Employment: Growth, Informalisation & other Issues Class 12 Economics
Introduction
People engage in various types of work, including farming, factory jobs, and home-based work like handicrafts and IT programming. Work provides income, self-worth, and societal contribution. Mahatma Gandhi emphasised education and training in various crafts. Studying working people offers insights into employment quality and helps address social issues like exploitation and child labour.
Worker & Employment
- A person who engages in a productive activity to earn a living is known as a worker.
- Employment means doing work to earn a living. A worker is anyone involved in activities that contribute to the country's gross national product, whether they are paid by an employer or are self-employed. Even if someone is temporarily not working due to illness or other reasons, they are still considered a worker.
Employment in India at a Glance:
- Workforce Size (2024): Approximately 607.7 million workers
- Workforce Distribution: Mostly in rural areas
- Gender Distribution: About 77% men and the rest women. Women make up one-fourth of the rural workforce and one-fifth of the urban workforce.
- Employment Patterns: Some workers are employed year-round. Others work only for a few months
- Wage Issues: Many workers do not receive fair wages.
- Women often do unpaid work like cooking, fetching water, and farm labour, which is not counted as employment. Economists believe such work should be recognised as work.
Participation of People in Employment
- The worker-population ratio measures how much of the population is working and contributing to the country's production of goods and services. A higher ratio means more people are engaged in economic activities, while a lower ratio means fewer people are working.
- The population is the total number of people living in a place at a certain time. The worker-population ratio is calculated by dividing the number of workers by the total population and multiplying by 100.
- In India, about 41 out of every 100 people are workers. The ratio is similar for both rural (42) and urban (38) areas. The difference exists mainly because rural areas have fewer education and job opportunities, so people start working early. In urban areas, people have better education and job options and often wait for suitable jobs that match their skills.
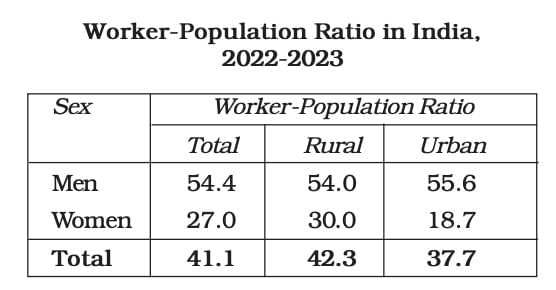
- There are more men in the workforce than women, particularly in urban regions.
- In urban settings, for every 100 females, only about 19 are involved in economic activities. In rural areas, approximately 30 out of 100 rural women participate in the job market.
- This disparity is partly due to the fact that when men earn well, families often discourage women from seeking employment.
- Women typically engage in tasks such as cooking, collecting water and fuelwood, and assisting in farming. They often do not receive wages, either in cash or grains, and sometimes are unpaid.
- This limited view of work results in the non-recognition of women's contributions, leading to an undercount of the number of women workers in the country.
- Disguised unemployment is a prevalent issue in rural India.
Self-Employed and Hired Workers
The worker-population ratio doesn't reveal much about workers' status or working conditions. However, understanding a worker's status in an enterprise helps determine the quality of employment and their authority at work.
