Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Political Science Class 11 > Chapter Notes: Political Theory : An Introduction
Political Theory : An Introduction Class 11 Political Science
Introduction
Political theory analyses the basic questions like; How a country must be organised, why do we need a government or what do we owe to each other as citizens.
What is Political Theory?
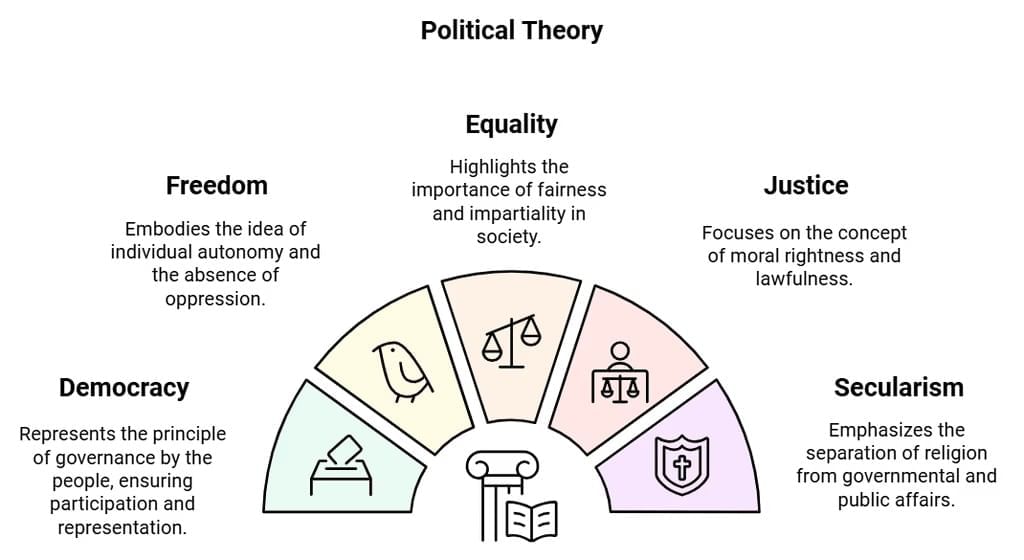
- Political theory is concerned with the ideas and principles that systematically shape the constitution, governments, and social life. Certain values and principles, such as democracy, freedom, and equality, have inspired people and guided policies.
- The origins of these values and words need to be understood rationally and political theory helps us in that respect. Political theory explains what freedom, equality, justice, democracy, secularism, and other concepts mean.
Why do we study Political Theory?
- Different countries, such as America and India have tried to protect their fundamental values by enshrining them in their constitutions. The values such as equality, freedom, dignity, justice, peace etc have been influenced by the ideas of philosophers such as Kautilya, Aristotle, Jean Jacques Rousseau, John Locke, Karl Marx among other prominent ones.
- Although Rousseau, Marx, and Gandhi were not politicians, their ideas influenced generations of politicians around the world. It thus becomes necessary that we have a sound understanding of these political terms.
- Political theorists study the foundations of modern polity and also consider our current political experiences to identify trends and future possibilities.
Who influenced the values of the Indian constitution?
- The constitution of India is based on ideas and principles that have been debated since the time of Kautilya. Political thinkers and activists such as MK Gandhi, B.R. Ambedkar have shaped the pillars of the Indian constitution.
