Evolution of Modern Human - UPSC PDF Download
Stages of Evolution of Man
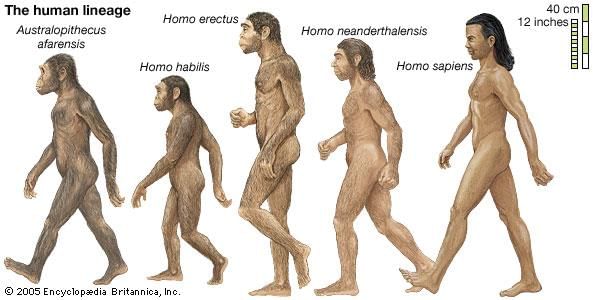
The genus of the human being today is called Homo and the man today is called as Homo sapiens. From simple life forms that were unicellular to the development of multicellular organisms gave rise to the vertebrates. The vertebrates began evolving that led to the development of mammals. Among the mammals, humans are most closely related to primates such as the orangutan
The family to which human beings belong is called Hominidae. It was in the Miocene age that the family Hominidae split from the Pongidae(apes) family. Dryopethicus was the first in the evolution of man in the stages of evolution and some believe him to be the common ancestor of man and apes.
Dryopethicus
He was the earliest known ancestor of man. At the same time as his existence, Ramapethicus existed who was more human-like than Dryopethicus. Dryopethicus inhabited the European region and some parts of Asia and Africa. Stages of evolution of humans began from him. After Dryopethicus and Ramapethicus came to the genus Australopethicus which preceded the genus Homo.
Australopithecus
- Australopithecus ramidus: Was 1.2 meters tall and the fossils show the foramen magnum that was large to indicate upright walking. The forelimbs were different from those of the earlier ape-like ancestors. They had teeth like humans.
- Australopithecus afarensis– ‘Lucy’ the famous fossil belonged to this species. They are said to have inhabited the African mainland. And they were shorter than the Australopithecus ramidus and had a small skull with flat noses and no chin. They were able to walk on two legs but the legs were slightly bowed which made their walk slightly ape-like. The bowed legs, fingers, and toes enabled them to climb trees and live there. They had large teeth and jaws.
- Australopithecus africanus– These also inhabited the African mainland. They were bipedal and had a small skull with small brains than Homo erectus but larger than their predecessors. Also, they had large teeth compared to current day humans and were herbivorous. They had large jaws.
- Australopithecus robustus– He was taller than his predecessors but still ape-like. They also weighed more than their ancestors. After the Australopithecus genus came the Homo genus. The first man in the genus was Homo habilis.
Homo
- Homo habilis– He had a face similar to his ancestors. The skull and brain size indicate that he may have been able to speak. The earliest tools made were from this era. Homo habilis is known as the ‘handy man’ because he was the first to make and use tools. He was around 5 feet tall and erect.
- Homo erectus– after Homo habilis came, the Homo erectus who was also upright. He had a smaller but longer face, less prominent or absent chin, larger brain size and prominent speech. He knew how to make and use tools, he made a fire and knew how to control it. Homo erectus was carnivorous. He knew the existence of groups and they began spreading from Africa to Asia and Europe. The Java Man and Peking Man had brain capacities similar to modern man at 1300cc. They were cave dwellers.
- Homo sapiens– After Homo erectus came, the Homo sapiens who separated into two types:
1) Homo sapiens neanderthelensis
They had a brain size larger than modern man and were gigantic in size. Also, they had a large head and jaw and were very powerful and muscular. They were carnivores and the tools from the era indicate they were hunters. They were also cave dwellers but their caves were more comfortable and they lived in groups and hunted for food gathering.
2) Homo sapiens sapiens
Also known as ‘modern-day man’ is what we are today. Compared to the Homo sapiens neanderthelensis, they became smaller in size and the brain size reduced to 1300cc. There was also a reduction in the size of the jaw, rounding of the skull and chin. Cro- Magnon was the earliest of the Homo sapiens. They spread wider from to Europe, Australia, and the Americas. They were omnivores, had skilful hands, developed the power of thinking, producing art, more sophisticated tools and sentiments.
Evolution is not a thing of the past and is continuing even now. Humans are undergoing ‘natural selection’ for many different traits based on their life and environment in the present. It is believed that the jaw size is reducing further and the wisdom teeth are soon going to become extinct.
FAQs on Evolution of Modern Human - UPSC
| 1. What is the theory of evolution? |  |
| 2. How did modern humans evolve? |  |
| 3. What are some key characteristics of modern humans? |  |
| 4. How does DNA provide evidence for human evolution? |  |
| 5. What are the main factors that have influenced human evolution? |  |


















