Branches of Science, Elements and Compounds | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Different Branches of Science |

|
| Common and Chemical Names of Some Compounds |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Science is a vast field of study that helps us understand the natural world and its fundamental principles. It is divided into various branches, each focusing on a specific area of knowledge. The Branches of Science include disciplines such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and specialized fields like Genetics, Ecology, and Astronomy, all of which contribute to advancements in technology, medicine, and industry.
Understanding the Elements and Compounds is essential to the study of Chemistry, as they form the basis of all matter. Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom, while compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically combine. The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic numbers, and each element has unique properties that define its behavior in chemical reactions. Compounds, on the other hand, have distinct compositions and play crucial roles in various natural and industrial processes.
This chapter explores different branches of science, the classification and properties of elements, and the significance of chemical compounds in daily life. By understanding these fundamental concepts, we gain insights into how the universe operates at both macroscopic and microscopic levels.
Different Branches of Science
Branch ➜ Concerning Field
- Aeronautics ➜ Science of flight of aeroplanes.
- Astronomy ➜ Study of heavenly bodies.
- Agronomy ➜ Science dealing with crop plants.
- Angiology ➜ Deals with the study of the blood vascular system.
- Anthology ➜ Study of flowers.
- Anthropology ➜ Study of human beings, their culture, society, and evolution.
- Apiculture ➜ Honey industry (Bee Keeping)
- Araneology ➜ Study of spiders.
- Batracology ➜ Study of frogs.
- Biochemistry ➜ deals with the study of chemical reactions in relation to life activities.
- Biotechnology ➜ Deals with the use of micro-organisms in commercial processes for producing fine chemicals such as drugs, vaccines, hormones, etc. on a large scale.
- Cardiology ➜ Study of heart.
- Craniology ➜ Study of skulls.
- Cryptography ➜ Study of secret writing.
- Cryogenics ➜ Study concerning the application and uses of very low temperature.
- Cytology ➜ Study of cells.
- Dermatology ➜ Study of skin.
- Ecology ➜ The study of the relationship between organisms and the environment.
- Entomology ➜ Study of insects.
- Etiology ➜ Study of the cause of disease.
- Eugenics ➜ Study of improvement of the human race by applying laws of heredity. It is related to future generations.
- Evolution ➜ Deals with the study of the origin of new from old.
- Exobiology ➜ Deals with life or possibilities of life beyond the earth.
- Floriculture ➜ Study of flower yielding plants.
- Geology ➜ Study of condition and structure of the earth.
- Genetics ➜ Study of heredity and variations.
- Gerontology ➜ Study of aging and its effects on humans.
- Horticulture ➜ Study of garden cultivation.
- Haematology ➜ Study of blood.
- Herpetology ➜ Study of reptiles and amphibians.
- Iconography ➜ Teaching by pictures and models.
- Immunology ➜ science which deals with the study of resistance of organisms against infection.
- Jurisprudence ➜ Science of law.
- Kalology ➜ Study of human beauty.
- Lexicography ➜ Compiling of a dictionary.
- Mycology ➜ Study of fungi.
- Myology ➜ Study of muscles.
- Nephrology ➜ Study of kidneys.
- Neurology ➜ Study of the nervous system.
- Numismatics ➜ Study of coins and medals.
- Obstetrics ➜ Branch of medicine dealing with pregnancy.
- Oneirology ➜ Study of dreams.
- Ophthalmology ➜ Study of eyes.
- Ornithology ➜ Study of birds.
- Osteology ➜ Study of bones.
- Palaeontology ➜ Study of fossils.
- Philately ➜ Stamp collecting.
- Philology ➜ Study of languages.
- Phonetics ➜ Concerning the sounds of a spoken language.
- Physiography ➜ Study of physical features of the Earth, including landforms and climate.
- Pedology ➜ Study of soils.
- Pathology ➜ Study of disease-causing organisms.
- Phycology ➜ Study of algae.
- Physiology ➜ Science deals with the study of functions of various parts of organisms.