Relevance of Political Theories in India
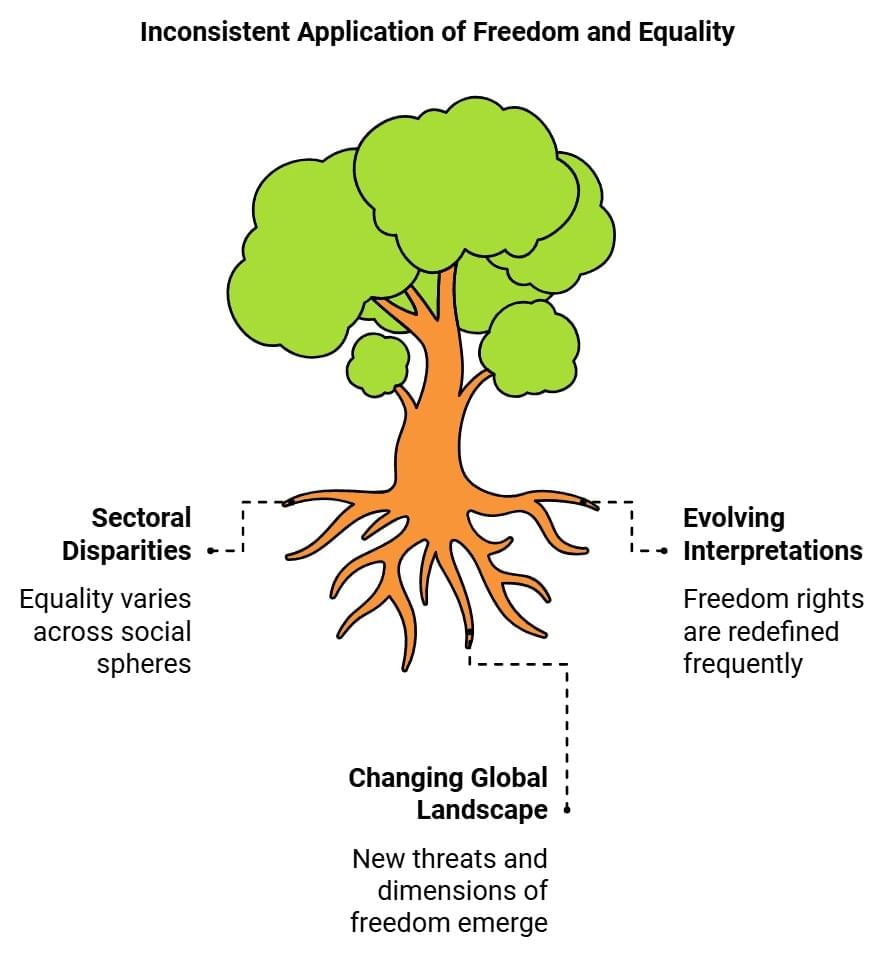
India is free and independent, but questions regarding freedom and equality have not ceased to crop up. We can broadly find the relevance of modern political thought in India as it concerns with the following:
- Firstly, the issue concerning freedom, equality and democracy arise in many areas of social life and they are being implemented in different sectors at different phases.
E.g: Equality may exist in the political sphere in the form of equal rights but it may not exist to the same extent in the social and economic spheres. - Secondly, though freedom is guaranteed in our Constitution, we encounter new interpretations all the time.
E.g: The right to life has been interpreted by the courts to include the right to livelihood.
The Right to information has been granted to a new law. The fundamental rights guaranteed by our Constitution have been amended and expanded over time through judicial interpretations and government policies which are designed to address new problems. - Thirdly, as our world changes, we may discover new dimensions of freedom as well as new threats to freedom.
E.g: global communications technology is making it easier for activists to network with one another across the world for protecting tribal cultures or forests. But it also enables terrorists and criminals to network.
As a result, questions are raised regarding how much freedom should be given to people using the net.
Putting Political Theory To Practice
- The only aspect focused on the political theory is that which deals with the origins meanings and significance of the political ideas that we are familiar with such as freedom, equality, citizenship, justice, development, nationalism, secularism. Various political theorists have provided diverse definitions of freedom or equality and you may find the distinct definition of equality or freedom or justice.
- Political theorists clarify the meaning of political concepts by looking at how they are understood and used in ordinary language. They also debate and examine the diverse meanings and opinions in a systematic manner.
- This is because terms like equality concern our relationships with other human beings rather than with things. Human beings, unlike things, have opinions on issues like equality.
- Example: People often jump the queue in shops or doctor’s waiting rooms or government offices. Some people cannot have the access to these shops and other goods and services because of monetary constraints.
- Thus, our idea of equality is quite complex, also the reason behind the many definitions is because the meaning of equality is dependent on the context.
As in the case of equality and other subjects such as Freedom, Citizenship, Rights, Justice, Development, Equality, Nationalism and Secularism; the political theorists engage with everyday opinions, debate possible meanings and thrash out policy options.
Why should we study Political Theory?