Workers fall into three categories:
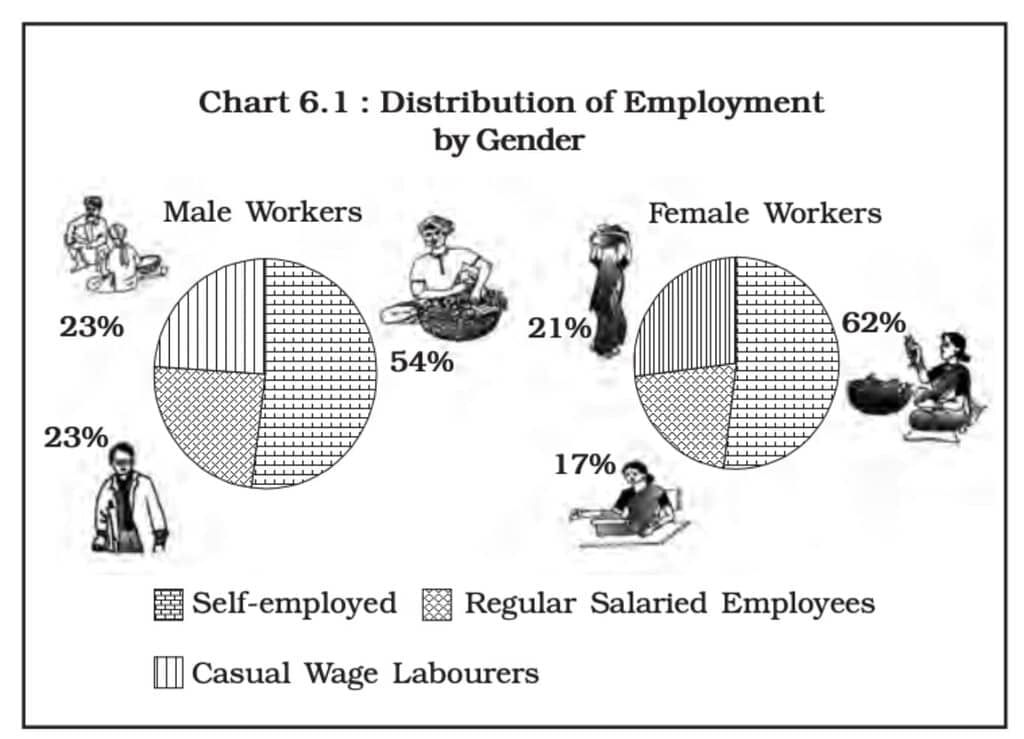
- Self-employed: These are individuals who own and run a business to earn a living. Approximately 57 per cent of the workforce in India is self-employed.
- Casual wage labourers: This group includes construction workers, making up about 22 per cent of India's workforce. Casual wage work is also a significant source of income for women.
- Regular salaried employees: This group sees a higher proportion of men employed, with men representing 24 per cent and women 17 per cent.
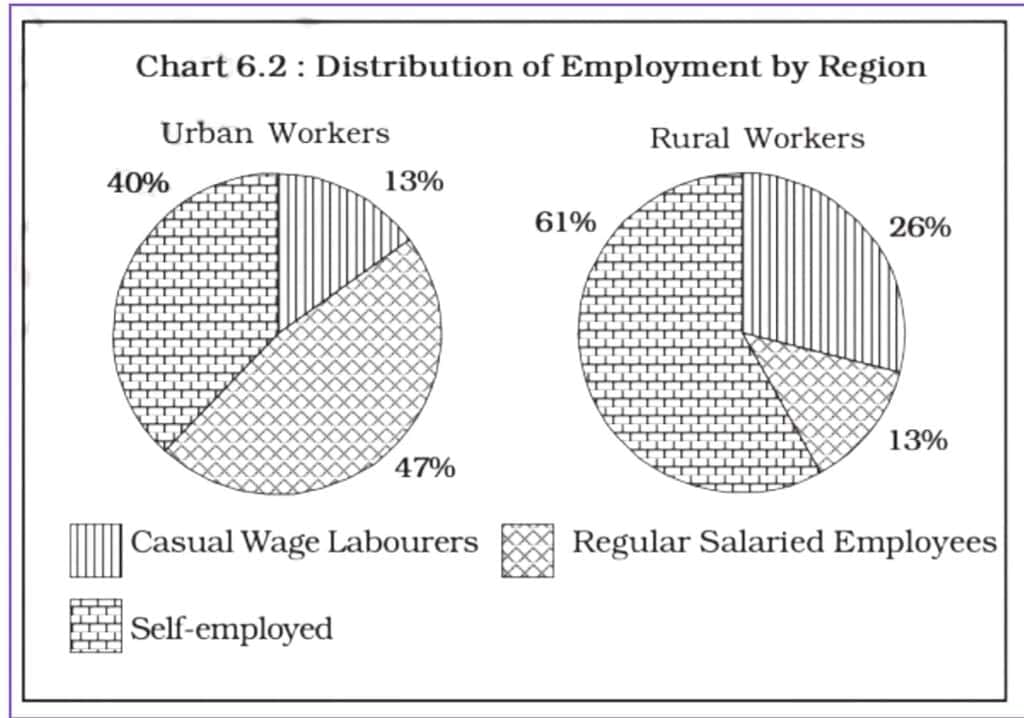
- Most of India's workforce is self-employed, especially in rural areas where people work independently on their farms.
