Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Combustion and Flame
Q1: What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Ans: The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels include:
- They are the cleanest burning fossil fuels available.
- Both are less polluting and non-corrosive.
- They can be easily transported through pipelines.
- These fuels are widely available and affordable.
- CNG and LPG are simple to store and transport.
- Due to their high calorific value, they are commonly used for cooking.
Q2: Differentiate between LPG and wood as fuel.
Ans: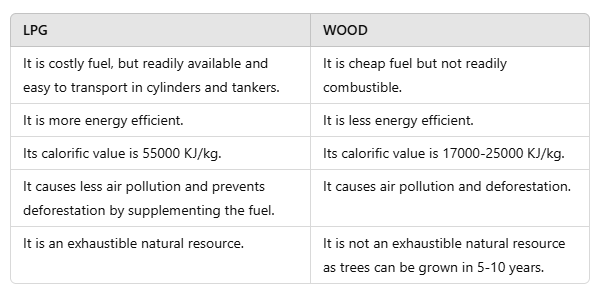
Q3: Explain working and principles of a fire extinguisher.
Ans: The most common fire extinguisher is water. It is effective for fires involving materials like wood and paper. However, it is not suitable for:
- Electrical fires: Water can conduct electricity, posing a risk to those trying to extinguish the fire.
- Oil and petrol fires: Water is heavier than oil, causing it to sink and allowing the oil to continue burning on top.
For fires involving electrical equipment and flammable materials, carbon dioxide (CO2) is a better choice. Its advantages include:
- CO2 is heavier than oxygen, effectively covering the fire and cutting off its oxygen supply.
- This helps control the fire and often does not damage electrical equipment.
CO2 is stored as a liquid under high pressure in cylinders. When released, it expands and cools, forming a blanket around the fire and lowering the temperature of the fuel, making it an excellent extinguisher.
Q4: Explain why the process of rusting can be called as slow combustion.
Ans: Rusting of iron is a slow oxidation process in which iron using oxygen and water is oxidised and is rusted out, it produces heat at very slow rate. The combustion process is also an oxidation process and is a chemical reaction by which a fuel and an oxidiser react to produce heat and light, thus we can say rusting of iron is a slow combustion process, although combustion is much faster than rusting.
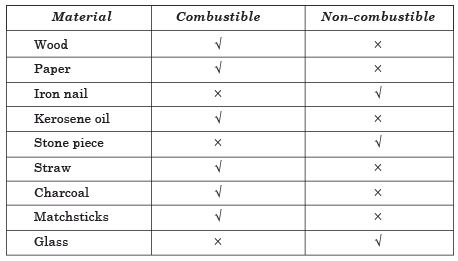
Q5: Complete the following table: 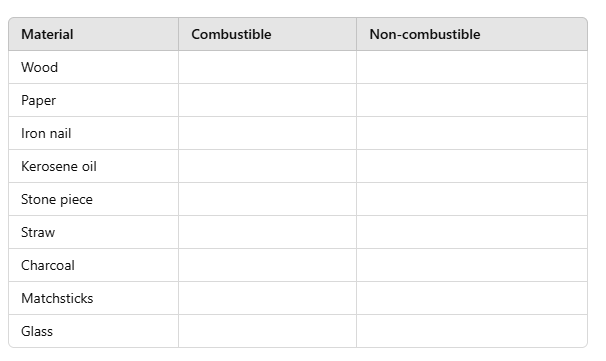
Ans. Combustible and Non-combustible Substances
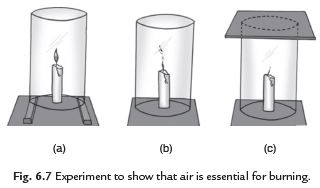
Q6: What are the essential conditions for combustion? Explain with the help of an activity.
