Human Capital Formation in India Class 12 Economics
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Capital |

|
| Sources of Human Capital Formation |

|
| Physical Capital |

|
| Human Capital Formation & Human Development |

|
| Education |

|
| Future Prospects |

|
| Conclusion |

|
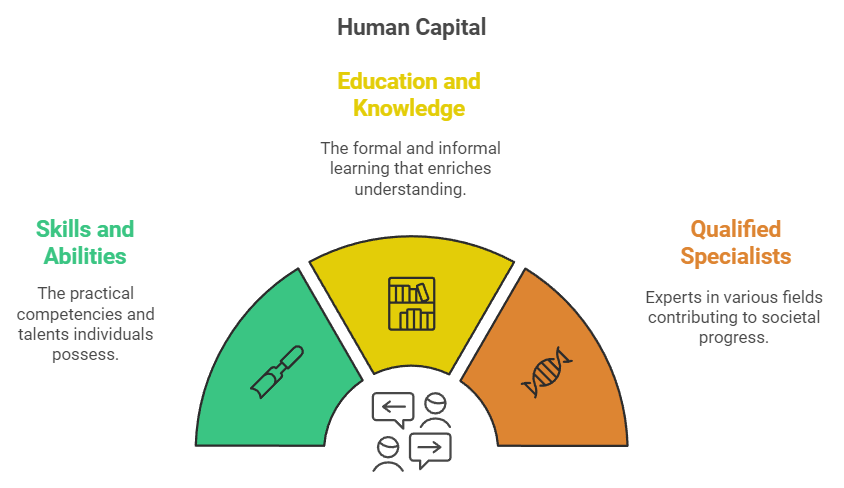
Human Capital
- Human capital refers to the total set of skills, abilities, knowledge, education, and expertise that people in a country possess at any given time.
- Investing in human capital is seen as an effective way to promote growth.
- To develop qualified teachers and other experts, societies need a solid foundation of human capital.
- This includes having knowledgeable and trained individuals who can serve as educators and professionals.
- Thus, it is essential to invest in human capital to create more skilled individuals from existing resources.
- Key areas for investment include education, on-the-job training, health, migration, and information.
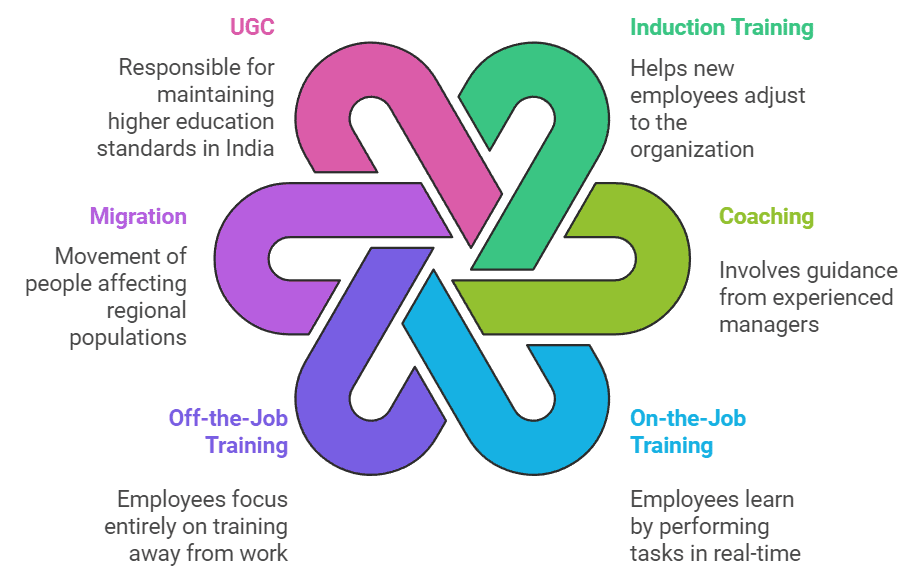
Sources of Human Capital Formation
- Expenditure on Education
- Expenditure on Health
- On-the-Job Training
- Study Programmes for Adults
- Migration
- Expenditure on Information
Induction Training
- This type of training is provided to newly recruited employees to help them become familiar with the workings of the organisation. It helps new employees adjust and become familiar with their tasks and responsibilities in the organisation.
Coaching
- In this method, new employees are assigned an experienced manager who acts as a coach. The coach guides the employees to observe their approach towards work, solve problems, and find solutions to complex problems.
On-the-Job-Training
- In this method, employees learn a job by performing it on a real-time basis while learning and developing expertise at the same time.
Migration
- Migration refers to the movement of people from one area to another or from one country to another, usually across political and administrative borders. It affects the growth of the population of a region by increasing or decreasing the number of people living there. Migration can be permanent, temporary, or daily.
