Past Year Questions: Determinacy and Indeterminacy | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: The plane frame shown in the figure has fixed support at joint A, hinge support at joint F, and roller support at joint 1 . In the figure, A to I indicate joints of the frame. [2024, Set-1]
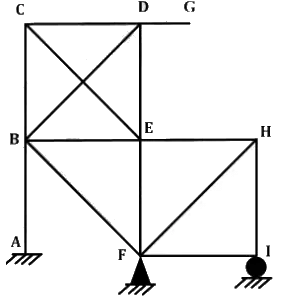 If the axial deformations are neglected, the degree of kinematic indeterminacy is (integer).
If the axial deformations are neglected, the degree of kinematic indeterminacy is (integer).
Ans: 9
Sol: From inextensibility of BF and BA,
ΔBx = 0 ΔBy = 0
From inextensibility of BE and EF,
ΔEx = 0 ΔEy = 0
From inextensibility of CE and BC
ΔCx = 0 ΔCy = 0
From inextensibility of BD and CD,
ΔDx = 0 ΔDy = 0
From inextensibility of DG,
ΔGx = 0
From inextensibility of EH and HF,
ΔHx = 0 ΔHy = 0
From inextensibility FI,
Δlx = 0
⇒ If at joint (F),FB, FE, FH, FI are rigidly connected then possible displacements at F = θF.
If at joint I, FI and IH are rigidly connected, possible displacements at I = θI.
Hence unknown joint displacements are
θB, θC, θD, θE, θF, θG, ΔGy, θH, θI
⇒ Dk = 9
Note: However, if somebody assumes all members at joint (F) to be connected with pin then at (F) we have unknown joint displacements as
θFB, θFE, θFH, θFI.
Similarly, if at joint I if somebody assumes FI and HI to be pin connected then unknown joint displacements at I are θIF, θIH.
Hence, Dk will increase by 4.
⇒ Dk = 9 + 4 = 13
Q1: Consider the following three structures:
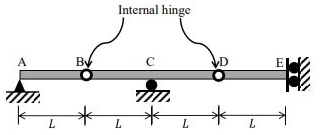
Structure I: Beam with hinge support at A, roller at C, guided roller at E, and internal hinges at B and D.
Structure II: Pin-jointed truss, with hinge support at A, and rollers at B and D.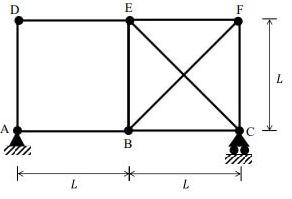
Structure III: Pin-jointed truss, with hinge support at A and roller at C.
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE? [2023, Set-1]
(a) Structure I is unstable
(b) Structure II is unstable
(c) Structure III is unstable
(d) All three structures are stable
Ans: (a, b and c)
Sol: Unstability in beam can be checked
(i) If support reactions are not enough.
(ii) If reactions are concurrent.
(iii) If reactions are parallel.
(iv) If there is mechanism.
where as for truss also along with the above given points the triangular panels are generally stable.
But, a virtual inspection must be conducted to understand the stability
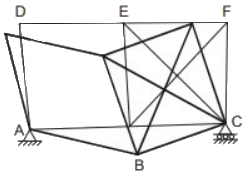
(I) It is unstable as it shows mechanisms.
Also to understand if we apply a vertical force at slider side, the deflected shape will be as follows.
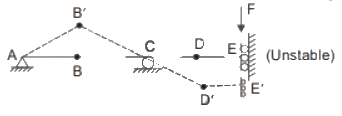
(II) The frame is internally stable but all the reactions are concurrent and meeting at hinge A, and the frame can rotate about A. Hence, it is unstable.
