Photosynthesis: Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Photosynthesis? |

|
| Site of Photosynthesis |

|
| Photosynthesis Apparatus |

|
| Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis |

|
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide.
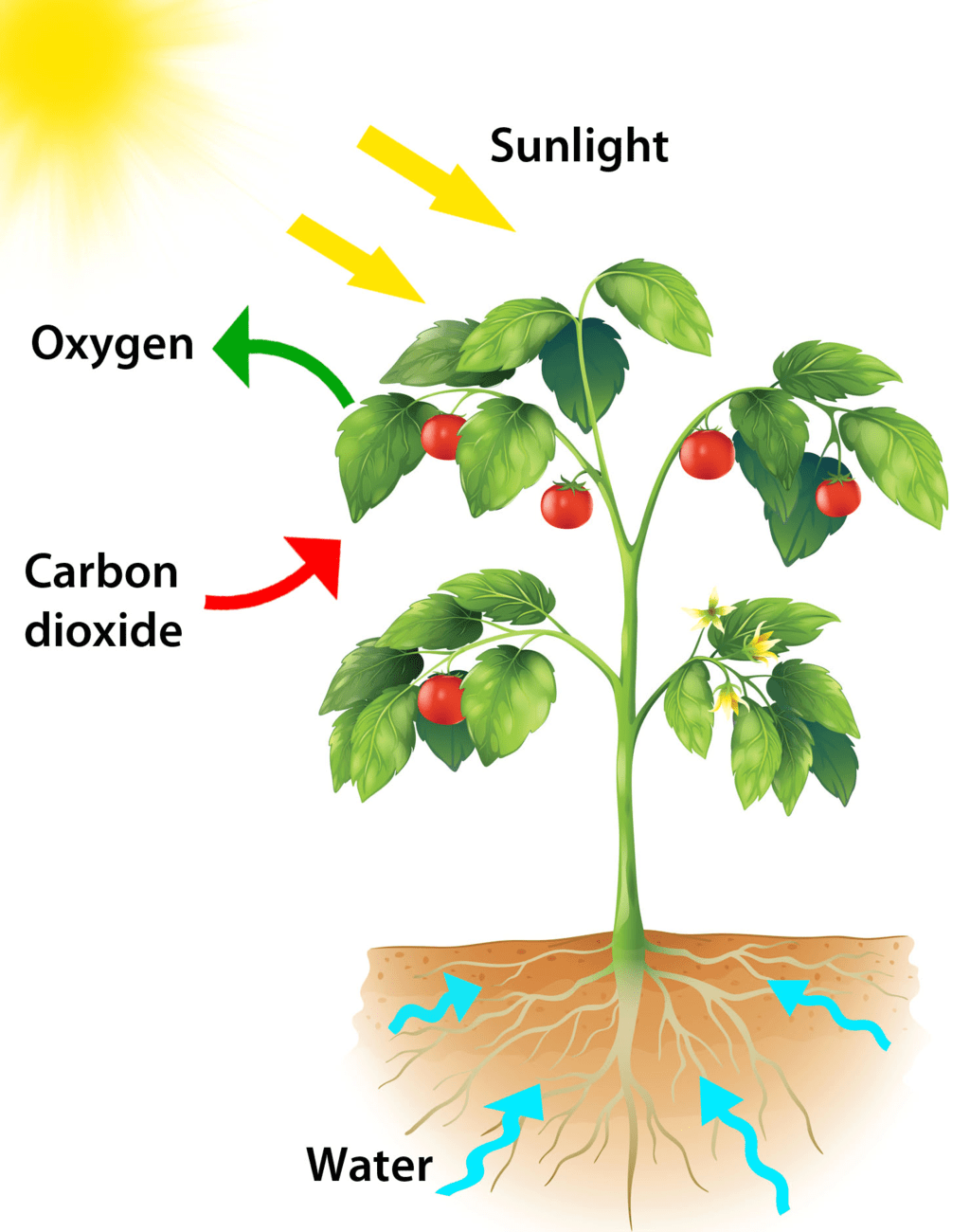 Plant absorbing sunlight
Plant absorbing sunlight
- The process of photosynthesis is used by plants, algae, and certain bacteria that convert light energy into chemical energy.
- The glucose formed during the process of photosynthesis provides two important resources to organisms: energy and fixed carbon.
Site of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in special organelles known as chloroplasts. This organelle has its own DNA, genes and hence can synthesize its own proteins. Chloroplasts consist of stroma, fluid, and a stack of thylakoids known as grana. There are three important pigments present in the chloroplast that absorb light energy, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids. Photosynthesis primarily takes place in the green leaves of plants, but it can also occur in other green parts of the plant. Examples of other parts where photosynthesis may occur include green stems and unripe fruits.
Chloroplasts in Mesophyll Cells
- Within the leaves, photosynthesis occurs in the mesophyll cells, which contain a large number of chloroplasts.
- The chloroplasts are usually aligned along the walls of the mesophyll cells to capture the optimum amount of incident light.
Chloroplast Structure and Function
- The chloroplast consists of a membranous system including grana, stroma lamellae, and the matrix stroma.
- Grana are responsible for trapping light energy and synthesizing ATP and NADPH.
- In the stroma, enzymatic reactions synthesize sugar, which is then converted into starch.
Light Reactions vs. Dark Reactions
- The reactions occurring in the chloroplasts can be divided into light reactions and dark reactions.
- Light reactions, also known as photochemical reactions, are directly driven by light and involve the synthesis of ATP and NADPH.
- Dark reactions, or carbon reactions, are dependent on the products of light reactions (ATP and NADPH) but do not occur in darkness. They are crucial for the synthesis of sugar.
 Chloroplast
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis Apparatus
The photosynthesis apparatus includes the following essential components:
 Photosynthesis Apparatus Components
Photosynthesis Apparatus Components
1. Pigments
Pigments not only provide color to the photosynthetic organisms but are also responsible for trapping sunlight. The important pigments associated with photosynthesis include:
- Chlorophyll: It is a green-colored pigment that traps blue and red light. Chlorophyll is subdivided into, “chlorophyll a”, “chlorophyll b”, and “chlorophyll c”. “Chlorophyll a” is widely present in all photosynthetic cells. A bacterial variant of chlorophyll known as bacteriochlorophyll can absorb infrared rays.
- Carotenoids: These are yellow, orange, or red-colored pigments that absorb bluish-green light. Xanthophyll and carotenes are examples of carotenoids.
3. Antennae
Antennae are the collection of 100 to 5000 pigment molecules that capture light energy from the sun in the form of photons. The light energy is transferred to a pigment-protein complex that converts light energy to chemical energy.
4. Reaction Centers
The pigment-protein complex responsible for the conversion of light energy to chemical energy forms the reaction center.
Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis
What are Pigments?
Pigments are materials capable of absorbing light at particular wavelengths. Pigments are chemical substances, which exhibit wavelengths of visible light, making them appear colorful. Plants, flowers, algae, certain photosynthetic bacteria, and even the skin of animals have a particular type of pigments, which provide colors and also have an ability to absorb some wavelengths.
Introduction to Leaf Pigments and Photosynthesis
- Plants display a variety of shades of green in their leaves, even within the same plant. This diversity is due to different pigments present in the leaves.
- Pigments are substances that absorb light at specific wavelengths. The main pigments involved in photosynthesis are chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids.
Chromatographic Separation of Leaf Pigments
When leaf pigments are separated through paper chromatography, four distinct pigments are observed:
 This separation shows that the green color of leaves is not due to a single pigment but a combination of these pigments.
This separation shows that the green color of leaves is not due to a single pigment but a combination of these pigments.
Role of Pigments in Photosynthesis
- Pigments play a crucial role in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy and converting it into chemical energy.
- Chlorophyll a is the most abundant and important pigment for photosynthesis. It absorbs light most effectively in the blue and red regions of the light spectrum.
- Accessory pigments like chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids help by absorbing light at different wavelengths and transferring the energy to chlorophyll a. They also protect chlorophyll from damage.
Absorption Spectrum of Chlorophyll a
- The absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a shows two peaks of maximum absorption: One in the blue region (around 430 nm) and the other in the red region (around 660 nm).
- This means that chlorophyll a absorbs blue and red light most efficiently, which corresponds to the wavelengths where photosynthesis occurs at a higher rate.

