India Location Class 11 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| India's Geography |

|
| Size |

|
| India and Its Neighbours |

|
| Key Points |

|
| Some Solved Questions |

|
India's Geography
- India extends from Kashmir in the north to Kanniyakumari in the south and Arunachal Pradesh in the east to Gujarat in the west.
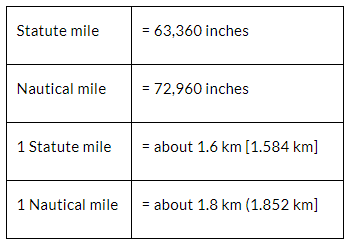
- India’s territorial limit further extends towards the sea up to 12 nautical miles (about 21.9 km) from the coast.
- The southern boundary extends up to 6°45' N latitude in the Bay of Bengal.
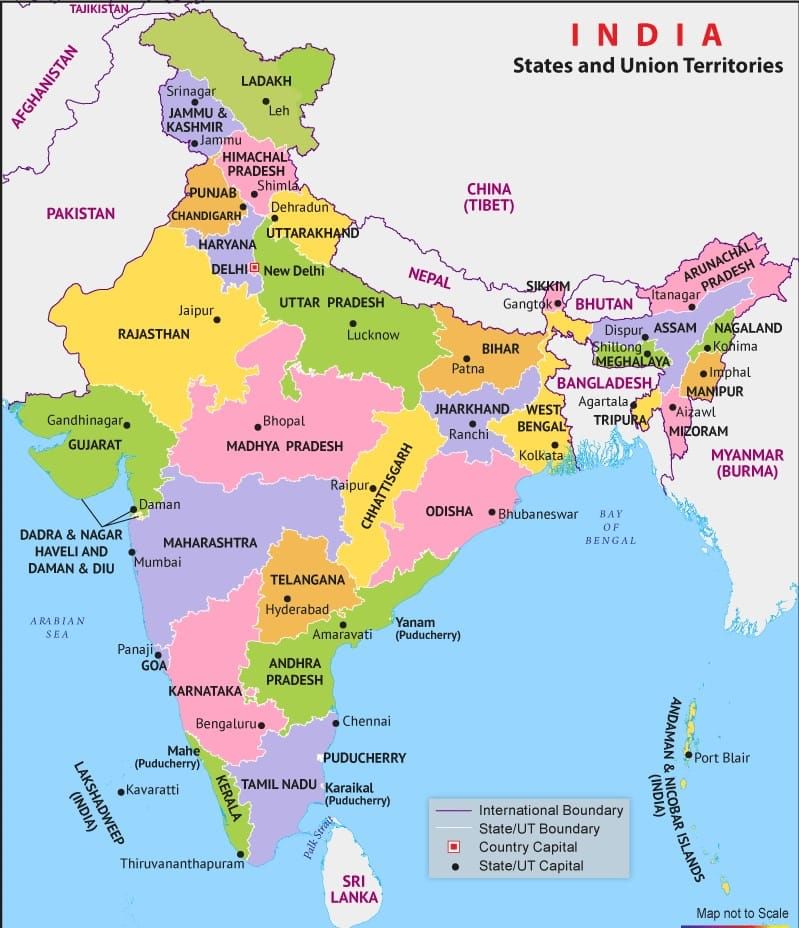
- The latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India is roughly about 30 degrees, whereas the actual distance measured from north to south extremity is 3,214 km, and that from east to west is only 2,933 km.
- The distance between two longitudes decreases towards the poles, whereas the distance between two latitudes remains the same everywhere.
- The southern part of the country lies within the tropics, and the northern part lies in the subtropical zone or the warm temperate zone. This location is responsible for large variations in landforms, climate, soil types and natural vegetation in the country.
- From the values of longitude, it is quite discernible that there is a variation of nearly 30 degrees, which causes a time difference of nearly two hours between the easternmost and the westernmost parts of our country
- A general understanding among the countries of the world is to select the standard meridian in multiples of 7°30' of longitude. That is why 82°30' E has been selected as the ‘standard meridian’ of India. Indian Standard Time is ahead of Greenwich Mean Time by 5 hours and 30 minutes.
- There are some countries where there is more than one standard meridian due to their vast east-to-west extent. For example, the USA has seven time zones.
Size
- India's vast size contributes to its rich physical diversity.
- Lofty mountains like the Himalayas, Hindukush, and Sulaiman ranges form formidable barriers.
- Major rivers such as Ganga, Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Krishna, Godavari, and Kaveri traverse the landscape.
- Northeast and southern regions are characterised by green forested hills.
- Marusthali, or Thar Desert, dominates the western expanse with its vast sandy terrain.
- Geographically, India is part of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Himalayas, Hindukush, Purvachal hills, and the Indian Ocean.
- The peninsular part of India extends into the Indian Ocean, creating a coastline of 6,100 km on the mainland and 7,517 km including island groups like Andaman and Nicobar in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea.
- India's diverse physical landscape supports varied resources and ecosystems, from fertile river plains to mineral-rich mountains and coastal fisheries.
India and Its Neighbours
- India shares its land borders with seven countries: Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh. It also shares maritime borders with Sri Lanka and the Maldives.
- India is located in the south-central part of the continent of Asia, bordering the Indian Ocean and its two arms extending in the form of the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
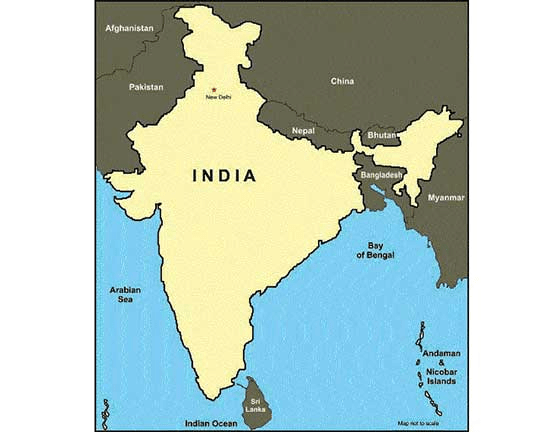 Neighboring Countries of India
Neighboring Countries of India
- This maritime location of Peninsular India has provided links to its neighbouring regions through the sea and air routes.
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait.
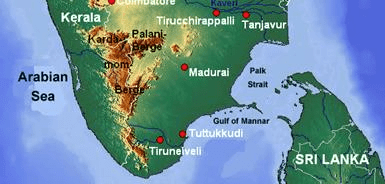 Gulf of Mannar
Gulf of Mannar
Key Points
- India extends from 6°45' N latitude in the Bay of Bengal to the northernmost Kashmir, covering vast latitudinal and longitudinal extents.
- The distance between latitudes remains constant, while the distance between longitudes decreases towards the poles.
- India's vast latitudinal extent results in diverse climates, landforms, and vegetation zones.
- The longitudinal extent of India causes a two-hour time difference between its eastern and western extremities.
- The standard meridian of India, 82°30' E, helps standardise time across the country despite this time difference.
