Life Processes - 2 Chapter Notes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Respiration |

|
| Glycolysis |

|
| Respiration in Humans |

|
| Transportation in Human Beings |

|
| Blood Pressure |

|
| Blood Vessels |

|
| Lymph |

|
| Excretion in Humans |

|
| Excretion in Plants |

|
Respiration
- Organisms like yeast do not use oxygen; instead, they perform an incomplete breakdown of glucose into ethanol, carbon dioxide, and energy. Since this process occurs without air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration.
- During vigorous exercise in our body muscles, anaerobic respiration also occurs, resulting in the formation of lactic acid and energy. The accumulation of lactic acid in our muscles during sudden activity causes cramps.
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
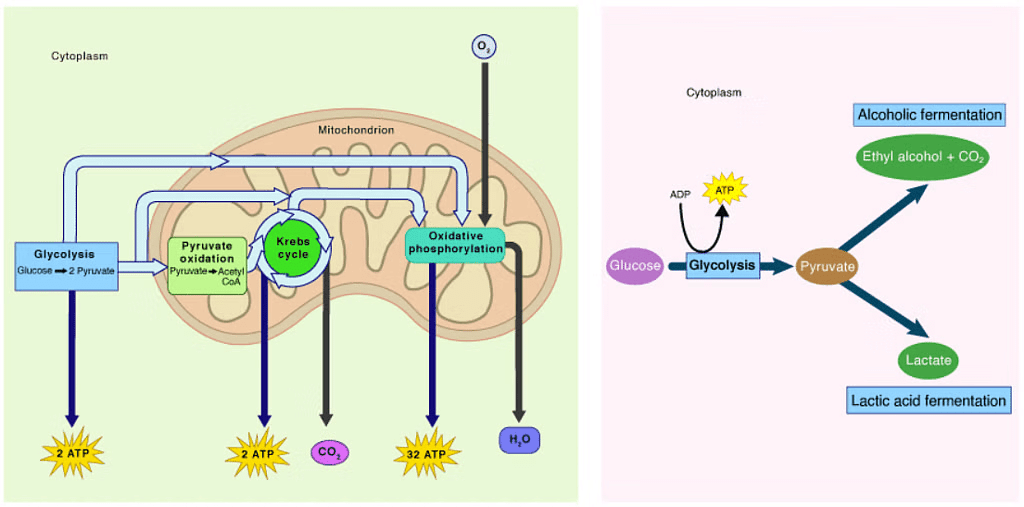
Glycolysis
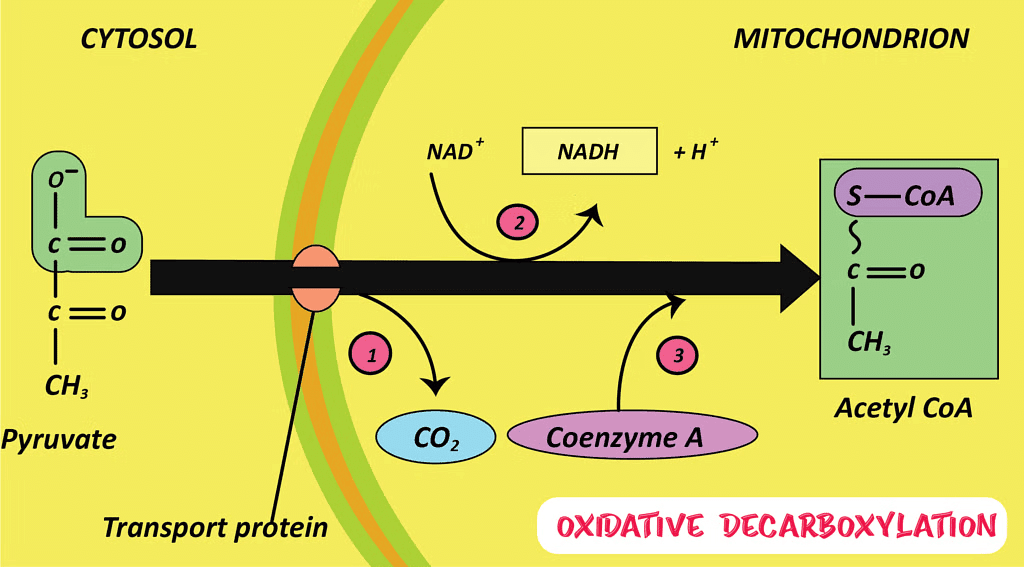
- The first step in the breakdown of glucose—a six-carbon molecule—into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. This step is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- Breakdown of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to produce three molecules of carbon dioxide and water, along with the release of energy. Since this process occurs in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
- The energy released during cellular respiration is immediately used to synthesize a molecule called ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), which is used to fuel all other activities in the cell.
The energy released during aerobic respiration is significantly greater than that released during anaerobic respiration. In these processes, ATP is broken down to provide energy for various endothermic reactions taking place in the cell.
Respiration in Humans
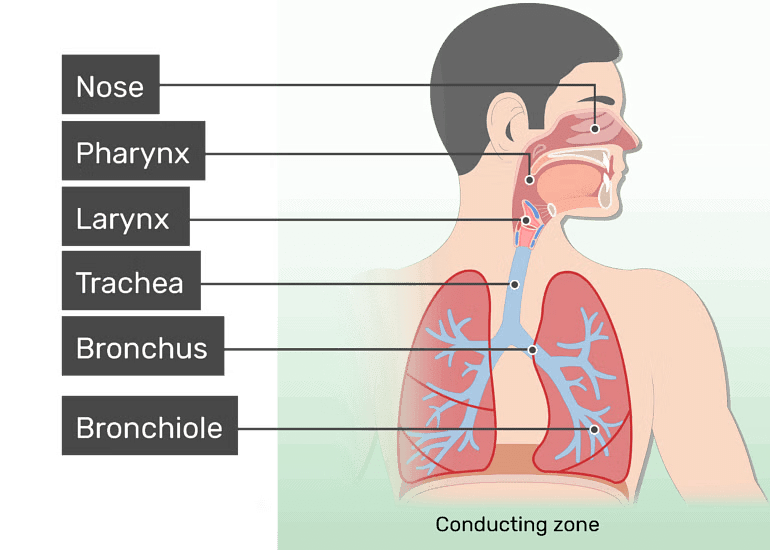
