NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - Market Around Us
Q1: In what ways is a hawker different from a shop owner?
Ans: The following are the differences between hawkers and vendors:
Hawker | Shop Owner |
Moves from one place to another, selling goods on the go, often on streets or public places. | Operates from a fixed location, typically within a building or a designated shop space. |
Usually operates with a mobile setup, such as a cart or a portable stall. | Owns or rents a physical store or shop. |
May have a limited inventory due to the portable nature of their business. | Can have a larger and more diverse inventory since they have a fixed space. |
Might have flexible hours, operating during specific times or events. | Generally follows regular business hours. |
May have lower overhead costs as they do not require a fixed location. | Bears the cost of maintaining a physical store, including rent, utilities, and staff salaries. |
Has the flexibility to reach different locations, covering a broader customer base. | Serves a local or specific community, and customers need to visit the shop's location. |
Q2: Compare and contrast a weekly market and a shopping complex on the following: 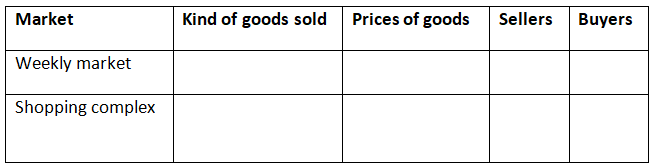 Ans:
Ans: 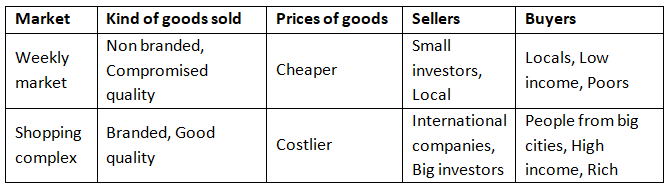
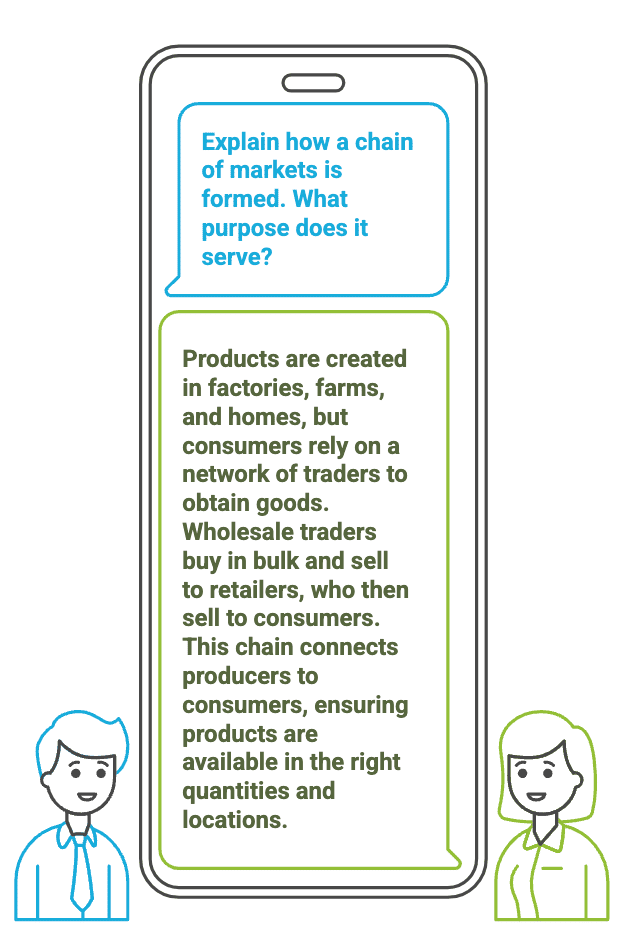
Q3: Explain how a chain of markets is formed. What purpose does it serve?