- India's area of 3.28 million sq. km makes it the seventh-largest country globally.
- India's physical diversity includes lofty mountains, large rivers, green hills, and sandy expanses.
- The Himalayas, along with other ranges, form a natural barrier contributing to the unique regional identity of the Indian subcontinent.
- India's maritime location provides a long coastline of 7,517 km, connecting it with neighbouring regions through sea and air routes.
- India's neighbours include Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Maldives.
Some Solved Questions
Q.1. What is the location of India?
Ans: India’s location is between 8°4′ and 37°6’N latitudes (Mainland) and 68°7’ and 97°25’E longitudes.
Q.2. What is the difference between local time and standard time?
Ans: Local time is the time based on the position of the sun at a particular place. It varies from one longitude to another because the sun rises and sets at different times in different locations.
Standard time, on the other hand, is the official time of a country or region set for uniformity. It is the time of a specific central meridian chosen for a country and is the same across a particular time zone.
For example, in India, the local time of Kolkata (located further east) is ahead of the local time of Mumbai. But the Indian Standard Time (IST) is the same across the country, based on the 82.5° E longitude.
Q.3. How is the central position of India beneficial to us? Explain it.
Ans: Geographically, India occupies a central position on the Asian continent. This position is beneficial to us in many ways:
- India is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. Europe and the eastern part of North America are at roughly equal distances from India.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through the center of India, making it a tropical country.
- India has a long coastline with many deep and natural harbours, which support maritime trade.
- The Indian Ocean provides a favourable sea route for international trade.
- India is surrounded by natural boundaries that are strategically and geographically advantageous.
- The Indian Ocean plays a key role in the origin and direction of the monsoons.
- The towering Himalayan mountain range acts as a climatic barrier. It protects northern India from cold polar winds and forces the monsoon winds to shed rainfall over the Indian subcontinent.
Q4. What are the three major physical divisions of India? Describe them.
Ans: India is divided into three major physical divisions based on landforms and geographical features. These are:
The Himalayan Mountains:
Located in the north, the Himalayas are the highest mountain range in the world. They act as a natural barrier and protect India from cold winds. They are divided into three parallel ranges – the Greater Himalayas (Himadri), the Middle Himalayas (Himachal), and the Outer Himalayas (Shiwalik).The Northern Plains:
These plains lie to the south of the Himalayas and are formed by the deposition of alluvium brought by rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra. They are flat, fertile, and densely populated, making them suitable for agriculture.The Peninsular Plateau:
This region lies to the south of the Northern Plains and is a triangular landmass made of old and hard rocks. It includes the Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau. It is rich in minerals and has uneven terrain with hills and valleys.
These physical divisions give India a varied landscape and influence its climate, agriculture, and human activities.
Q5. Name a few places in India through which the standard meridian passes.
The five states in India through which the Indian Standard Meridian (82.5’ E) passes are Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
|
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on India Location Class 11 Geography
| 1. भारत का क्षेत्रफल कितना है और यह विश्व में किस स्थान पर है ? |  |
| 2. भारत के पड़ोसी देश कौन-कौन से हैं ? |  |
| 3. भारत की भौगोलिक स्थिति का क्या महत्व है ? |  |
| 4. भारत के भौगोलिक विभाजन के मुख्य भाग कौन से हैं ? |  |
| 5. भारत की भौगोलिक विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |






















