Class 5 Science - Skeletal System and Nervous System - Question Answers
Q1: What is skeletal system?
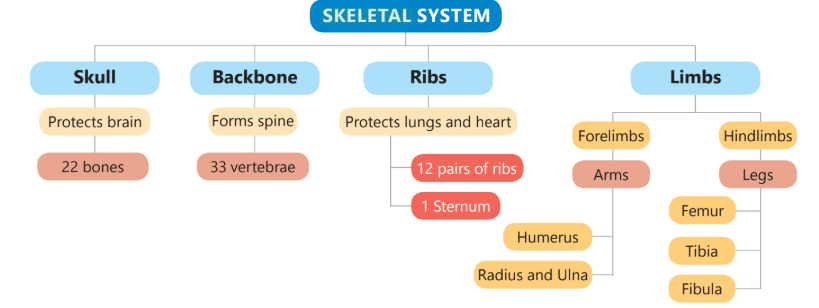
Ans: The skeletal system is the framework of bones that gives support to our body.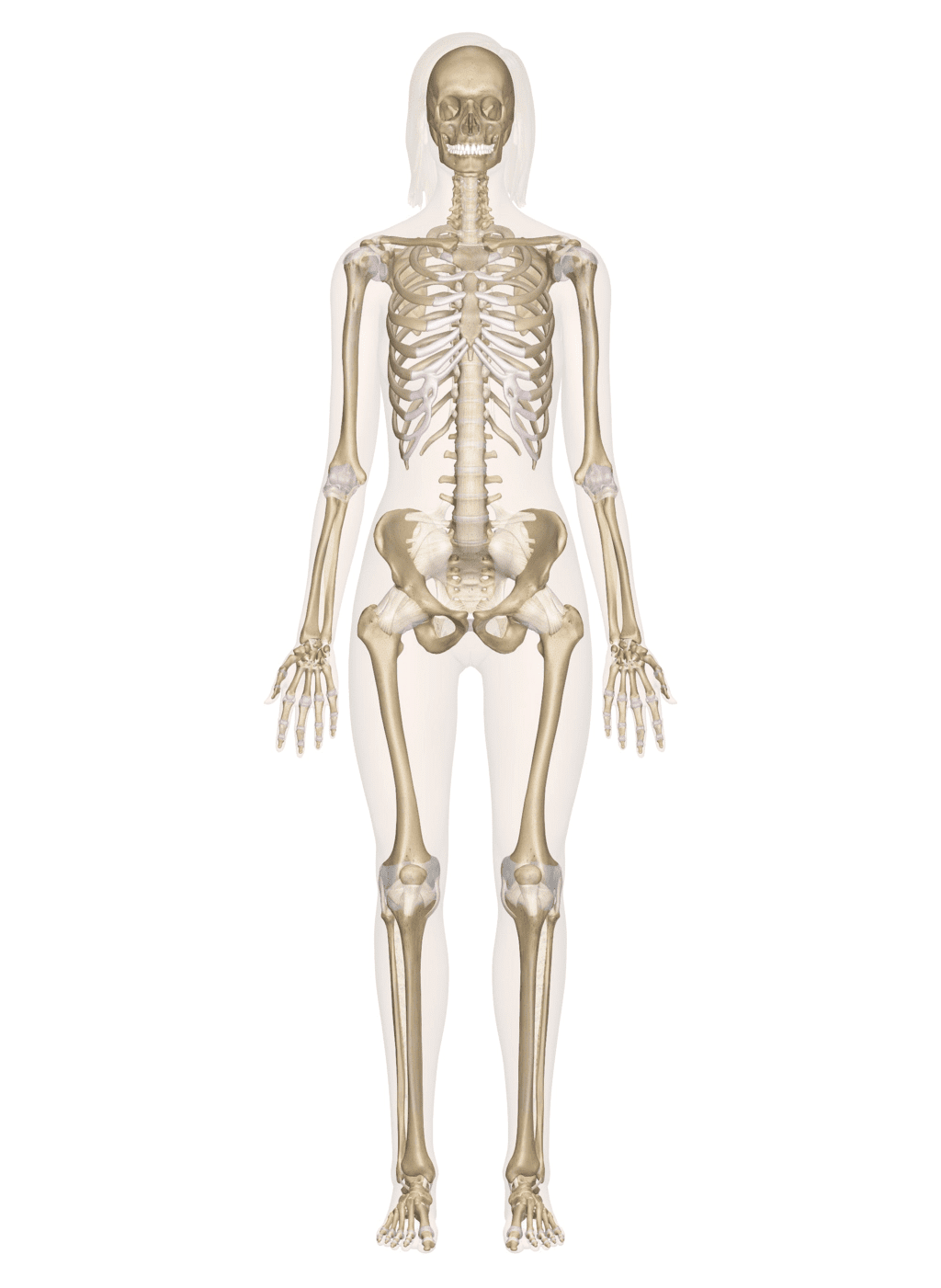 Skeletal SystemQ2: Describe the different parts of the skeleton system.