- Pisciculture ➜ Study of fish.
- Pomology ➜ Study of fruits.
- Seismology ➜ Study of earthquakes.
- Sericulture ➜ Silk industry (culture of silk moth and pupa).
- Serpentology ➜ Study of snakes.
- Telepathy ➜ communication between two minds at a distance with the help of emotions.
- Taxonomy ➜ Study of classification of organisms.
- Virology ➜ Study of the virus.
Elements, Symbols And Atomic Numbers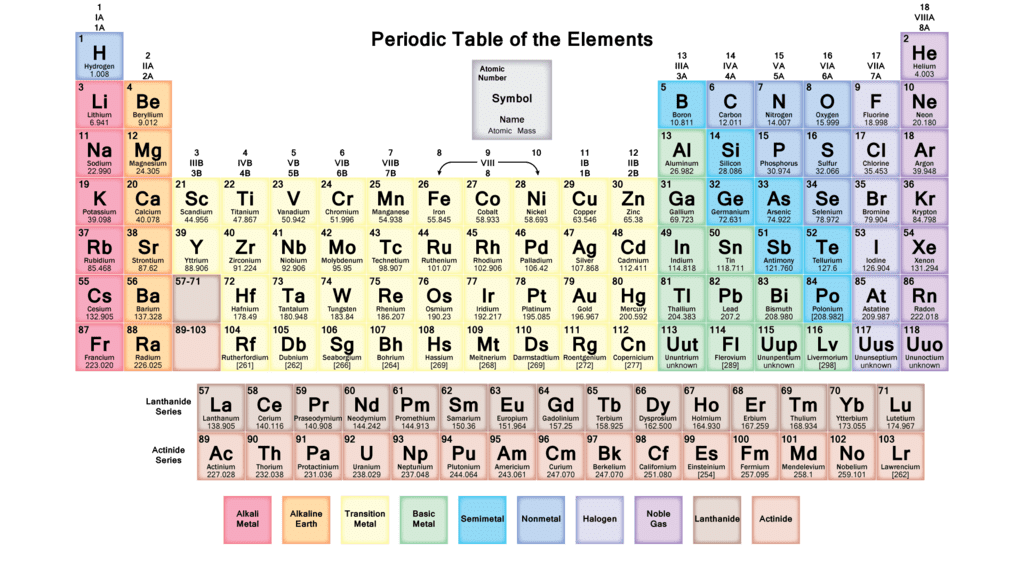
Element(Symbol) ➜ Atomic Number
- Hydrogen (H) ➜ 1
- Helium (He) ➜ 2
- Lithium (Li) ➜ 3
- Beryllium (Be) ➜ 4
- Boron (B) ➜ 5
- Carbon (C) ➜ 6
- Nitrogen (N) ➜ 7
- Oxygen (O) ➜ 8
- Fluorine (F) ➜ 9
- Neon (Ne) ➜ 10
- Sodium (Natrium) (Na) ➜ 11
- Magnesium (Mg) ➜ 12
- Aluminum (Al) ➜ 13
- Silicon (Si) ➜ 14
- Phosphorous (P) ➜ 15
- Sulphur (S) ➜ 16
- Chlorine (Cl) ➜ 17
- Argon (Ar) ➜ 18
- Potassium (Kalium) (K) ➜ 19
- Calcium (Ca) ➜ 20
- Scandium (Sc) ➜ 21
- Titanium (Ti) ➜ 22
- Vanadium (V) ➜ 23
- Chromium (Cr) ➜ 24
- Manganese (Mn) ➜ 25
- Iron (Ferrum) (Fe) ➜ 26
- Cobalt (Co) ➜ 27
- Nickel (Ni) ➜ 28
- Copper (Cuprum) (Cu) ➜ 29
- Zinc (Zn) ➜ 30
- Germanium (Ge) ➜ 32
- Bromine (Br) ➜ 35
- Krypton (Kr) ➜ 36
- Zirconium (Zr) ➜ 40
- Silver (Ag) ➜ 47
- Tin (Stannum) (Sn) ➜ 50
- Antimony (Stabnium) (Sb) ➜ 51
- Iodine (I) ➜ 53
- Barium (Ba) ➜ 56
- Gold (Aurum) (Au) ➜ 79
- Mercury (Hydragerm) (Hg) ➜ 80
- Lead (Plumbum) (Pb) ➜ 82
- Bismuth (Bi) ➜ 83
- Radium (Ra) ➜ 88
- Thorium (Th) ➜ 90
- Uranium (U) ➜ 92
- Plutonium (Pu) ➜ 94
- Curium (Cm) ➜ 96Question for Branches of Science, Elements and CompoundsTry yourself:What is atomic number for Sodium (Natrium)(Na)?View Solution
Common and Chemical Names of Some Compounds
Common Name ➜ Chemical Name (Chemical Formula)
- Dry ice ➜ Solid Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Slaked Lime ➜ Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
- Bleaching Powder ➜ Calcium Oxychloride (CaOCI2)
- Nausadar ➜ Ammonium Chloride (NH4CI)
- Caustic Soda ➜ Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Rock Salt ➜ Sodium Chloride (NaCI)
- Caustic Potash ➜ Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
- Potash Alum ➜ Potassium Aluminium Sulphate (K2SO4.AI2(SO4)3.24H2O)
- Epsom ➜ Magnesium Sulphate (MgSO4.7H2O)
- Quick Lime ➜ Calcium Oxide (CaO)
- Plaster of Paris ➜ Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate (CaSO4).1/2 H2O
- Gypsum ➜ Calcium Sulphate (CaSO4.2H2O)
- Green Vitriol ➜ Ferrous Sulphate (FeSO4.7H2O)
- Mohr’s Salt ➜ Ammonium Ferrous Sulphate (FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4.6H2O)
- Blue Vitriol ➜ Copper Sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O)