(a)Graph showing the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a, b and the carotenoids (b) Graph showing action spectrum of photosynthesis (c) Graph showing action spectrum of photosynthesis superimposed on absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a
Action Spectrum of Photosynthesis
- The action spectrum of photosynthesis indicates the wavelengths at which photosynthesis occurs most effectively. It closely matches the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a.
- However, there is not a perfect overlap, indicating that photosynthesis also occurs at other wavelengths, albeit to a lesser extent.
Accessory Pigments
- Accessory pigments, such as chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids, play a vital role in expanding the range of light wavelengths that can be used for photosynthesis.
- They absorb light energy that chlorophyll a cannot absorb and transfer this energy to chlorophyll a for photosynthesis.
- Additionally, accessory pigments protect chlorophyll a from damage caused by excessive light.
Conclusion
- Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis, absorbing light mainly in the blue and red regions of the spectrum.
- Accessory pigments broaden the range of light that can be used for photosynthesis and protect chlorophyll a from damage.
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Photosynthesis: Pigments Involved in Photosynthesis - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the process of photosynthesis and why is it important for life on Earth? |  |
| 2. Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells? |  |
| 3. What are the main pigments involved in photosynthesis and what roles do they play? |  |
| 4. What are the two main stages of photosynthesis and what happens in each? |  |
| 5. How does the process of photosynthesis impact the environment? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