- In human beings, air enters the body through the nostrils. As it passes through, fine hairs filter the air, ensuring it is free of dust and other impurities.
- From the nostrils, air moves through the pharynx and into the lungs via the trachea.
- The trachea contains incomplete C-shaped rings of cartilage, preventing the air passage from collapsing when no air is present.
- The trachea divides into bronchi and bronchioles within the lungs, culminating in thin-walled, balloon-like structures called alveoli, where gas exchange occurs due to their extensive network of blood vessels.
 Respiration in humans
Respiration in humans - Upon inhalation, the chest cavity expands. The contraction of external intercostal muscles pushes the rib cage outward and upward, while the diaphragm flattens.
- This increase in chest cavity volume results in decreased pressure, causing air to rush into the lungs through the external nostrils. This process is known as inspiration or inhalation.
- During expiration or exhalation, stale air rich in carbon dioxide is expelled.
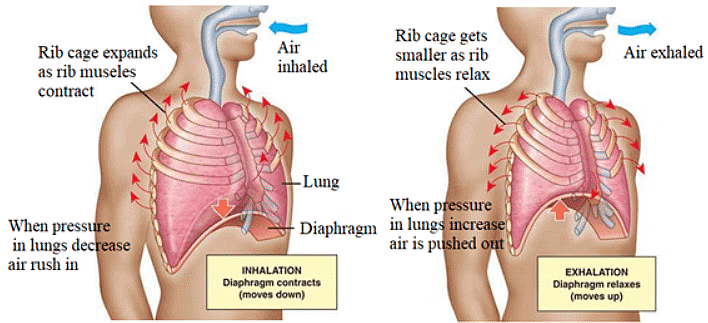 Inspiration and expiration
Inspiration and expiration - This occurs due to the relaxation of inspiratory muscles, pulling the rib cage inward. The diaphragm relaxes, taking a dome shape, which reduces the size of the thoracic cavity and compresses the lungs.
- In humans, the respiratory pigment hemoglobin is found in red blood cells (RBCs), which has a high affinity for both O2 and CO2. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen and is primarily transported in dissolved form in the blood.
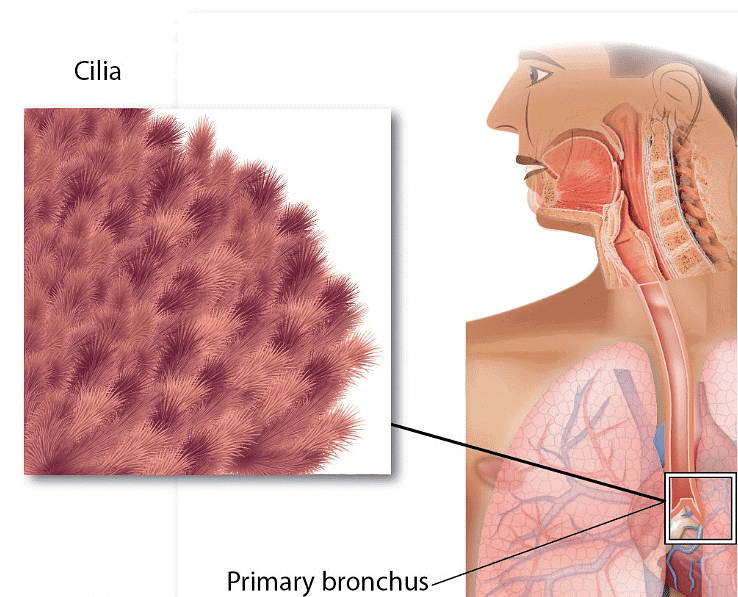
- The upper respiratory tract, including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, is lined with small hair-like cilia that help remove germs and dust from inhaled air.
Transportation in Human Beings