Skeletal SystemQ2: Describe the different parts of the skeleton system.
Ans: The different parts of the skeleton system are:
1. Skull: The skull acts like a helmet and protects the brain.
2. Rib cage: The rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
3. Backbone: The backbone surrounds and protects the spinal cord.
4. Limbs: (Arms and legs) help us in doing many activities and in moving from one place to another.
Q3: What is a rib cage and how many pairs of ribs do most people have?
Ans: Ribs form a cage of bones around the chest called the rib cage. Most people have 12 pairs of ribs.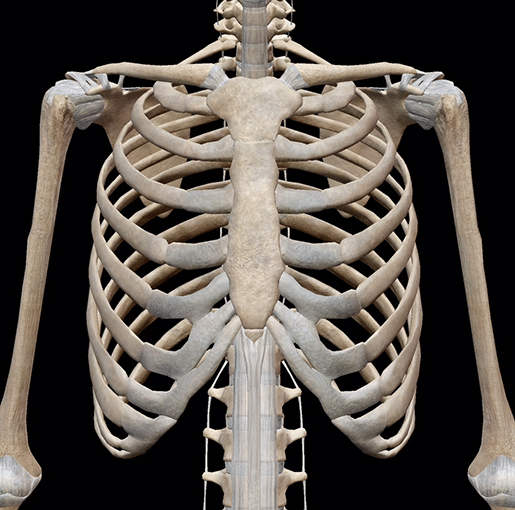 Rib CageQ4: What is cartilage? Name any two organs of the human body that have cartilage.
Rib CageQ4: What is cartilage? Name any two organs of the human body that have cartilage.
Ans: Cartilage is a tough, elastic substance. It holds the bones together at the joints. Ears and nose have cartilage.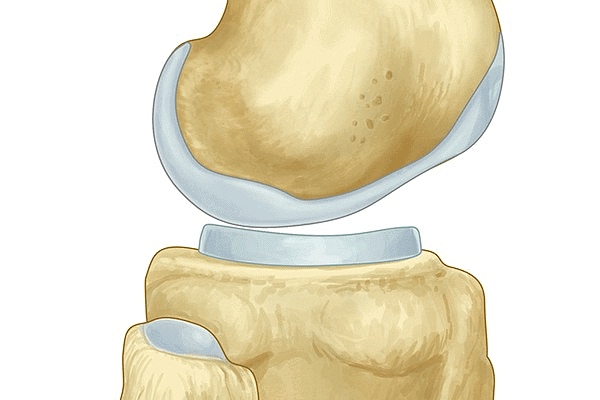 Cartilage between bonesQ5: Write any four functions of the skeletal system.
Cartilage between bonesQ5: Write any four functions of the skeletal system.
