Primary, Secondary Metabolites and Biomacromolecules | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Metabolites? |

|
| Plant Metabolites |

|
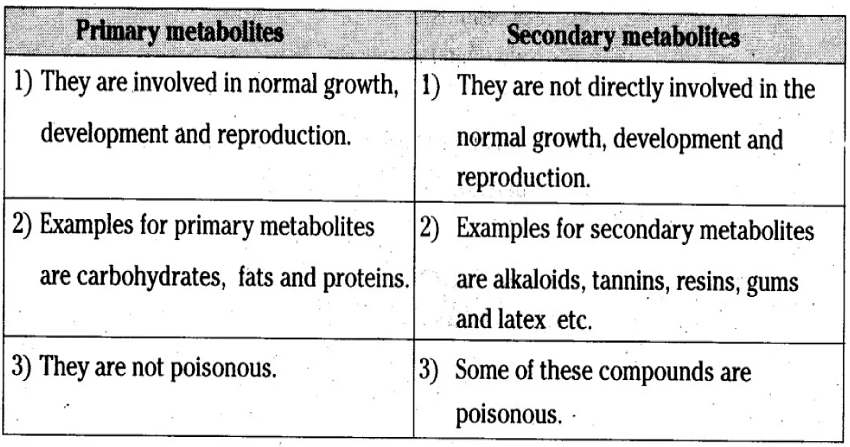
| Difference between Primary and Secondary Metabolites |

|
| Human Metabolites |

|
| Biomacromolecules |

|
What are Metabolites?
Metabolites are the intermediate products produced during metabolism, catalyzed by various enzymes that occur naturally within cells. Eg., antibiotics, and pigments. The term metabolites are usually used for small molecules. The various functions of metabolites include; fuel, structure, signalling, catalytic activity, defence and interactions with other organisms.The metabolites are produced by plants, humans and microbes.
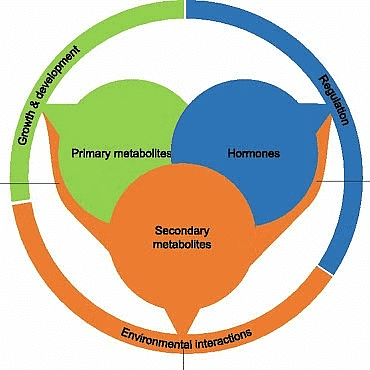
Plant Metabolites
Plant metabolites are of two types:
1. Primary Metabolites
- These are the chemical compounds produced during the growth and development, processes.
- They are also involved in the primary metabolic processes of respiration and photosynthesis.
- The primary metabolites are formed in the growth phase. They maintain the physiological functions of the body and are known as central metabolites.
- They are the intermediate products of anabolic metabolism, which are used by the cells for the formation of essential macromolecules.
- Amino acids, vitamins, organic acids, are some of the primary metabolites produced industrially. Alcohol is the major primary metabolite produced on a large scale, industrially.
2. Secondary Metabolites
- These compounds are produced by the organisms that are not required for primary metabolic processes. However, they can be important ecologically or otherwise.
- Secondary metabolites are considered to be the end products of primary metabolites because they are derived by the pathways in which the primary metabolites involve.
- For eg., antibiotics, toxins, pheromones, enzyme inhibitors, etc. Streptomycetes and related actinomycetes are the sources of novel secondary metabolites.
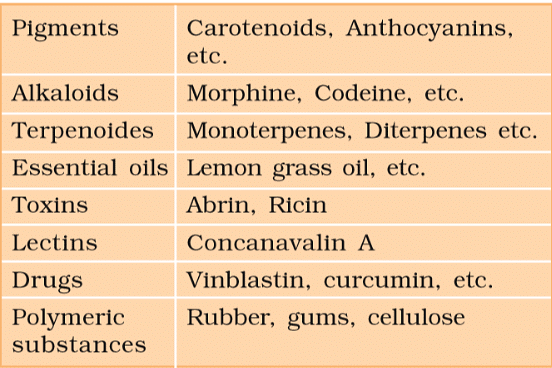 Some Secondary Metabolites
Some Secondary Metabolites
Difference between Primary and Secondary Metabolites
Human Metabolites
- Humans have 2500 metabolites.
- Prostaglandin produces a metabolite Arachidonic acid. Both the molecules have the same physical properties, functional groups and are linked by a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- Cholesterol produces steroid hormones, catecholamines arise from the amino acid tyrosine.
Biomacromolecules
Living things are made up of a lot of water, some proteins, a bit of carbohydrates, a small amount of lipids, nucleic acids like DNA, and some ions. The small molecules dissolve easily in acid, while the bigger ones, like proteins and DNA, don't. Lipids are kind of in between; they're small but end up with the bigger molecules because they form structures that don't dissolve in water.
- Acid soluble pool: This is a group of small molecules found in living organisms with weights ranging from 18 to around 800 daltons. These are often called micromolecules or biomolecules.
- Acid insoluble fraction: These are bigger molecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides found in living things. They have molecular weights of ten thousand daltons and above, except for lipids. Lipids are smaller but still end up in this fraction because they form membranes that don't dissolve in water.
The acid soluble pool contains small molecules, while the acid insoluble fraction mainly contains big molecules like proteins, DNA, sugars, and fats. Even though fats are small, they end up in the big molecule group because they're part of structures like cell membranes that don't dissolve in water. The acid soluble pool shows what's in the liquid part of the cell, while the acid insoluble fraction shows what's in both the liquid and solid parts, including structures like cell organs.
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Primary, Secondary Metabolites and Biomacromolecules - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are primary metabolites in plants? |  |
| 2. How do secondary metabolites differ from primary metabolites in plants? |  |
| 3. What are human metabolites and why are they important? |  |
| 4. What are biomacromolecules and how do they relate to primary and secondary metabolites? |  |
| 5. How do primary and secondary metabolites impact plant health and interactions with the environment? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|