Blood carries numerous substances such as salts, vitamins, hormones, and waste products. The transportation system in humans includes the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and circulatory fluids (blood and lymph).
Our pump- The Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ approximately the size of a fist. A mammalian heart consists of four chambers: the upper chambers, known as auricles or atria, and the lower chambers called ventricles.
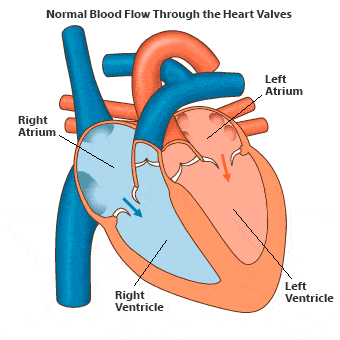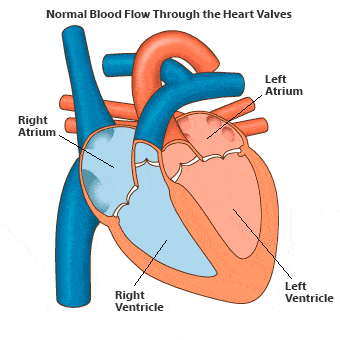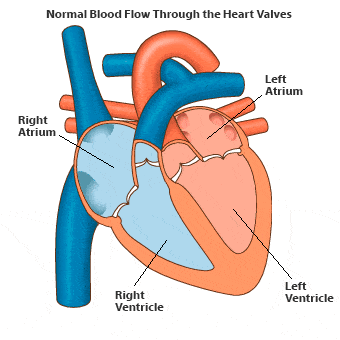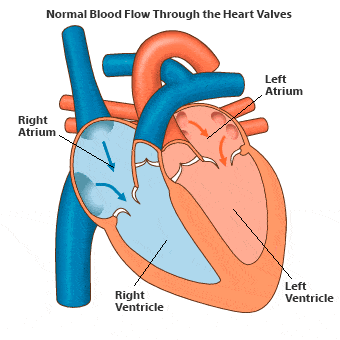
- Double circulation occurs in humans, meaning the same blood passes through the heart twice to complete one cycle.
- The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood, while the left side pumps oxygenated blood. There is no mixing of these blood types.
- Deoxygenated blood returns to the right auricle via two large veins: the superior and inferior vena cava.
- When the right atrium contracts, the right ventricle dilates, allowing blood to flow into it before being pumped to the lungs for oxygenation.
- The left ventricle's contraction sends oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta, the largest artery. The walls of the ventricles are thicker than those of the auricles, as they must pump blood to various organs. Valves prevent backflow of blood during contractions.
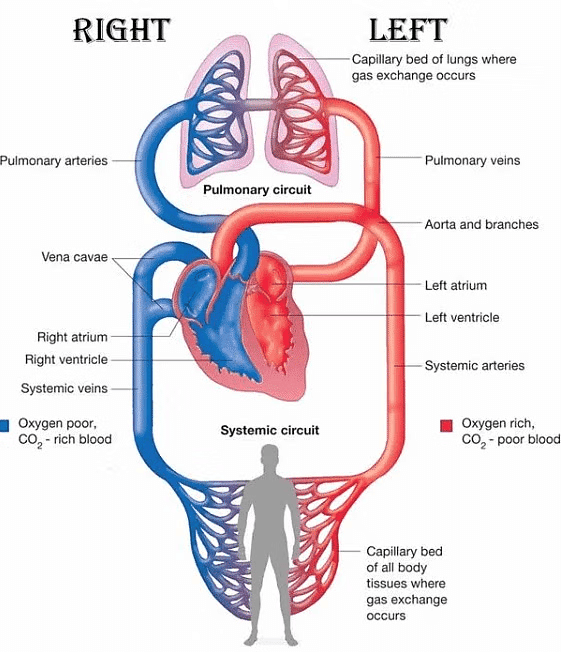 Double circulatory system
Double circulatory system - In mammals and birds, the separation between the left and right sides of the heart is advantageous because it prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This is crucial for animals with high energy demands, like birds and mammals, which need to maintain body temperature.
- Fish have a two-chambered heart, consisting of one ventricle and one auricle. Blood is pumped to the gills for oxygenation and then directly distributed to the body, resulting in blood passing through the heart only once.
