Rotating Magnetic Field | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
In this article, we will explain how a rotating magnetic field is created. Imagine a part of an electric motor called the stator, where the wiring is set up in a way that each section is 120 degrees apart from the others.
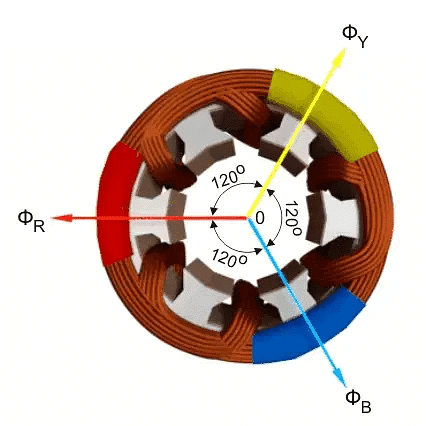
Even though the total of three electric currents in a balanced system adds up to zero, the resulting magnetic field they create doesn't add up to zero. Instead, it stays at a constant value and rotates in space as time passes.
The magnetic strength made by each current in every section can be shown with these equations. This is similar to how the current works in a three-part system, as the magnetic strength is in sync with the current.
Where, φR, φY and φB are the instantaneous flux of corresponding Red, Yellow and Blue phase winding, φm amplitude of the flux wave. The flux wave in the space can be represented as shown below.
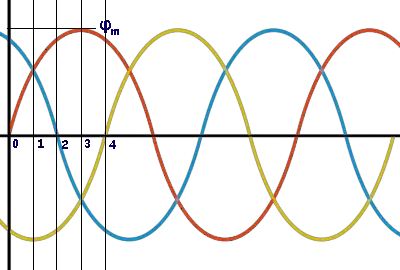
Here are the values of the magnetic strength at point 0 on the graph:
- Red (φR):
- Yellow (φY):
- Blue (φB):
At this point, the total of these strengths (φr) is 1.5 times the maximum (φm).
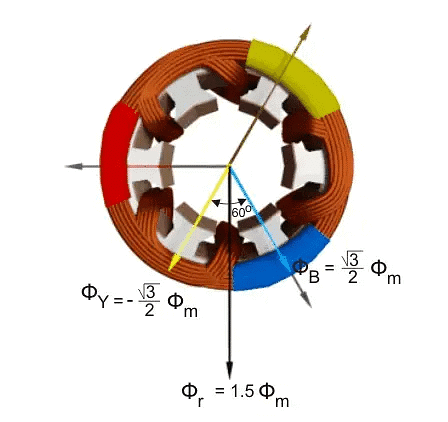
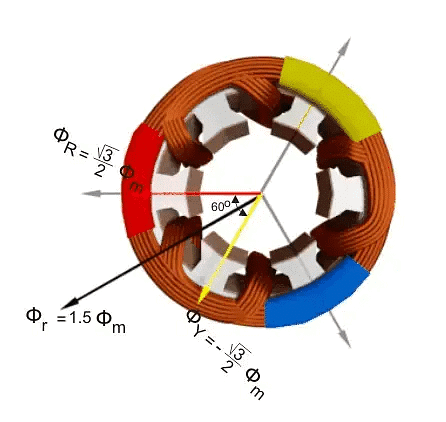
Now, let's look at point 1 on the graph, where the angle is 30 degrees. At this point:
- Red (φR):
- Yellow (φY):
- Blue (φB):
The total of these strengths (φr) is still 1.5 times the maximum (φm), but now it's rotated 30 degrees clockwise without changing its value.
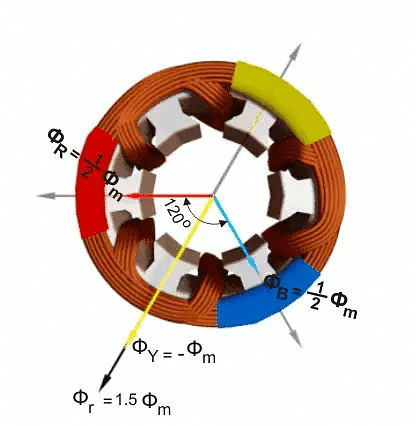
Now, looking at the graph of the magnetic strength waves, let's focus on point 2, where the angle is 60 degrees.
- The value of Red (φR) is
- The value of Yellow (φY) is
- The value of Blue (φB) is
At this moment, the total of these strengths (φr) is still 1.5 times the maximum (φm), and it's shown in the figure below. Here, we can see that the resulting magnetic direction has moved 30 degrees more clockwise without changing its strength.
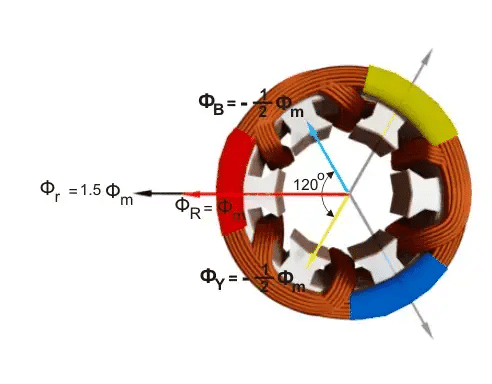
Next, let's look at point 3 on the graph, where the angle is 90 degrees.
- The value of Red (φR) is
- The value of Yellow (φY) is
- The value of Blue (φB) is
Again, the total of these strengths (φr) is 1.5 times the maximum (φm), and it's shown in the figure below. Here, we see that the resulting magnetic direction has moved another 30 degrees clockwise without changing its strength.
In this manner, we can demonstrate that when a balanced power is supplied to the three-phase stator wiring, a rotating or revolving magnetic field is created in space.
|
19 videos|95 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Rotating Magnetic Field - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a rotating magnetic field? |  |
| 2. How is a rotating magnetic field created? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of a rotating magnetic field in electric motors? |  |
| 4. Can a rotating magnetic field be used for wireless power transfer? |  |
| 5. Are there any practical applications of a rotating magnetic field? |  |