- Casual wage labour is also common.
- In urban areas, more people are either self-employed or work as regular salaried employees because businesses need workers on a regular basis.
- Men and women both work in all categories, but the proportion of women in regular salaried jobs is slightly lower than men.
- Should unpaid work by women also be counted as employment?
Employment in Firms, Factories and Offices
As a country grows, workers tend to shift from farming to industries and services. This often involves moving from rural areas to cities. Eventually, as time goes on, the industrial sector starts to see a decrease in employment share as the service sector rapidly expands.
We usually categorise all economic activities into eight different industrial divisions:
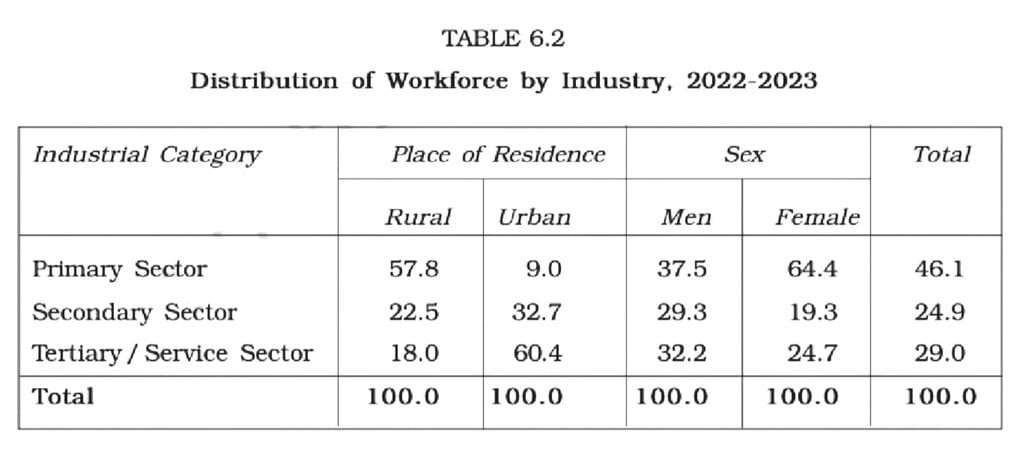
- Primary Sector: This includes agriculture, mining, and related activities. Approximately 60 per cent of the workforce in rural India relies on agriculture, forestry, and fishing.
- Secondary Sector: This covers manufacturing, electricity, construction, and other industries. About 20 per cent of rural workers are engaged in manufacturing, construction, and similar activities. The secondary sector employs roughly one-third of the urban workforce.
- Service Sector: This involves trade, transport, storage, and various services. The service sector employs around 20 per cent of rural workers, while about 60 per cent of urban workers are found in this sector.
In 1972-73, around 74 per cent of the workforce was in the primary sector, which decreased to about 46 per cent by 2022-23. This shows a significant shift from farm work to non-farm work. Many countries, including India, have developmental strategies aimed at reducing reliance on agriculture.
More women work in the primary sector than men, with around 64 per cent of women employed in this area, compared to 38 per cent of men. Men typically have more opportunities in both the secondary and service sectors.
Growth and Changing Structure of Employment
- India's economic growth and employment have been important for planning for nearly seventy years.
