Apomixis & Parthenocarpy | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Apomixis
- The term ‘Apomixis’ was introduced by Winkler(1908). ‘Apomixis is the substitution of sexual reproduction, which does not involve meiosis and syngamy.’
- Apoximis refers to the formation of the plant from a seed without fertilization or normal sexual reproduction. This mechanism produces clones, hence can be considered as a form of asexual reproduction.
It is of two types:
(i) Vegetative Reproduction: It is a type of asexual reproduction, mostly in plants when a plant part is detached and produces new progeny. Apomixis: Vegetative Propagation
Apomixis: Vegetative Propagation
(ii) Agamospermy: Process which involves sex cells but takes place without fertilisation or meiosis.
(a) 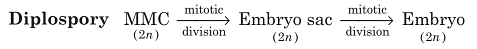
(b) Adventitive Embryony: The nucellar or integumentary cells produce a diploid embryo.
(c) Apospory: Cell, outside the embryo sac produces aposporic embryo sac.
Parthenocarpy
It is the process of producing fruits without fertilisation.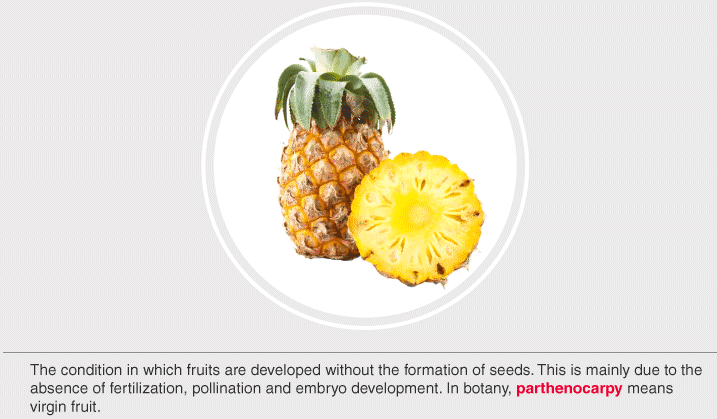
On the basis of its causes, it is of three types:
(i) Genetic Parthenocarpy: Parthenocarpic fruits are produced because of hybridisation or mutation.
(ii) Environmental Parthenocarpy: The environmental condition like fog, frost, high temperature and freezing led to the non-functioning of the reproductive organ and results in parthenocarpy.
(iii) Chemical Induced Parthenocarpy: The artificial application of IAA, α-NAA, gibberellin leads to the production of parthenocarpic fruits.
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on Apomixis & Parthenocarpy - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is apomixis? |  |
| 2. How does apomixis differ from parthenocarpy? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of apomixis in plants? |  |
| 4. Can apomixis occur naturally in all plant species? |  |
| 5. Are there any disadvantages to apomixis in plants? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















