acids. Over time, these acids gradually damage the teeth and lead to tooth decay.
Q8: Glucose is considered as the source of instant energy, why?
Ans: Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrate and can be easily broken down to provide energy. This property makes glucose a source of instant energy for the body. Furthermore, glucose mixes directly into the bloodstream, ensuring it is readily available for immediate use by our cells.
Q9: What is mastication?
Ans: Mastication is the process of chewing food. It involves mixing saliva with the chewed food, which helps to moisten it. This action is essential as it facilitates the swallowing of food.
Q10: Define peristalsis?
Ans: The powerful muscles in the oesophagus gently push food down to the stomach in a wave-like action known as peristalsis.
Q11: What are secreted inside the stomach?
Ans: Gastric juice is secreted by the walls of the stomach and contains hydrochloric acid (HCl) and pepsin. HCl plays a crucial role in killing germs present in food. After mixing with food, it provides an acidic medium that is essential for activating the pepsin enzyme. Pepsin is responsible for digesting proteins into peptides.
Q12: Explain digestive enzymes?
Ans: There are different types of enzymes which are used for the digestion of different food materials like carbohydrates, fats, protein etc. The process of digestion involves the association of several catalytic organic compounds such as amylase, pepsin, lipase, trypsin etc. These organic compounds are known as digestive enzymes.
Q13: What do you mean by absorption in terms of digestion of food?
Ans: The process of absorption occurs after food has been digested in the stomach. It involves the transfer of nutrients from the food into the blood vessels located in the walls of the intestine. This critical step allows the body to utilize the nutrients for energy and growth.
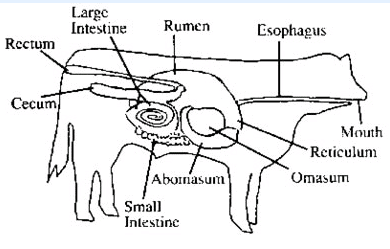
Q14: Name and explain the type of carbohydrates that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans.
Ans: Cellulose is the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Ruminants possess a large, sac-like structure located between the small intestine and large intestine, which is essential for the digestion of cellulose. The cellulose in their food is broken down by the action of specific bacteria that are absent in humans.
Q15: What role does villi performs in the small intestine?
Ans: The villi increase the surface area for the absorption of digested food. Their surface is designed to effectively absorb the digested materials and transfer them into the blood. Once absorbed, these substances are transported via blood vessels to various organs of the body.
Q16: Describe nutrition in amoeba.
Ans: Amoeba is a single-celled organism commonly found in pond water. It possesses a cell membrane, a dense, rounded nucleus, and numerous bubble-like vacuoles. Amoeba is known for its ability to constantly change shape and position. For movement and capturing food, it extends one or more finger-like projections called pseudopodia or false feet. Amoeba primarily feeds on microscopic organisms. When it detects food, it extends its pseudopodia around the food particle, effectively engulfing it. The food is then trapped in a food vacuole, where it is digested by digestive juices.
Q17: Differentiate between assimilation and egestion.
Ans: The process of assimilation involves the transportation of absorbed, digested food materials through the blood vessels to various organs in the body. Here, these materials are utilised to build complex substances, such as the proteins essential for bodily functions. On the other hand, egestion refers to the removal of waste, specifically faecal matter, through the anus at regular intervals.
Q18: What is rumination?
Ans: Rumination is a process in which partially digested food is regurgitated as small lumps and then chewed again. Animals that engage in this process are known as ruminants.
Q19: How does digestion occur in ruminants grass-eating animals?
Ans: Ruminants quickly swallow grass and store it in a separate part of the stomach called the rumen. Here, the food undergoes partial digestion and is referred to as cud. Later, the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps, and the animal chews it. This process is known as rumination. The cellulose present in grass is digested in the rumen by the action of specific bacteria, which are not found in humans.
Q20: Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Ans: Similarity: Both amoeba and human beings use digestive juices for digestion of food.
Difference: Humans need to chew food whereas in amoeba, there is no chewing of food.
Q21: What is the site of production of bile? Which component of the food does it digest?
Ans: Bile is produced in the liver and is stored in a sac-like structure called the gallbladder. It plays an important role in the digestion of fats, acting on them to convert them into a simpler form.
Q22: What is the role of pseudopodia in amoeba’s life?
Ans: Pseudopodia play a crucial role in the life of an amoeba by aiding in both movement and the capture of food. These structures, often referred to as false feet, allow the amoeba to extend its body and envelop prey, facilitating the process of feeding.
Q23: What happens to the food in mouth and oesophagus of the digestive tract?
Ans: When food is ingested, the salivary glands secrete saliva, which acts on it in the mouth. The saliva breaks down starch into sugars. The oesophagus is a long, narrow, muscular tube that directly leads to the stomach. It is about 25 cm long and passes downwards through the neck, thorax, and abdominal cavity. The oesophagus gently pushes masticated food down to the stomach in a wave-like action called peristalsis.
Q24: What happens to the food in stomach of the digestive tract?
Ans: The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucus, hydrochloric acid, and digestive juices. The mucus protects the lining of the stomach. The hydrochloric acid kills many bacteria that enter with food and creates an acidic environment in the stomach. Additionally, the digestive juices break down proteins into simpler substances.
Q25: What happens to the food in small intestine of the digestive tract?
Ans: The small intestine is highly coiled and is about 7.5 metres long. Liver is the largest gland in the body. It secretes bile juice that is stored in a sac called the gall bladder. It digests fats. The pancreas is cream colour red gland secretes pancreatic juice that acts on carbohydrates and proteins and changes them into simpler forms. The carbohydrates get broken into simple sugars such as glucose, fats into fatty acids and glycerol, and proteins into amino acid, she digested food can now pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine having thousands of finger-like villi. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials. The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body.
Q26: What happens to the food in large intestine of the digestive tract?
Ans: The food that remains undigested and unabsorbed enters the large intestine from the small intestine. The large intestine is approximately 1.5 metres in length. Its primary function is to absorb water and some salts from the undigested food material.
Q27: Draw a labelled diagram of human digestive system.
Ans :
Q30: Draw a labelled diagram showing digestive system of cow.
Ans :
Long Answer Question
Q1: Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables / grass? Discuss.
Ans: Animals, including most bacteria and non-green plants, as well as humans, do not have the ability to synthesize their own food. Therefore, they rely on autotrophs for their food supply, either directly or indirectly. Green plants, such as leafy vegetables and grass, trap solar energy and manufacture their food in the form of glucose. While leafy vegetables and grass are nutritious, they may not provide sufficient energy for human survival alone. Humans require a varied diet that includes proteins and other nutrients that are not typically found in high quantities in raw, leafy vegetables or grass. In conclusion, although leafy vegetables and grass play a vital role in a healthy diet, relying solely on them may not meet all the nutritional needs of humans.
|
111 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Nutrition in Animals
| 1. What is the importance of nutrition in animals? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of nutrition in animals? |  |
| 3. How do herbivores digest plant material? |  |
| 4. What is the role of enzymes in animal nutrition? |  |
| 5. How does the process of absorption take place in animal nutrition? |  |

