- From 1950 to 2010, India's GDP increased consistently, but employment rose by no more than 2 per cent.
- In the late 1990s, employment growth slowed further, creating a gap between GDP growth and job creation.
- This situation, known as jobless growth, means that the Indian economy has been able to produce more goods and services without creating jobs.
- India has aimed to decrease the number of people relying on agriculture. In 1972-73, around 74% of the workforce was in the primary sector (mostly agriculture), which had fallen to about 46% by 2022-23.
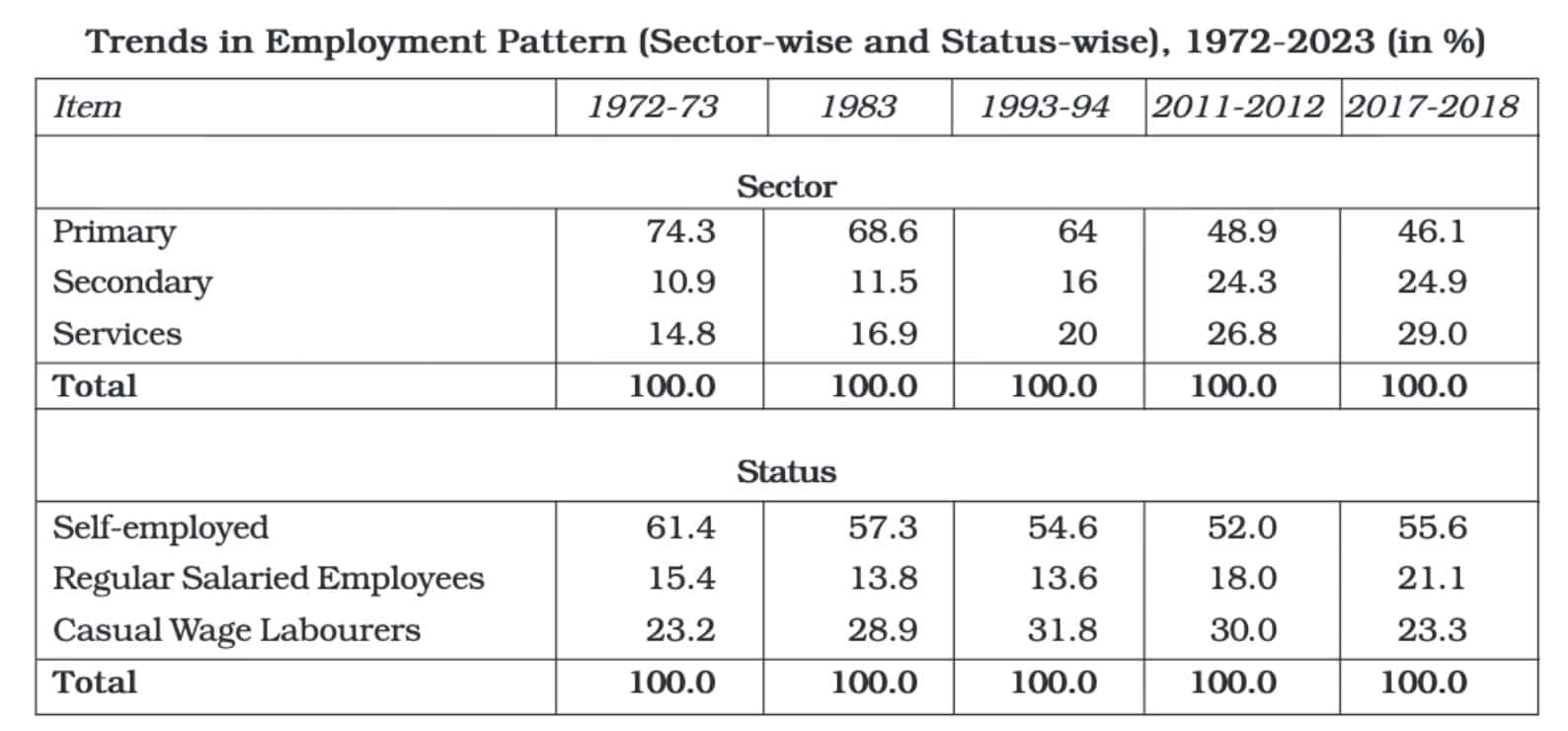
- Between 1972 and 2018, many people moved from self-employment and regular salaried jobs to casual wage work.
