Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Acids, Bases and Salts
Q1: What is an acid?
Ans: An acid is a hydrogen-containing chemical compound which, when dissolved in water, gives hydrogen ion (H+) or hydrated hydrogen ion (H2O.H+) or hydronium ion (H3O+). They are sour in taste.
Example: HCL ⇌ H+ + Cl-
Q2: What is a base?
Ans: Bases are substances that slippery to touch when in aqueous form. They taste bitter and change the color of red litmus paper to blue. Bases also dissociate in the water like acids, but instead of producing H+ they produce OH- i.e. hydroxyl ion.
Example: NaOH ⇌ Na+ + OH-
Q3: What are alkalis?
Ans: Bases may be soluble or insoluble in water. The soluble bases are called alkalis. Thus, all alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis. Bases have a bitter taste and soapy touch.
Examples: NaOH and Cu (OH)2 both are bases, but, since NaOH is soluble in water, it is an alkali. On the other hand, since Cu (OH)2 is insoluble in water, it is not an alkali.
Q4: How are natural indicators prepared? Give examples of a flower, root, stem and leaf that can be used as an indicator.
Ans: Natural Indicator is a type of indicator that can be found naturally and can determine whether the substance is an acidic substance or a basic substance. Some examples of natural indicators are red cabbage, turmeric, grape juice, turnip skin, curry powder, cherries, beetroots, onion, tomato, etc
Q5: Define pH.
Ans: pH is the concept of measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+ (aq)] in a particular solution. The p in pH stands for 'potenz' (German, meaning power).
On the pH scale we can measure pH from "0" (highly acidic) to 14 (highly alkaline).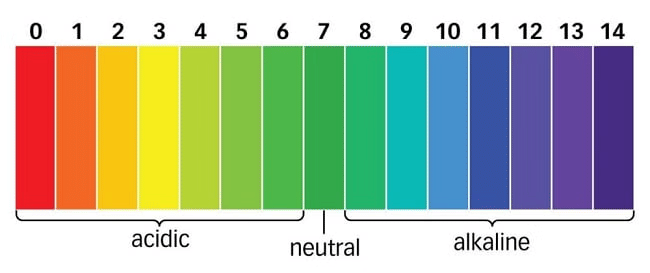
Q6: Why common indicators cannot determine pH value of a solution?
Ans: Common indicators such as litmus, methyl orange, and phenolphthalein can indicate whether a solution is acidic or alkaline, but they cannot give precise pH values. These indicators only provide a color change at specific pH ranges, which limits their ability to differentiate between close pH values.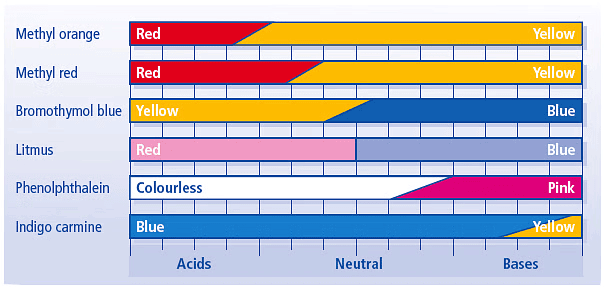 For example, litmus can show whether a solution is acidic (pH < 7) or basic (pH > 7), but it cannot accurately indicate slight differences between pH 5, 6, and 7. Similarly, methyl orange has a narrow range and does not provide accurate pH readings between 3 and 8. This lack of precision is why common indicators cannot determine the exact pH value of a solution.
For example, litmus can show whether a solution is acidic (pH < 7) or basic (pH > 7), but it cannot accurately indicate slight differences between pH 5, 6, and 7. Similarly, methyl orange has a narrow range and does not provide accurate pH readings between 3 and 8. This lack of precision is why common indicators cannot determine the exact pH value of a solution.
Q7: Why the salts solutions of strong acid and strong alkali are neutral?
Ans: Let us take the example of potassium sulphate, which is a salt of strong acid [sulphuric acid] and strong base [potassium hydroxide solution]. From the above equation, it is clear that water is always partially ionised and hence the solution of potassium sulphate is neutral in nature.