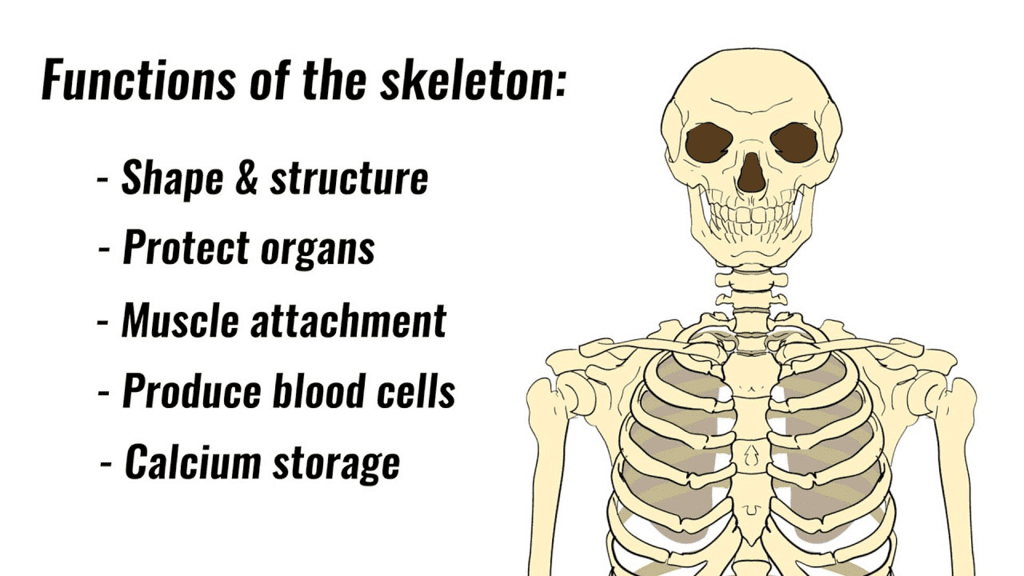
Ans: The functions of the skeletal system are:
1. The skeleton gives shape and support to our body.
2. It protects the soft internal organs:
(i) The skull protects the brain.
(ii) The rib cage protects the heart and the lungs.
(iii) The backbone protects the spinal cord.
3. It allows the movement of different body parts.
4. Many bones in our body are hollow. They are filled with a jelly-like substance called bone marrow. Blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
Q6: Why do we need muscles? Describe the different types of muscles in a human body.
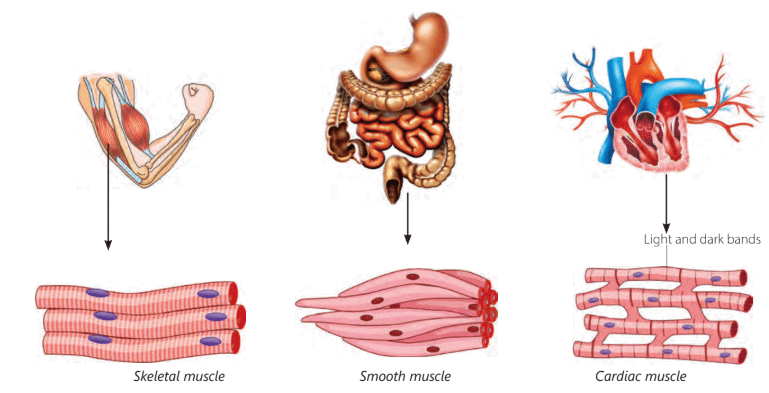
Ans: We need muscles to make movement possible and to hold the bones together. They also help in important processes like digestion. The different kinds of muscles are involuntary muscles and voluntary muscles.
1. Voluntary muscles: The movement of these muscles can be controlled by us. We can start or stop the movement by these muscles according to our wish. For eg: skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles.
2. Skeletal muscles: Skeletal muscles help in movement. For eg muscles in arms. These are the only type of muscles we can control directly.
3. Involuntary muscles: Involuntary muscles are the muscles whose movement cannot be controlled by us. Smooth and cardiac muscles are two types of involuntary muscles.
4. Cardiac muscles: Muscles in the heart are examples of cardiac muscles. We do not have any control over this type of muscles. They work automatically.