Ans. Take a candle. Light it and fix it on a table. Put a glass chimney over the candle and rest it on wooden blocks in such a way that air can enter the chimney. We see that candle remains lighted. Remove the blocks and let the chimney rest on the table. We see that the flame flickers and produces smoke. Now put a glass plate over the chimney. We see that flame goes off because air is not available. This activity shows that air is essential to burn a fuel at its ignition temperature.
Q7: Describe the history of the matchstick.
Ans. History of matchstick is about five thousand years old. The modern safety match was developed only about 200 years ago. A mixture of antimony trisulphide, potassium chlorate and white phosphorus with some glue and starch was applied on the head of a match made of suitable wood. When it struck against a rough surface, white phosphorus got ignited and combustion of matchstick started. These days red phosphorus is used in place of white phosphorus.
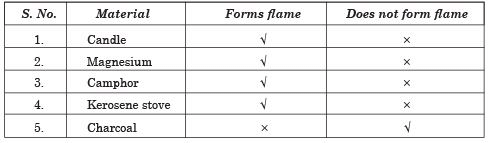
Q8: Complete the following table. 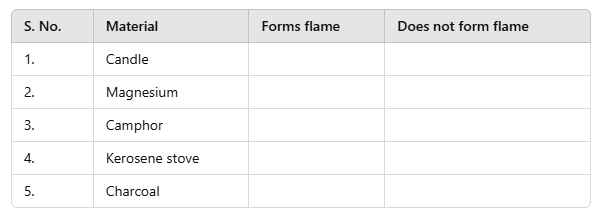
Ans. Materials forming Flame on Burning
Q9: Write three examples of each type of fuel in tabular form.
Ans. 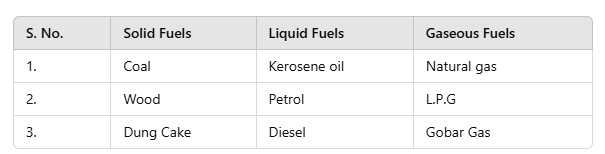
Q10: Make a table to show the calorific value of various fuels.
Ans. 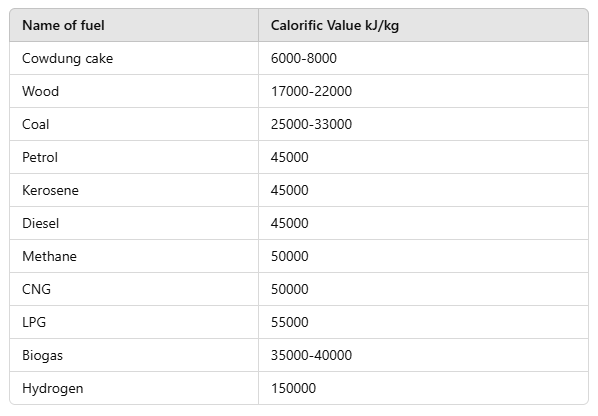
Q11: What is deforestation? Write its effect on environment.
Ans. Cutting of trees is called deforestation.
Effects: Deforestation is very harmful to the environment.The following are the effects of deforestation:
1. The annual rainfall is disturbed in that area.
2. The frequent floods come.
3. Balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is disturbed.
4. It causes respiratory problem.
5. Trees provide us with useful substances which are lost due to deforestation.
Q12: What are the ill-effects due to the increasing consumption of fuel?
Ans. The increasing consumption of fuels has several harmful effects on the environment:
- Carbon fuels, such as wood, coal, and petroleum, release unburnt carbon particles. These fine particles can cause respiratory diseases, including asthma.
- Incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide, a poisonous gas that can be deadly, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Excessive fuel use contributes to global warming, leading to rising temperatures and melting polar ice.
- Burning fuels releases sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which can cause acid rain. This type of rain is harmful to crops, buildings, and soil.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - Combustion and Flame
| 1. What is combustion and how does it occur? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of combustion? |  |
| 3. What is the role of flames in combustion? |  |
| 4. How do different fuels affect the combustion process? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of combustion? |  |

