- White Vitriol ➜ Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO4.7H2O)
- Marsh Gas ➜ Methane (CH4)
- Vinegar ➜ Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
- Potash Ash ➜ Potassium Carbonate (K2CO3)
- Hypo ➜ Sodium Thiosulphate (Na2S2O3.5H2O)
- Baking Powder ➜ Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
- Washing Soda ➜ Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3.10H2O)
- Magnesia ➜ Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
- Chalk (Marble) ➜ Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)
- Lunar Caustic ➜ Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
- Laughing Gas ➜ Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Chloroform ➜ Trichloro Methane (CHCl3)
- Vermelium ➜ Mercuric Sulphide (HgS)
- Borax ➜ Borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O)
- Alcohol ➜ Ethyl Alcohol (C2H5OH)
- Sugar ➜ Sucrose (C12H22O11)
- Heavy Water ➜ Deuterium Oxide (D2O)
- Globar’s Salt ➜ Sodium Sulphate (Na2SO4.10H2O)
- T.N.T. ➜ Tri Nitrotoluene (C6H2CH3(NO2)3)
- Calomel ➜ Mercurous Chloride (HgCl)
- Sand ➜ Silicon Oxide (SiO2)
Conclusion
The study of Branches of Science allows us to categorize knowledge into specialized fields, making scientific exploration more systematic and effective. From the study of living organisms in Biology to the investigation of celestial bodies in Astronomy, each branch contributes to the overall progress of human civilization.
In the realm of Chemistry, Elements and Compounds play a foundational role in shaping the physical and chemical properties of substances. The elements that make up the periodic table are the building blocks of all matter, while compounds demonstrate how different elements interact to form substances essential for life, industry, and scientific innovation.
By delving into these topics, we develop a deeper appreciation for the scientific principles that govern our world. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of nature but also empowers us to apply scientific discoveries in fields like medicine, engineering, environmental science, and technology, ultimately improving the quality of human life.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Branches of Science, Elements and Compounds - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the different branches of science? |  |
| 2. What are elements, symbols, and atomic numbers? |  |
| 3. What are the common and chemical names of some compounds? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of studying science? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a physical and a chemical change? |  |
















