Continuous Charge Distribution | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
INTRODUCTION TO CONTINUOUS CHARGE DISTRIBUTION
With the help of Coulomb’s Law and Superposition Principle, we can easily find out the electric field due to the system of charges or discrete system of charges. The word discrete means every charge is different and has the existence of its own. Suppose, a system of charges having charges as q1, q2, q3……. up to qn. We can easily find out the net charge by adding charges algebraically and net electric field by using the principle of superposition.
This is because:
- Discrete system of charges is easier to solve
- Discrete system of charges do not involve calculus in calculations

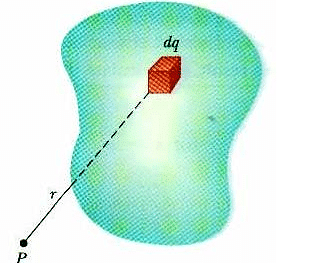
Fig: A system in which charge is distributed over a conductor, is called continuous charge distribution system
But how to calculate electrostatics terms in continuous charge system? For an Example if there is a rod with charge q, uniformly distributed over it and we wish to find the electric field at some distance ‘r’ due it. It would be illogical and irrelevant to simply add electric field using principle of superposition as the charge is uniformly distributed over the rod. So we take a small element of the rod and integrate it with proper limits.
We consider element, based on how density of charge is centered on the material or object. If the charge is uniformly distributed over the surface of the conductor, then it is called Surface Density. If the charge varies linearly along the length of the conductor, then it is called Linear Charge Density. And if the charge changes with volume of the conductor, then it is called Volume Charge Density.
WHAT IS CONTINUOUS CHARGE DISTRIBUTION?
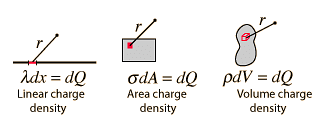
Fig: Types of Charge Distribution
The continuous charge distribution system is a system in which the charge is uniformly distributed over the conductor. In continuous charge system, infinite numbers of charges are closely packed and have minor space between them. Unlikely from the discrete charge system, the continuous charge distribution is uninterrupted and continuous in the conductor. There are three types of the continuous charge distribution system.
- Linear Charge Distribution
- Surface Charge Distribution
- Volume Charge Distribution

Fig: Types of charge distribution system
LINEAR CHARGE DENSITY
When the charge is non-uniformly distributed over the length of a conductor, it is called linear charge distribution. It is also called linear charge density and is denoted by the symbol λ (Lambda).
Mathematically linear charge density is λ = dq/dl
The unit of linear charge density is C/m. If we consider a conductor of length ‘L’ with surface charge density λ and take an element dl on it, then small charge on it will be
dq = λl
So, the electric field on small charge element dq will be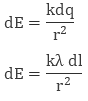
To calculate the net electric field we will integrate both sides with proper limit, that is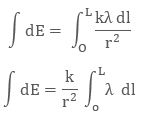
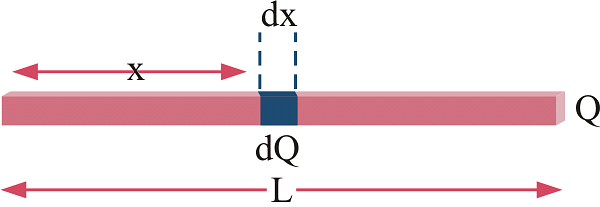
Fig: We take small element x and integrate it in case of linear charge density
SURFACE CHARGE DENSITY
When the charge is uniformly distributed over the surface of the conductor, it is called Surface Charge Density or Surface Charge Distribution. It is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma) symbol and is the unit is C/m2.
It is also defined as charge/ per unit area. Mathematically surface charge density is σ = dq/ds
where dq is the small charge element over the small surface ds. So, the small charge on the conductor will be dq = σds
The electric field due to small charge at some distance ‘r’ can be evaluated as 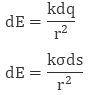
Integrating both sides with proper limits we get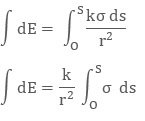
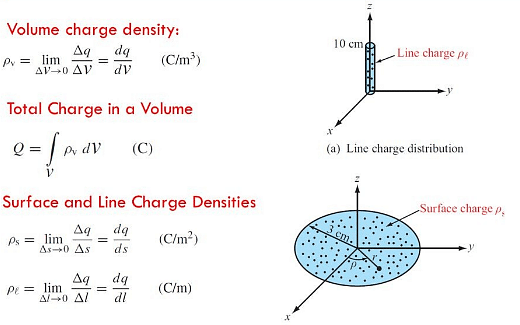
VOLUME CHARGE DENSITY
When the charge is distributed over a volume of the conductor, it is called Volume Charge Distribution. It is denoted by symbol ρ (rho). In other words charge per unit volume is called Volume Charge Density and its unit is C/m3. Mathematically, volume charge density is ρ = dq/dv
where dq is small charge element located in small volume dv. To find total charge we will integrate dq with proper limits. The electric field due to dq will be
dq = ρ dv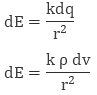
Integrating both sides with proper limits we get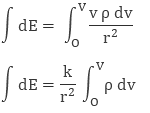
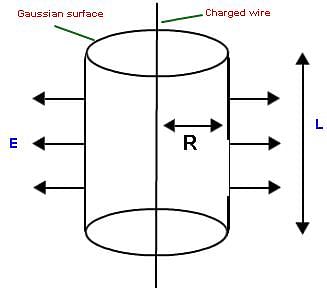
Fig: We can easily find electric field in different geometries using charge distribution system
|
98 videos|387 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Continuous Charge Distribution - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is continuous charge distribution? |  |
| 2. How is continuous charge distribution different from discrete charge distribution? |  |
| 3. What are the types of continuous charge distributions? |  |
| 4. How is the electric field calculated for continuous charge distributions? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life examples of continuous charge distributions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|