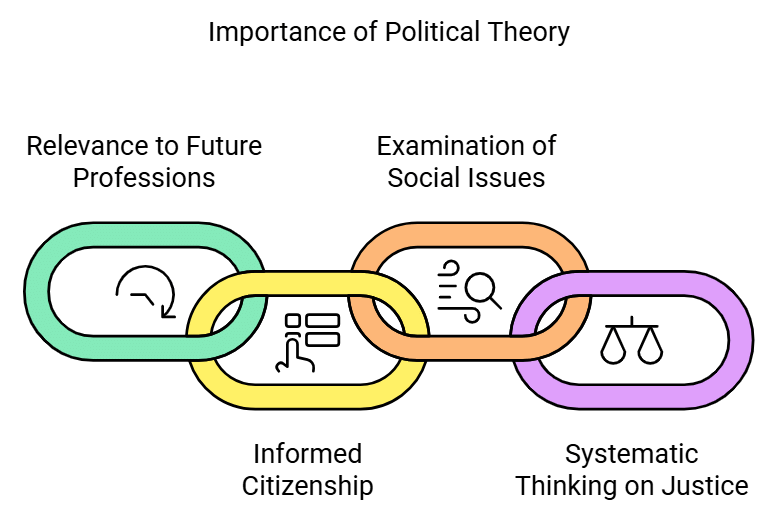
- Firstly, political theory is relevant to all of the aforementioned target groups. Even as high school students, we may choose one of the aforementioned professions in the future, making it relevant to us indirectly at present.
- Secondly, as citizens entitled to vote and make decisions on other issues, it is helpful to possess a basic knowledge of the political concepts and institutions that shape the world in which we live in order to act responsibly.
- Thirdly, freedom, equality, and secularism are not abstract issues in our lives. Discrimination of various sorts is encountered by people every day in families, schools, colleges, shopping malls, and other places. Political theory encourages us to examine our ideas and emotions about political matters.
- Finally, as students, we enjoy participating in debates and elocution competitions. We have opinions about what is right or wrong, just or unjust, but we are unsure if they are reasonable. Political theory exposes us to systematic thinking on justice or equality so that we can refine our opinions and argue in an informed manner, for the sake of the common good.
The document Political Theory : An Introduction Class 11 Political Science is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Political Science Class 11.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Political Theory : An Introduction Class 11 Political Science
| 1. What is the significance of studying Political Theory in the modern context? |  |
Ans. Studying Political Theory is significant in the modern context as it helps individuals understand the foundational principles of governance, justice, and power. It provides critical tools for analyzing political systems and ideologies, fostering informed citizenship, and promoting active engagement in democratic processes. Political Theory encourages a deeper understanding of contemporary issues like human rights, equality, and social justice, which are crucial for addressing the challenges faced by society today.
| 2. How have ancient philosophers influenced modern Political Theory? |  |
Ans. Ancient philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, and Confucius laid the groundwork for modern Political Theory by exploring concepts of justice, governance, and the role of the state. Their ideas about democracy, ethics, and the social contract continue to influence contemporary political thought, providing frameworks for analyzing political structures and the moral obligations of individuals and governments. Their works emphasize the importance of virtue and ethics in politics, which remain relevant in discussions of political accountability and civic responsibility today.
| 3. What role did Indian leaders play in shaping the values of the Indian Constitution? |  |
Ans. Indian leaders like B.R. Ambedkar, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Mahatma Gandhi played crucial roles in shaping the values of the Indian Constitution. They drew inspiration from various sources, including the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity, as well as the experiences of colonial rule. The Constitution reflects their commitment to social justice, secularism, and democracy, aiming to create a framework that upholds the rights and dignity of all citizens while promoting unity in diversity.
| 4. How can Political Theory be applied to real-world governance in India? |  |
Ans. Political Theory can be applied to real-world governance in India by informing policy-making, legal frameworks, and political discourse. Theoretical concepts such as justice, liberty, and rights can guide lawmakers in creating fair and equitable policies. Additionally, political theories encourage public debate and participation, fostering a culture of accountability and transparency in governance. By integrating theoretical insights into practice, policymakers can address social issues more effectively and enhance democratic engagement among citizens.
| 5. Why is it important for students to study Political Theory? |  |
Ans. It is important for students to study Political Theory as it equips them with critical thinking skills and a comprehensive understanding of political systems and ideologies. This knowledge is essential for fostering informed citizenship, enabling students to engage in discussions about governance, rights, and responsibilities. Furthermore, studying Political Theory empowers students to analyze current events, challenge injustices, and contribute to the improvement of society, thus playing an active role in shaping the future of democracy and social justice.
Related Searches

















