Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Reproduction in Plants
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is vegetative propagation. Explain three artificial methods of Vegetative Propagation.
Ans: Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from the vegetative parts of a plant, such as roots, stems, leaves, and buds. Example: Banana plants are propagated from stem cuttings.
- Cutting: Here the cuttings of the "parent" plant are removed and placed in a suitable environment so that they can grow into a whole new plant. For example rose cutting.
- Layering: The stem is bent down and the target region buried in the soil. The buried part of stem develops roots and is detached from the plant and develops into new plant.
- Grafting: In grafting a shoot or bud of a selected, desired plant (scion) is grafted onto the stock of another type of plant.
Q2: How does sexual reproduction take place in flowering plants?
Ans:
The sexual reproduction in flowering plants involves pollination and fertilization.
Pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination. Pollen grains are transferred mainly by wind, water and insects. They are called as pollinating agents.
Fertilization: The fusion of a male gamete with egg is known as fertilization. The fertilized egg is known as zygote which develops into embryo.
Q3: Explain different parts of a flower?
Ans: Following are the parts of flowers:
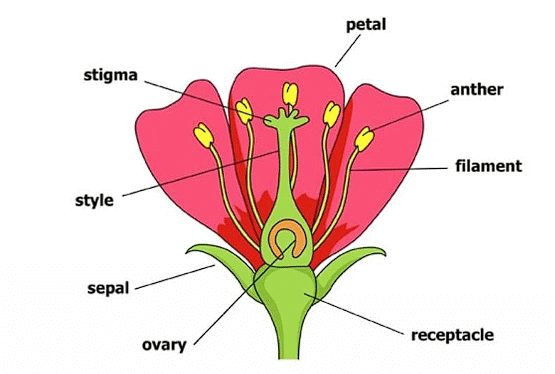
- Sepal: Green leafy part of flower that protect flower in bud condition.
- Petal: Coloured leafy part of flower that attract insect for pollination
- Stamen: The male parts of flower that contain pollen grain
- Pistil: The female parts of flower that contain ovary at bottom
Q4: State the advantages of vegetative reproduction?
Ans: Following are the advantages of vegetative reproduction:
- Vegetative production allows plants to produce new plants quickly without any reproductive organs.
- The plants produced by this method are exact copies of the parent plant.
- New varieties of plants having required characteristics can be developed by this method.
Q5: Explain different types of pollination found in flowering plants.
Ans : Pollination is of two types. They are:
- Self-pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant is known as self-pollination or autogamy.
- Cross pollination: The transfer of pollen grains of a flower to the stigma of another flower of a different plant of the same species is called cross pollination or allogamy
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain different modes of Asexual reproduction?
Ans: Unisexual reproduction involves modes of reproduction that require only one parent. The correct modes are:
(a) Fission: The mode of reproduction in which a unicellular organism splits into two equal halves and produces new ones is called binary fission. For example, amoeba and bacteria.
(b) Fragmentation: The mode of reproduction in which the body of a plant breaks up into smaller fragments, and each fragment grows into a new individual. Examples include Spirogyra and some algae.
(c) Budding: The mode of reproduction in which small buds develop, get separated, and mature into new organisms is called budding. Examples include yeast, Hydra, and Bryophylum.
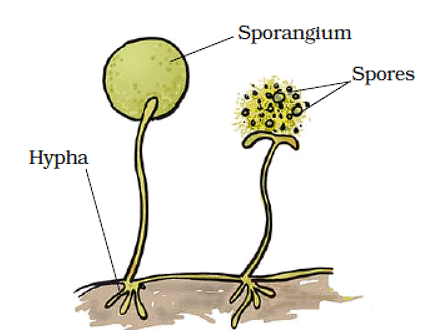
(d) Spore formation: The mode of reproduction that takes place by means of spores is called spore formation. Examples include some algae and fungi.
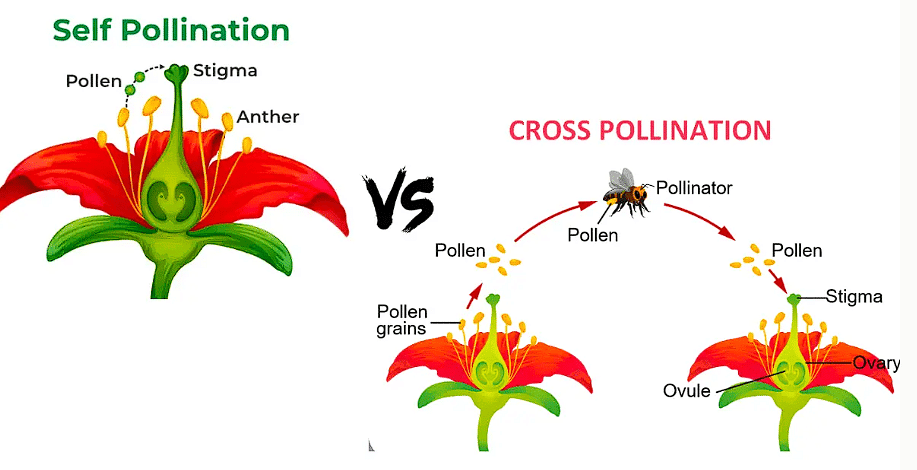
Q2: Show self-pollination and cross pollination via a labelled diagram.
Ans :
Self-Pollination
In self-pollination, pollen grains from the anther (male part) of a flower are transferred to the stigma (female part) of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
Cross-Pollination
In cross-pollination, pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species.
Q3: Explain reproduction through spore formation in fungus.
Ans: Fungi on a piece of bread grow from spores that are found in the air. These spores are very light and can travel long distances by floating. Spores are a type of asexual reproductive body. Each spore has a tough protective coat that helps it survive in harsh conditions, like high heat and low moisture. Because of this coat, spores can last a long time. When the conditions are right, a spore will start to grow and become a new fungus.
Q4: How does a fern reproduce?
Ans : In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds. The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part. A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule. In sexual reproduction a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote. The process of fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation. The zygote develops into an embryo. After fertilisation, the ovary grows into a fruit and other parts of the flower fall off. The fruit is the ripened ovary. The seeds develop from the ovules. The seed contains an embryo enclosed in a protective seed coat .Seeds and fruits of plants are carried away by wind, water and animals and reproduced again on the grounds.
Q5: Explain reproduction in plants by spore formation.
Ans: Some plants, like ferns and mosses, reproduce using spores. Spores are tiny cells made in special parts called sporangia, often under leaves. They are light and spread by wind. When it’s wet and warm enough, spores grow into new plants. For example, in ferns, spores turn into a small plant that later makes a new fern. This doesn’t use seeds or flowers. Spores have a tough coat to survive tough conditions. This helps plants spread to new places easily. Unlike seeds, spores don’t need a parent plant nearby to start growing. This method is fast and simple for these plants.
|
112 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Reproduction in Plants
| 1. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 2. What is pollination in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of seeds produced by plants? |  |
| 4. How do flowers play a role in plant reproduction? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of fruit in plant reproduction? |  |






