(III) The frame is unstable because it cannot resist shear in DE and AB since DE and AB are slender members.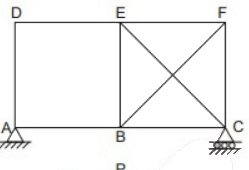
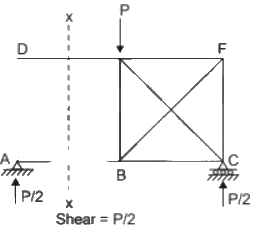
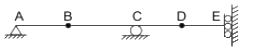
Q1: Consider a beam PQ fixed at P, hinged at Q, and subjected to a load F as shown in figure (not drawn to scale). The static and kinematic degrees of indeterminacy, respectively, are [2022, Set-2]
(a) 2 and 1
(b) 2 and 0
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 2
Ans: (a)
Sol:
Static indeterminacy, SI = r - 3 = (3 + 2) - 3 = 2
Kinematic indeterminacy = 0 + 1 = 1
Q1: The degree of static indeterminacy of the plane frame as shown in the figure is______ [2019, Set-2]
Ans: 15
Sol:
Static indeterminacy Ds = Dse + Dsi - Force releases
External indeterminacy, Dse = r - s
No. of support reactions, r = 7
Number of equilibrium equations, s = 3
Dse = 7 - 3 = 4
Internal indeterminacy Dsi = 3 x No of Closed boxes
= 3 x 4 = 12
Force releases = 1 [At the internal hinge]
Ds = 4 + 12 - 1 = 15
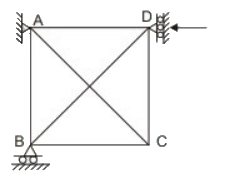
Q1: Consider the frame shown in the figure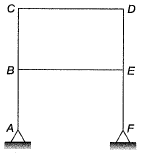
If the axial and shear deformations in different members of the frame are assumed to be negligible, the reduction in the degree of kinematic indeterminacy would be equal to [2017, Set-2]
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Ans: (b)
Sol:
DOF of Joints: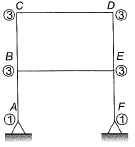
When all members are extensible,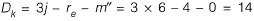
Dk (when extensible) = 14
Dk(when inextensible) = Dk (when extensible) - No. of axially rigid member
= 14 - 6 = 8
So, reduction in 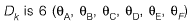
Note : Shear deformation is not considered in calculation of DK.
Q2: A planar truss tower structure is shown in the figure.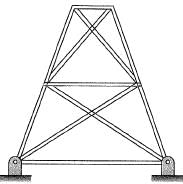
Consider the following statements about the external and internal determinacies of the truss.
P. Externally Determinate
Q. External Static indeterminacy = 1
R. External Static Indeterminacy = 2
S. Internally Determinate
T. Internal Static Indeterminacy = 1
U. Internal Static Indeterminacy = 2
Which one of the following options is correct? [2017: 2 Marks, Set-I]
(a) P-False; Q-True; R-False; S-False; T-False; U-True
(b) P-False; Q-True; R-False; S-False; T-True; U-False
(c) P-False; Q-False; R-True; S-False; T-False; U-True
(d) P-True; Q-True; R-False; S-True; T-False; U-True
Ans. (a)
Solution. Dse= re - 3 - s = 4 - 3 = 1
Dsi = m -(2j - 3) = 15 - (2 x 8 - 3)
= 2
Trick : For a truss formed due to combination of simple triangles.
Dsi = No. of double diagonal panels = 2
Dse = R - 3 = 4 - 3 = 1
[2016: 1 Mark, Set-II]
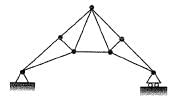

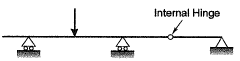
Note: Stable for vertical loading unstable for horizontal loading.
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Determinacy and Indeterminacy - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the difference between determinacy and indeterminacy in economic models? |  |
| 2. How do policymakers use the concepts of determinacy and indeterminacy? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of indeterminate models in macroeconomics? |  |
| 4. How does the concept of determinacy affect inflation targeting? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of indeterminacy for economic forecasts? |  |