From the above equation, it is clear that water is always partially ionised and hence the solution of potassium sulphate is neutral in nature.
Q8: A compound P forms the enamel of teeth. It is the hardest substance of the body. It doesn’t dissolve in water but gets corroded when the pH is lowered below 5.5.
(a) Identify the compound P.
(b) How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolate and sweets? What should we do to prevent tooth decay?
Ans: (a) The compound P is calcium phosphate
(b) Eating chocolates and sweets produce large amount of acid in the mouth which is not completely neutralised by the saliva produced in the mouth. Excess acid attacks the enamel and tooth decay starts as pH of the mouth falls below 5.5. The best way to prevent tooth decay is to clean the teeth by using toothpastes after eating food. Toothpastes which are generally basic neutralise the excess acid in the mouth.
Q9: How is washing soda prepared from sodium carbonate? Give its chemical equation. State the type of this salt. Name the type of hardness of water which can be removed by it?
Ans. Washing soda is prepared by recrystallisation of sodium carbonate: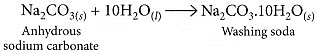 It is used to remove the permanent hardness of water. Hard water is treated with a calculated amount of washing soda when chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium present in hard water get precipitated as insoluble calcium and magnesium carbonates which can be easily filtered off. The water thus becomes soft.
It is used to remove the permanent hardness of water. Hard water is treated with a calculated amount of washing soda when chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium present in hard water get precipitated as insoluble calcium and magnesium carbonates which can be easily filtered off. The water thus becomes soft.
CaCl2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 (↓) + 2NaCl
MgSO4 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 (↓) + Na2SO4
Q10: (i) Dry pellets of a base ‘X’ when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also formed by chlor-alkali process. Write chemical name and formula of X. Describe chlor-alkali process with balanced chemical equation. Name the type of reaction occurs when X is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid. Write the chemical equation.
(ii) While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Ans:(i) X is sodium hydroxide, NaOH.
When sodium chloride solution (brine solution) is electrolyzed, sodium hydroxide solution is formed. H2 and Cl2 gases are liberated. This is chlor-alkali process.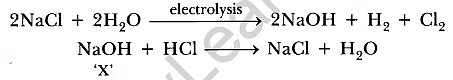 The above reaction is neutralization reaction.
The above reaction is neutralization reaction.
(ii) It is because process is highly exothermic. If water is added to acid, bottle of acid will break.
Q11: Describe an activity with diagram to illustrate that the reaction of metal carbonates and metal bicarbonates with acids produces carbon dioxide. Write the relevant equations of all the reactions that take place. Name any two forms in which calcium carbonate is found in nature.
Ans: Aim: To show acid reacts with metal carbonate to liberate carbon dioxide,
Material Required: CaCO3(marble chips), Woulfe-bottle, thistle funnel, dil. HCl, gas jar, matchbox, delivery tube bent at two right angles, lime water.
Procedure:
1. Take marble chips in a Woulfe-bottle.
2. Set the apparatus as shown in diagram.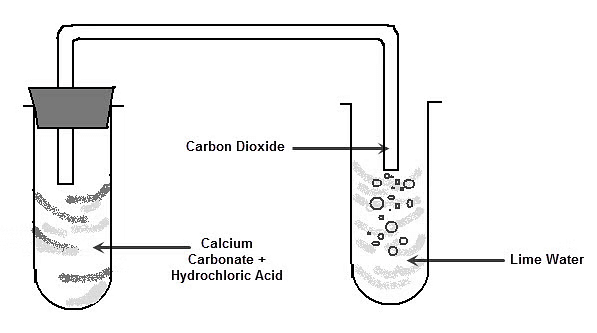
3. Add dil. HCl with the help of thistle funnel.
4. Collect the gas in gas jar by upward displacement of air.
5. Bring a burning matchstick near the gas jar and record your observations.
6. Pass the gas evolved through lime water and note down your observations.
Observations:
- The burning matchstick will get extinguished because carbon dioxide is neither combustible nor supporter of combustion.
- Lime water will turn milky due to formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
- It can be used as test for CO2 .