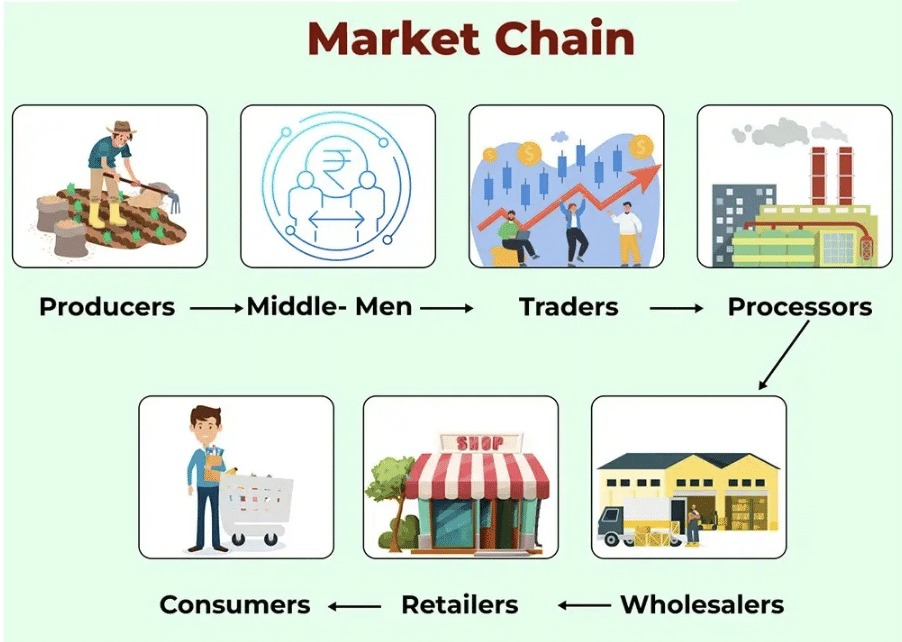
Ans: Products are created in factories, farms, and homes, but consumers do not buy directly from these sources. Instead, they rely on a network of traders to obtain goods.
- Wholesale Traders: These traders purchase goods in large quantities, such as 25 to 100 kilos of vegetables, from producers.
- Distribution: Wholesale traders then sell these goods to retailers, who are the final sellers to consumers.
 Formation of Chain
Formation of Chain - Market Demand: The amount of goods sold is influenced by consumer demand.
- Retailers: These include shop owners, hawkers, and market traders who sell directly to consumers.
This process creates a chain of markets, connecting producers to consumers through various intermediaries, ensuring that products are available in the right quantities and locations.
 Market Chain
Market ChainQ4: ‘All persons have equal rights to visit any shop in a marketplace.’ Do you think it is true of shops with expensive products? Explain with examples.
Ans: Everyone can go to any store they want, but when it comes to stores selling expensive things, it's not the same for everyone. Here's why:
- Money Differences: Wealthy individuals can easily afford expensive items, while those with less money may find these shops too costly.
- Shopping Choices: People often choose shops based on their financial situation. Wealthier shoppers might prefer upscale stores or large malls, while others may opt for more affordable options.
- Prices Matter: High prices in expensive shops can deter those with limited budgets, leading them to seek cheaper alternatives.
Example: For example, rich people might go to big supermarkets for their groceries, even though prices are higher. But people with less money might buy their fruits and veggies from smaller shops or street sellers, where things are cheaper.
Q5: ‘Buying and selling can take place without going to a marketplace.’ Explain this statement with the help of examples.
Ans: The age of the internet has created new ways to buy and sell goods without needing a physical marketplace. Here are some examples:
- Phone Orders: Customers can easily order items by phone using cards or payment apps. The products are then delivered directly to their homes.
- Online Purchases: With the internet, people can browse websites to order products. This includes local shops, such as Kirana stores, where customers can use apps to order groceries for home delivery.
- Payment Options: Payments can be made through Internet banking or upon delivery, making transactions more convenient.
Modern technology enables seamless buying and selling through methods like phone orders and online purchases, offering hassle-free payment options.
|
63 videos|552 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science - Market Around Us
| 1. What are the main types of markets discussed in "Market Around Us"? |  |
| 2. How do markets influence our daily lives according to the article? |  |
| 3. What factors should consumers consider when choosing a market to shop in? |  |
| 4. How do online markets differ from traditional markets as explained in the article? |  |
| 5. What role do local markets play in supporting the economy based on the article's content? |  |

