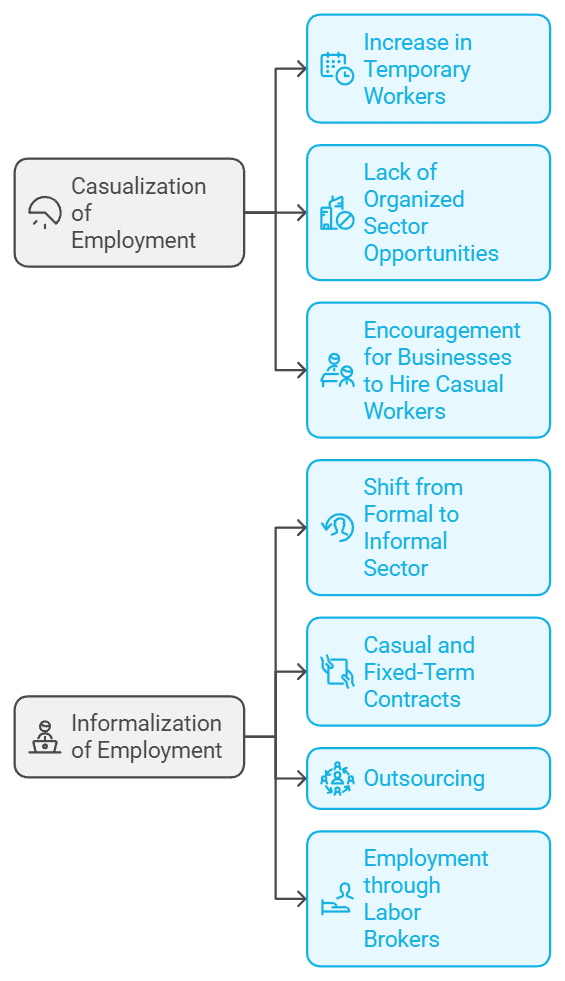
- This trend, known as the casualisation of the workforce, makes workers vulnerable as they have less job security and fewer benefits. A moderate increase in the share of regular salaried employees was noted from 2017 to 2023.
- Despite these changes, self-employment continues to be the main source of jobs in India. The secondary and service sectors are emerging as promising areas for the Indian workforce.
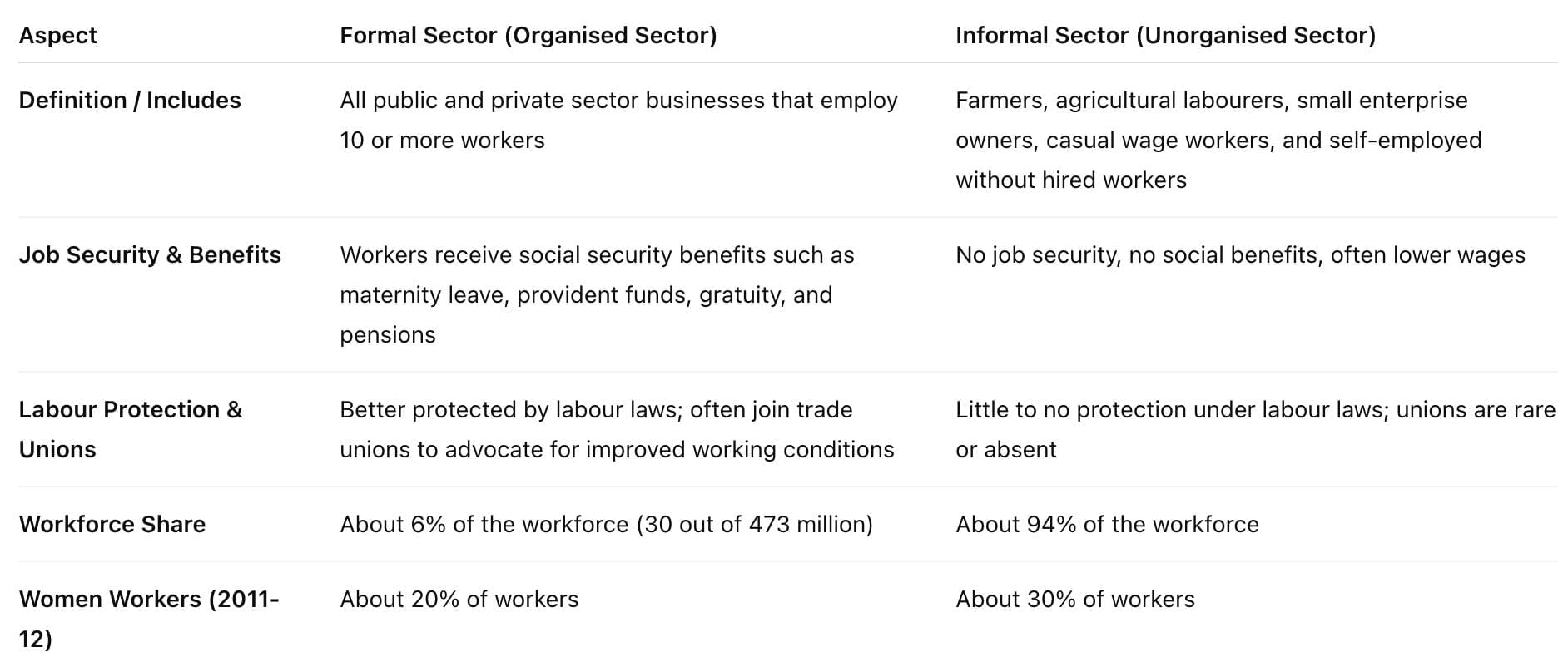
Informalisation of the Indian Workforce
India's workforce is divided into two main categories: the Formal Sector (Organised Sector) and the Informal Sector (Unorganised Sector).
Informal Sector: Issues and Government Efforts
Since the late 1970s, developing countries like India have started focusing on the informal sector because employment in the formal sector is not growing adequately. The informal sector consists of workers and enterprises that lack job security and government protection.
Problems Faced by Informal Sector Workers
- No regular income: Earnings are inconsistent and often very low.
- Lack of protection or regulation: Workers can be fired without compensation or notice.
- Outdated technology: Enterprises use old methods, affecting productivity and income.
- No accounts maintained: Informal enterprises rarely keep proper financial records.
- Poor living conditions: Many workers live in slums or as squatters, with limited access to basic facilities.
Government Efforts and Reforms
With guidance from the International Labour Organisation (ILO), the Indian government has taken steps to:
- Modernise informal sector enterprises to improve productivity and working conditions.
- Provide social security measures like insurance, pensions, and health benefits to informal workers.
However, there's still a long way to go to bring more informal workers into the formal economy and improve their quality of life.
Jobless Growth
- Scholars refer to the shift from self-employment and regular jobs to casual wage work as the casualisation of the workforce. This happens because the informal sector lacks protections, leading many to work as casual labourers. The flexible conditions and weak enforcement of labour laws also make it easier for businesses to hire more casual workers.
- Informalisation can involve moving from permanent jobs to casual and fixed-term contracts, outsourcing, and working through labour brokers. Many people who once had formal jobs may return to work as atypical employees. Developmental planning expected that as the economy grows, more workers would shift to formal jobs, reducing the number in the informal sector. In 2011-12, India had about 473 million workers, with only around 30 million in the formal sector.