- The chemical reactions taking place are as follows:
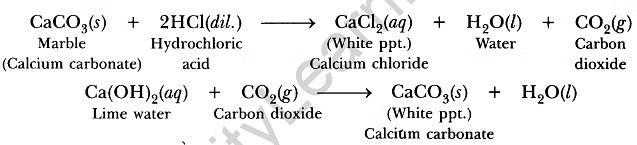
Conclusion: Metal carbonates react with dilute acids to liberate carbon dioxide. Limestone, chalk, marble are different forms of calcium carbonate. All metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids to form corresponding salts, water and carbon dioxide.
Q12: What are the practical applications of neutralisation reactions?
Ans: (i) Being alkaline in nature, cold milk is used to neutralise the acidity produced by HCl present in the gastric juice in the stomach.
(ii) Astronauts in space ships use this reaction to neutralise the dangerous levels of CO2.
(iii) Farmers add slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) to reduce acidity of soil.
(iv) Sting of ants and bees contains formic acid. This can be neutralised by rubbing soap, which contains free sodium hydroxide.
(v) Persons suffering from acidity are given antacid tablets, containing magnesium hydroxide which neutralises excess HCl produced, in stomach. Alternately, they are advised to sip cold milk, which neutralises HCl.
Q13: Define water of crystallisation. Give the chemical formula for two compounds as examples. How can it be proved that the water of crystallisation makes a difference in the state and colour of the compounds?
Ans: Water of crystallisation: It is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt, e.g., Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) has two molecules of water of crystallisation.
In hydrated copper sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O), there are five molecules of water of crystallisation.
Activity:
– Take few crystals of copper sulphate in a dry boiling tube. These are blue in colour.
– Heat the boiling tube by holding it with a test tube holder on the flame of the burner.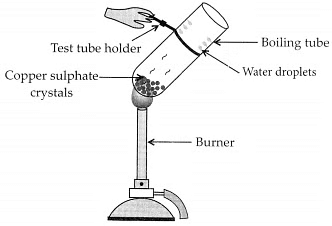 Observations : You will observe that the colour of copper sulphate crystals after heating becomes white. You may also notice water droplets on the mouth side of the boiling tube which are obtained from water of crystallisation.After adding 2-3 drops of water on the white sample of copper sulphate (obtained after heating) you will observe that the blue colour of copper sulphate crystals is restored.
Observations : You will observe that the colour of copper sulphate crystals after heating becomes white. You may also notice water droplets on the mouth side of the boiling tube which are obtained from water of crystallisation.After adding 2-3 drops of water on the white sample of copper sulphate (obtained after heating) you will observe that the blue colour of copper sulphate crystals is restored.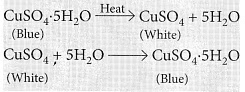
Q14: (a) A student dropped a few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write balanced chemical equations for both the changes observed.
(b) State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as a constituent of baking powder.
Ans: (a) When marble reacts with dilute HCl carbon dioxide gas is liberated.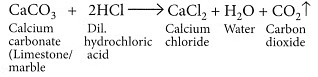 When CO2 gas is passed through lime water, insoluble calcium carbonate is formed which appears milky.
When CO2 gas is passed through lime water, insoluble calcium carbonate is formed which appears milky.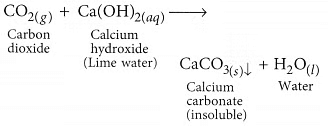 (b) (i) The excess acid formed in the stomach due to various reasons (one being overeating) is neutralised by sodium hydrogen carbonate. Hence, it is used as an ingredient of antacid.
(b) (i) The excess acid formed in the stomach due to various reasons (one being overeating) is neutralised by sodium hydrogen carbonate. Hence, it is used as an ingredient of antacid.
(ii) Baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) is a constituent of baking power. On heating it gives out CO2 which causes the cake to rise and make it soft and spongy.
Q15: What are the general characteristics of acids?
Ans:
- They have a sour taste.
- They turn blue litmus to red and methyl orange to red.
- They react with active metals to give hydrogen.