5. Smooth muscles: Muscles in the digestive system are examples of smooth muscles. We do not have any control over this type of muscles.
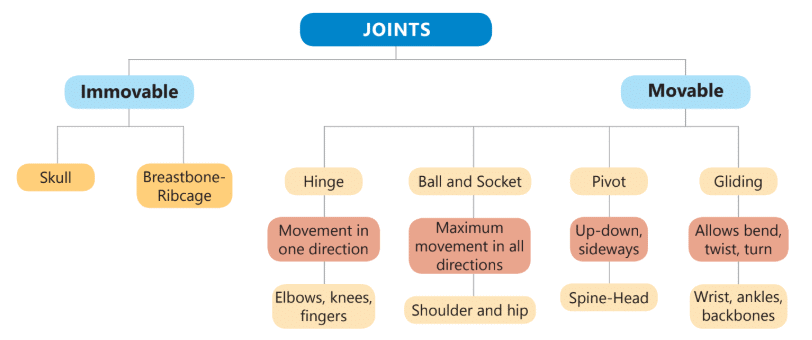
Q7: What are joints? Describe the different kinds of movable joints in our body.
Ans: A place where two bones meet is called joint.
The different kinds of movable joints are:
1. Ball and socket joint: This joint allows movement in many directions. For eg shoulder joint and hip joint. 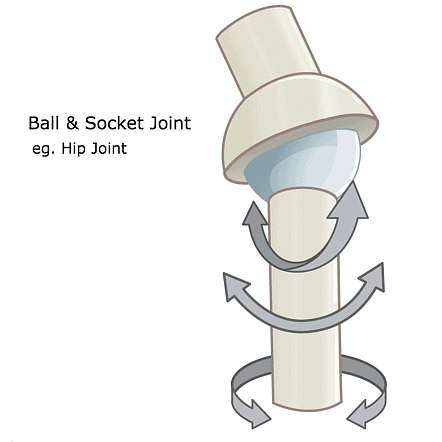 2. Hinge joint: This type of joint only allows back and front movement. It works like the hinges of a door. For eg bones in the knee, elbow, fingers and toes.
2. Hinge joint: This type of joint only allows back and front movement. It works like the hinges of a door. For eg bones in the knee, elbow, fingers and toes. 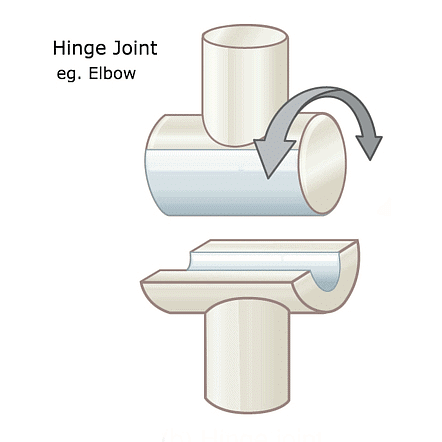 3. Pivot joint: This joint allow us to move our head up, down and sideways. It is found between the first two vertebrae of our backbone.
3. Pivot joint: This joint allow us to move our head up, down and sideways. It is found between the first two vertebrae of our backbone. 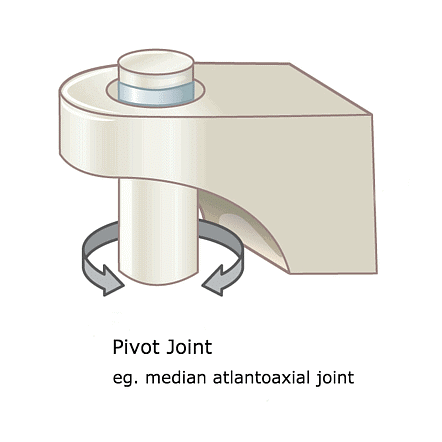 4. Gliding joint: The joint allows the bones to slide against each other in a gliding motion. For eg bones of wrist and ankle.