[Intext Questions]
Blood Pressure
- Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of blood vessels. This pressure is significantly higher in arteries compared to veins.
- The heart's contraction is known as systole, while its relaxation is referred to as diastole. Blood pressure during systole is called systolic pressure, and during diastole, it is termed diastolic pressure. The standard systolic pressure is 120 mm of Hg, and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
- Blood pressure is measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer. High blood pressure, or hypertension, arises from the narrowing of arterioles, leading to greater resistance to blood flow. This condition can cause an artery to rupture, resulting in internal bleeding.
-
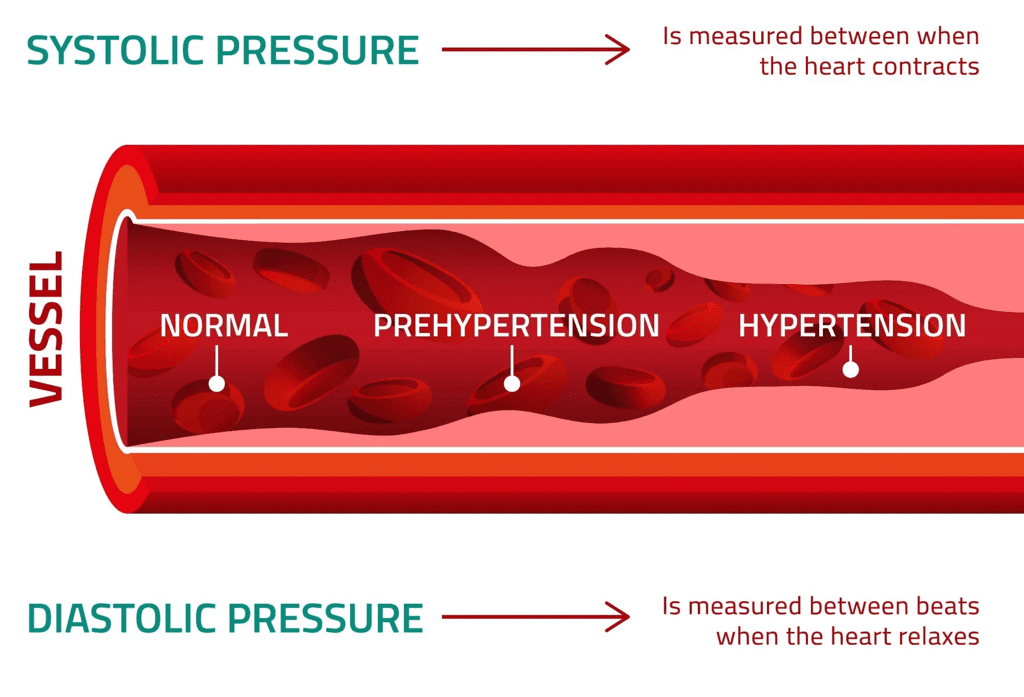 Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
Blood Vessels
- Arteries transport blood away from the heart to various body organs. Due to the high pressure of blood exiting the heart, arteries possess thick, elastic walls.
- Veins return deoxygenated blood from the body's organs back to the heart. They have thinner walls since the blood within is not under high pressure, and they feature valves that ensure blood flows in one direction.
- When reaching organs or tissues, arteries branch into smaller vessels to deliver blood to individual cells. The smallest vessels, known as capillaries, have walls that are just one cell thick, facilitating material exchange between blood and surrounding cells.
- Capillaries converge to form veins, which carry blood away from the organ or tissue and back to the heart.
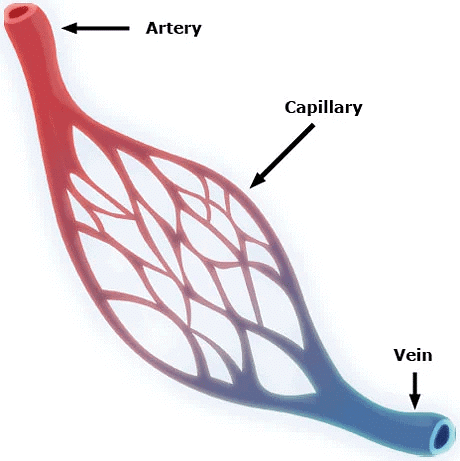 Arteries, Veins and Capillaries
Arteries, Veins and Capillaries
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Life Processes - 2