Off-the-Job-Training
- This type of training requires employees to leave their workplace and concentrate their entire time on the training objectives.
UGC
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) of India is a statutory organisation established in 1953 under the Ministry of Human Resource Development. Its head office is located in New Delhi. The UGC is responsible for coordinating, determining, and maintaining standards of higher education. It also provides recognition to universities in India and disburses funds to recognised universities and colleges.
Physical Capital
- Physical capital is one of the crucial elements in the production process, alongside labour and natural resources.
- It encompasses man-made items such as machinery, buildings, equipment, and more.
- These goods are used in the production process to transform raw materials into finished products.
- A substantial investment in physical capital is often required for new projects.
Difference between Physical Capital and Human Capital:-
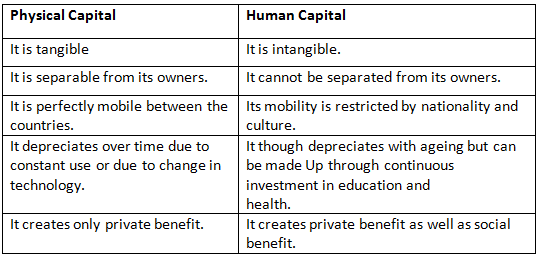
Human capital formation is the process of adding to the stock of human capital over a period of time.
Human Capital Formation & Human Development
- Formation of Human Capital - This term refers to the process of building up human capital over time. It includes gaining and improving the skills, knowledge, and experience of individuals, which is essential for economic growth. Key sources of human capital formation are investments in education, on-the-job training, health, migration, and information.
- Development of Human Capital - The idea of "human development" suggests that education and health are vital for people's well-being. When individuals can read and write and live a long, healthy life, they can make choices that are important to them. Human capital provides both private and social advantages, while physical capital only offers private benefits.