4. Gliding joint: The joint allows the bones to slide against each other in a gliding motion. For eg bones of wrist and ankle. 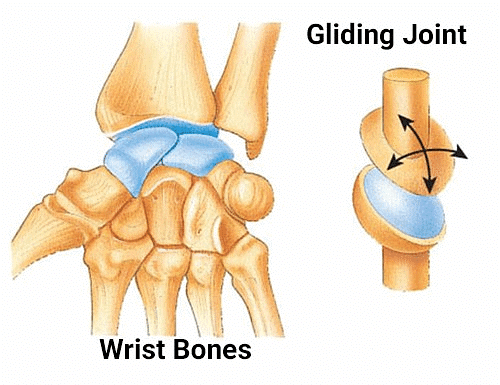
Q8: What are floating ribs?
Ans: The ribs that are not attached to the sternum are called floating ribs.
Q9: What would happen if our lower jaw is fixed like other bones in the skull?
Ans: We would not be able to talk and eat.
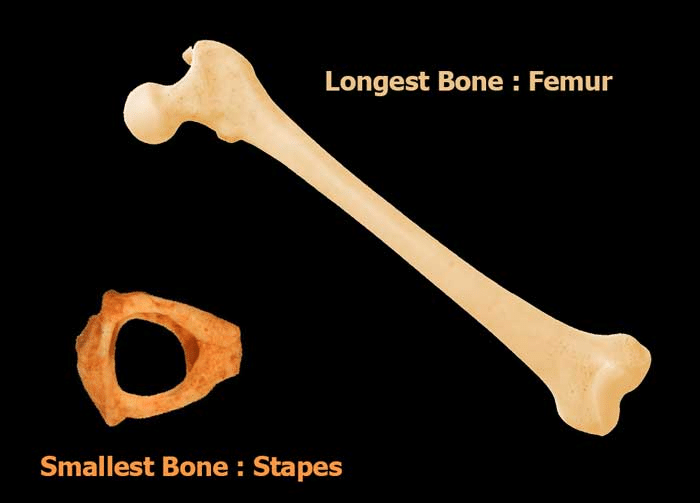
Q10: Which is the longest and the smallest bone in the body?
Ans: The longest bone: The thigh bone (femur).
The shortest bone: In the ear (stirrup).
Q11: How do muscles work to move our bones? Explain with the example of biceps and triceps.
Ans: Muscles help in the movement of bones by pulling them. However, muscles cannot push; they can only contract (shorten) and relax. This is why at least two muscles are needed to move a joint.
For example, in the arm, the biceps and triceps work together to move the lower arm:
- When we pull up our arm, the biceps contract (become shorter) and pull the lower arm bone upward. At the same time, the triceps relax.
- When we lower our arm, the triceps contract and pull the lower arm bone downward, while the biceps relax.
This coordinated action of muscles allows movement in different parts of the body.
Q12: (i) Why is it important to maintain a good posture? What problems can arise due to bad posture? (ii) What nutrients are required for strong bones and muscles? Name some food sources for these nutrients.
Ans: (i) Good posture is important for the health of our skeletal system because it helps in keeping our spine and other bones in the correct position. It prevents unnecessary strain on muscles and joints.If we do not maintain a good posture and practice bad habits like slouching, hunching, or slumping, it can create problems in our spine and other parts of the skeletal system. This may lead to back pain, joint pain, and poor muscle coordination over time.
(ii) For strong bones, our body needs calcium and vitamin D.
- Food sources for strong bones: Milk, curd (yoghurt), fish, and green leafy vegetables such as spinach.
For strong muscles, our body needs proteins.
- Food sources for strong muscles: Meat, fish, eggs, chickpeas, cottage cheese, milk, and curd.
|
42 videos|210 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Class 5 Science - Skeletal System and Nervous System - Question Answers
| 1. What is the primary function of the skeletal system? |  |
| 2. How does the nervous system interact with the skeletal system? |  |
| 3. What are the main types of bones in the human skeleton? |  |
| 4. What role does the spinal cord play in the nervous system? |  |
| 5. How do injuries to the skeletal system affect the nervous system? |  |