Unemployment
The National Statistical Office describes unemployment as a situation where individuals who are not working due to a lack of job opportunities are actively looking for work. This includes seeking employment through various channels like job exchanges, intermediaries, friends, and relatives, or directly applying to potential employers, while also being available to work under current conditions of pay and work. The formula to calculate the unemployment rate is:

Types of Unemployment
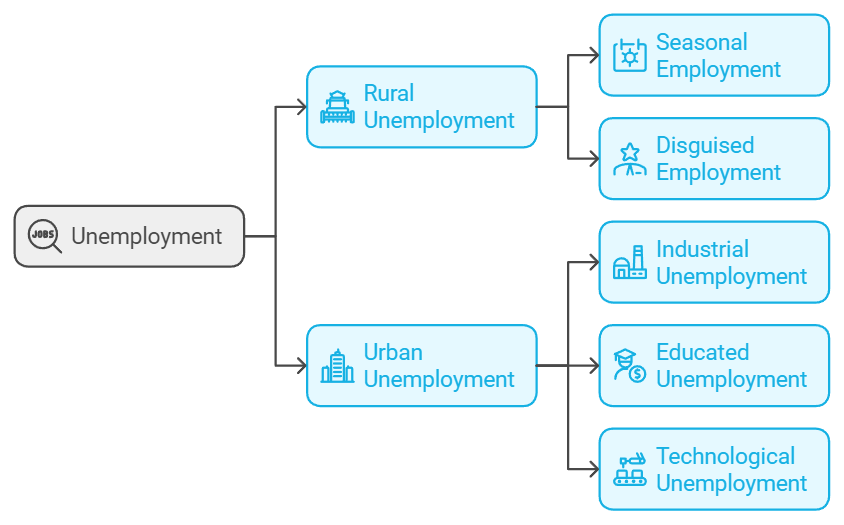
Rural Employment: Rural employment pertains to job opportunities in rural areas. There are two main types of rural unemployment:
- Seasonal unemployment happens when many individuals cannot find work during certain seasons, such as in agriculture or industries like ice cream production and wool manufacturing.
- Disguised unemployment is prevalent in rural India, occurring when the additional workforce does not contribute effectively, resulting in zero or negative productivity.
Urban Unemployment: Urban unemployment relates to job availability in urban settings and can be divided into three categories:
- Industrial unemployment involves workers who cannot secure jobs in the industrial sector due to various challenges.
- Educated unemployment refers to educated individuals who are unemployed or underemployed because their skills do not match available positions.
- Technological unemployment occurs when advancements in machinery and technology replace human workers.
Causes of Unemployment
- The slow economic growth in India has led to a situation called "jobless growth," where the GDP increases, but there are not enough new jobs, causing an excess supply of workers.
- Although the rapidly growing population in India contributes to increased unemployment, many people cannot stay jobless for long due to financial needs, often taking on undesirable or dangerous jobs.
- Poor employment planning is a significant cause of unemployment in India, as the country's five-year plans have not focused on job creation, resulting in a gap between economic growth and available jobs.
- The country's over-reliance on foreign technology, because local technology is expensive, has impacted job creation.
- Disguised unemployment is common in rural areas, where many people work in jobs that do not fully utilise their skills.
- Seasonal unemployment is another important factor in India, especially in rural areas, as agricultural work is often restricted to specific seasons.
Government and Employment Generation
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005, ensures 100 days of guaranteed wage work for all rural households that are willing to engage in unskilled manual labour. This initiative is part of the government's efforts to create job opportunities for those seeking employment in rural areas.
- Since gaining independence, both national and local governments have been dedicated to creating jobs and offering employment opportunities, helping low-income families maintain a decent standard of living through various initiatives.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Employment: Growth, Informalisation & other Issues Class 12 Economics
| 1. What are the main factors contributing to unemployment in the current economy? |  |
| 2. How does informal employment impact economic growth? |  |
| 3. What role does the government play in employment generation? |  |
| 4. How can firms improve employment rates in their industries? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of economic activity on employment trends? |  |