- They decompose carbonates to produced carbon dioxide and water.
- They turn blue litmus to red.
- They react with metals to give hydrogen.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 - They react with bases to form salt and water (Neutralization reaction).
HCL + NaOH → NaCL + H2O - They decompose carbonates to produced carbon dioxide and water.
Na2CO3 + 2HCL → 2NaCL + H2O + CO2.
Q16: Write the uses of chlorine.
Ans: The uses of Chlorine are given below as:
- Chlorine is used in the production of bleaching powder.
- Chlorine is used for making solvents for dry cleaning.
- Chlorine is used to sterilise drinking water supply, and the water in swimming pools.
- It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
Q17: Give reasons for the following:
(i) Only one half of water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as an antacid.
(iii) On strong heating, blue coloured copper sulphate crystals turn white.
Ans: (i) Only one half of water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris (CaSO4. 12 H2O) as one molecule of water is being shared by two molecules of calcium sulphate (CaSO4). So the effective water of crystallisation for one CaSO4 unit comes to half molecule of water.
(ii) Acidity can be neutralised by a base. Sodium hydrogen carbonate can be used as an antacid solution because it is a weak base and will react with excess acid produced in the stomach due to hyperacidity and will neutralise it.
(iii) Blue coloured copper sulphate crystals are hydrated copper sulphate, CuSO4.5H2O. On heating blue copper sulphate crystals looses its water of crystallisation and turns into anhydrous copper sulphate which is white in colour.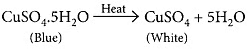
Q18: A white powder is added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking.
Ans: The white powder added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy is baking powder. Its main ingredients are sodium hydrogen carbonate and a mild edible acid like tartaric acid or citric acid. NaHCO3 decomposes to give out CO2 which causes the cake to rise and makes it soft and spongy. The function of tartaric acid or citric acid is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed during heating which can otherwise make the cake bitter. Reaction taking place when the powder is heated: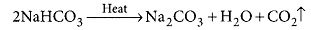
Q19: a) Write the chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate and anhydrous copper sulphate. Giving an activity illustrate how these are inter convertible.
(b) Write chemical names and formula of plaster of paris and gypsum.
Ans: (a) CuSO4.5H2O is hydrated copper sulphate. CuSO4 is anhydrous copper sulphate.
Aim: To show crystalline salts contain water of crystallization.
Material Required: CuSO4.5H2O (Blue vitriol), boiling tube, burner, cork,
delivery tube, test tube, clamp stand.
Procedure:
1. Take 2g of CuSO4.5H2O in a boiling tube fitted in a clamp stand.
2. Observe its colour. Fit it with cork and delivery tube bent at two right angles which dips into a test tube.
3. Heat crystals in boiling tube.
4. Observe vapours being condensed in test tube.
5. Cool the crystals and add few drops of water into it.
Observation: Water vapours get condensed in a test tube and colour of blue crystals changes into white. On adding water to anhydrous copper sulphate it changes into blue again.
Chemical Reaction: Conclusion: Crystalline substances have water of crystallization which are lost on heating. When we add water inCuSO4till a saturated solution is formed. On cooling, it gets converted into CuSO4.5H2Ocrystals and it shows that both are inter convertible.
Conclusion: Crystalline substances have water of crystallization which are lost on heating. When we add water inCuSO4till a saturated solution is formed. On cooling, it gets converted into CuSO4.5H2Ocrystals and it shows that both are inter convertible.
(b)
Q20: Explain the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on the following with chemical equation:
(i) Magnesium ribbon (ii) Sodium hydroxide (iii) Crushed egg shells
Ans: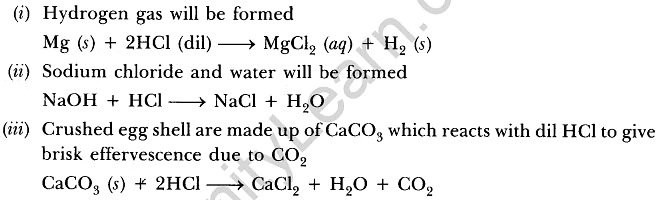
Q21: (a) Write the name given to bases that are highly soluble in water. Give an example.