Role of human capital formation in economic growth.
- Increases production levels
- Alters the emotional and physical conditions for growth.
- Improves the overall quality of life.
- Raises life expectancy rates.
- Enhances innovative skills.
- Promotes social justice and equality.
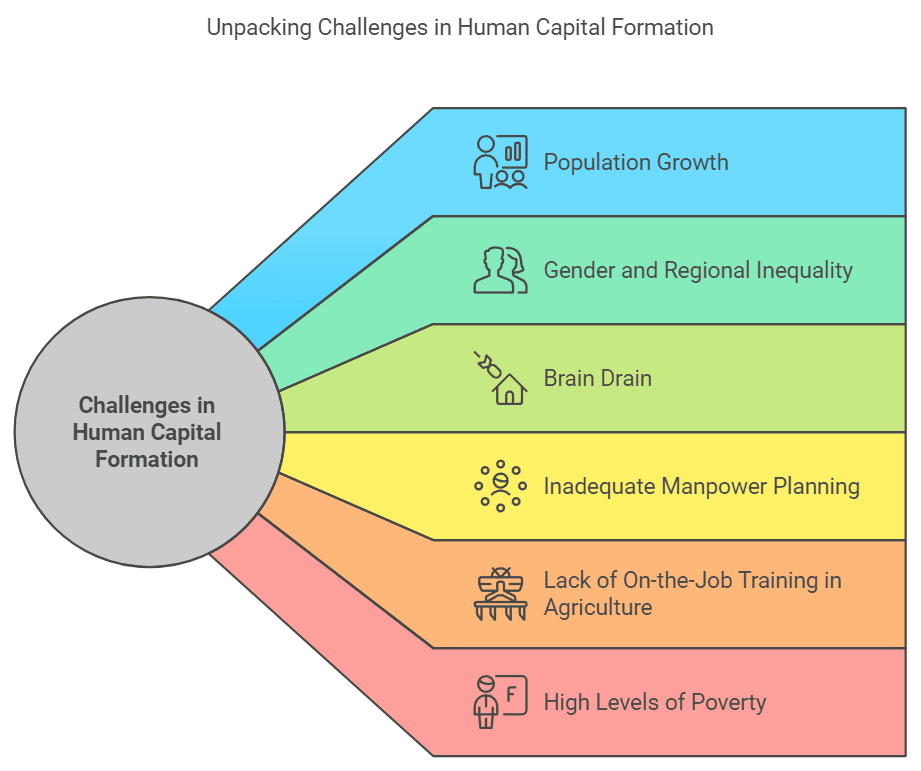
Problems facing human capital formation.
- Population growth
- Gender and regional inequality
- Brain drain (emigration of highly skilled individuals)
- Inadequate manpower planning
- Lack of on-the-job training in agriculture
- High levels of poverty
- Low academic standards
Education
This refers to the process of imparting knowledge, skills and training, particularly in educational institutions such as schools and colleges, to enhance one's knowledge and abilities.
Importance and objectives of education
- Education plays a vital role in producing responsible citizens.
- Education facilitates efficient utilization of resources within a country.
- Education helps in the development of science and technology.
- Education broadens people's mental horizons and perspectives.
- Education promotes cultural standards and awareness among citizens.
- Education plays a crucial role in the development of human personality.
Problems relating to the development of education in India
- A high number of people who cannot read or write.
- The current spending on education is just over 4 per cent of GDP, which is not enough compared to the target of around 6 per cent.
- The lack of vocational training in education has been a major challenge.
- Issues of gender equality that impact literacy rates.
- Limited access to education in rural areas.
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), which operates under the Ministry of Human Resource Development, aims to ensure effective planning and growth of the technical education system in India. AICTE acts as a legal authority responsible for setting, creating, and upholding norms and standards. Its key aims include:
- Providing quality assurance through accreditation.
- Monitoring, evaluating, and funding priority areas.
- Ensuring consistency in certification and awards.
- Managing and developing India's technical education system.
The government is dedicated to achieving complete literacy and has been increasing its spending in the education sector over the years to achieve this goal.
Future Prospects
- Universal Education –Despite improvements in literacy rates among adults and youth, the total number of illiterate individuals in India is still equivalent to the country's population at the time of independence. In 1950, when the Constitution of India was established, the Directive Principles stated that the government should ensure free and compulsory education for all children up to the age of 14 within ten years of the Constitution's inception. Emphasising education for everyone is crucial for achieving 100% adult literacy in India.
- Gender Equality –Although there has been progress in reducing the gender gap in literacy, enhancing education for women is vital for boosting their economic independence and social standing. Educating women positively influences fertility rates and healthcare for both women and children.
- Higher Education –The structure of education in India is steep, leading to fewer individuals attaining higher education. Unemployment rates among educated youth are alarmingly high. According to NSSO data from 2011-12, the unemployment rate for young men with a graduation degree or higher in rural areas was 19 percent. It is essential for the government to increase funding for higher education and enhance the quality of higher education institutions to equip students with necessary employable skills.
In order to enhance its economic and social outcomes for the people, India must prioritize education for all and reach its full potential.
Conclusion
- The economic and social advantages of human capital formation and human development are widely recognised.
- The union and state governments in India have been earmarking substantial financial outlays for the development of the education and health sectors.
- The percentage of expenditure on education from the total government expenditure highlights the importance of education in the government's plans.
- It is crucial for the government to provide education and health services free of charge to eligible citizens, especially those from socially oppressed classes.
- India possesses a rich stock of scientific and technical manpower globally. The current priority is to improve its quality and create conditions for its utilisation within India.
|
69 videos|377 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Human Capital Formation in India Class 12 Economics
| 1. What is human capital and why is it important for economic development? |  |
| 2. What are the main sources of human capital formation? |  |
| 3. How does education contribute to human capital formation in India? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between human capital formation and human development? |  |
| 5. What are the future prospects for human capital formation in India? |  |
