(b) How is tooth decay related to pH? How can it be prevented?
(c) Why does bee sting cause pain and irritation? Rubbing of baking soda on the sting area gives relief. How?
Ans: (a) Alkali, e.g. NaOH (Sodium hydroxide).
(b) Lower the pH, more will be tooth decay. Acid reacts with Ca3(PO4)2 and cause tooth decay.
It can be prevented by brushing teeth after every meal.
(c) It is due to formic acid. Sodium hydrogencarbonate (Baking soda) neutralises formic acid giving relief.
Q22: (a) Mention the pH range within which our body works. Explain how antacids
give relief from acidity. Write the name of one such antacid.
(b) Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How does the pH will change as it turns to curd? Explain your answer.
(c) A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. Why does this milk take a longer time to set as curd?
(d) Mention the nature of toothpastes. How do they prevent tooth decay?
Ans. (a) Our stomach has pH equal to 2. Antacids neutralizes excess of acid in our body and gives relief from hyperacidity. Sodium hydrogencarbonate is one of such antacid.
(b) pH will decrease as it turns to curd because curd is acidic due to the presence of lactic acid.
(c) It takes longer time to set as curd as bacteria do not work well in presence of sodium hydrogencarbonate, i.e. fermentation will take place slowly.
(d) Toothpastes are basic in nature. They neutralize the acid formed in mouth which causes tooth decay.
Q23: (a) Crystals of a substance changed their colour on heating in a closed test
tube but regained it after sometime when they were allowed to cool down. Name the substance and write its formula and explain the phenomenon involved.
(b) Name the compound whose one formula unit is associated with 10 water molecules. How is it prepared? Give equations of related reactions. Give two uses of the compound.
Ans: (a) CuSO4.5H2O is a blue crystalline solid. It becomes dirty white on heating due to loss of water molecules and it becomes amorphous.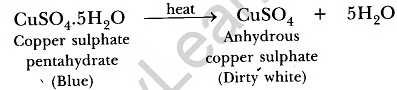 It regains its colour by absorbing water from atmosphere and becomes blue in colour.
It regains its colour by absorbing water from atmosphere and becomes blue in colour.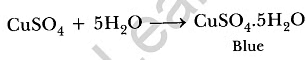 (b) Na2CO3. 10H2O. It is called sodium carbonate decahydrate or washing soda. It is prepared by passing CO2 gas through saturated solution of ammonical brine.
(b) Na2CO3. 10H2O. It is called sodium carbonate decahydrate or washing soda. It is prepared by passing CO2 gas through saturated solution of ammonical brine.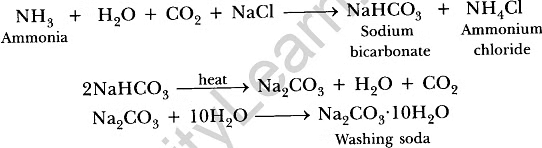 Uses:
Uses:
(i) It is used in the production of washing powder.
(ii) It is used for the manufacture of glass.
Q24: (a) Explain the following chemical properties of acids with the help of balanced chemical equations only.
(i) When an acid reacts with a metal carbonate.
(ii)When an acid reacts with a metal bicarbonate.
(iii) When an acid reacts with a metal oxide.
(b) You are given three solutions A, B and C with pH values 2, 10 and 13 respectively. Write which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration among the three and state the nature ‘acidic or basic’ of each solution.
Ans: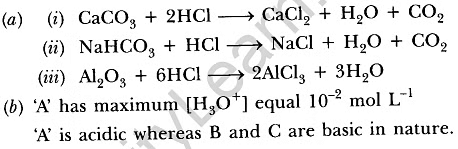
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Acids, Bases and Salts
| 1. What are acids and bases, and how do they differ from each other? |  |
| 2. What is the pH scale, and how is it used to classify substances as acids or bases? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acids and bases found in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How do neutralization reactions work, and what are their practical applications? |  |
| 5. What are salts, and how are they formed from acids and bases? |  |






