|
Download as PDF |
Lymph
- Another important fluid involved in transportation is lymph, also known as tissue fluid. Plasma, proteins, and blood cells escape through the pores in capillary walls into intercellular spaces, forming tissue fluid or lymph.
- Lymph resembles blood plasma but is colorless and contains less protein. It enters lymphatic capillaries from intercellular spaces, which merge to form larger lymph vessels that eventually connect to larger veins.
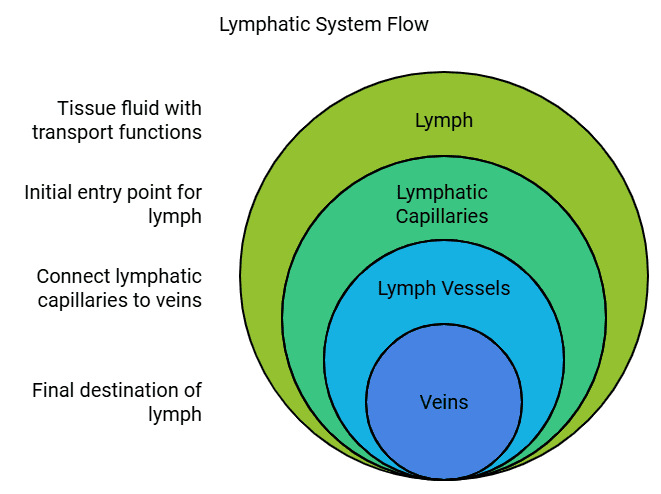
- Lymph plays a crucial role in carrying digested and absorbed fats from the intestine and draining excess fluid from the extracellular space back into the blood.
- Lymph is a colorless, light yellow, viscous fluid formed when some fluid passes from blood capillaries into intercellular spaces in the tissues through pores in the capillary walls. It contains less protein than blood plasma.
- Lymph drains into lymphatic capillaries from intercellular spaces, joining to form larger lymph vessels that eventually open into larger veins.
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine and drains excess fluid from the extracellular space back into the blood.
Transportation in Plants
- Xylem transports minerals and water from roots to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports the products of photosynthesis from leaves to other parts and storage organs.
- Xylem tissue consists of four components: xylem vessels, xylem tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma.
- Water and minerals are conducted from roots to other parts due to root pressure, transpirational pull, and cohesion-adhesion forces.
- The transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation and occurs in the part of the vascular tissue known as phloem. Phloem also transports amino acids and other substances to storage organs.
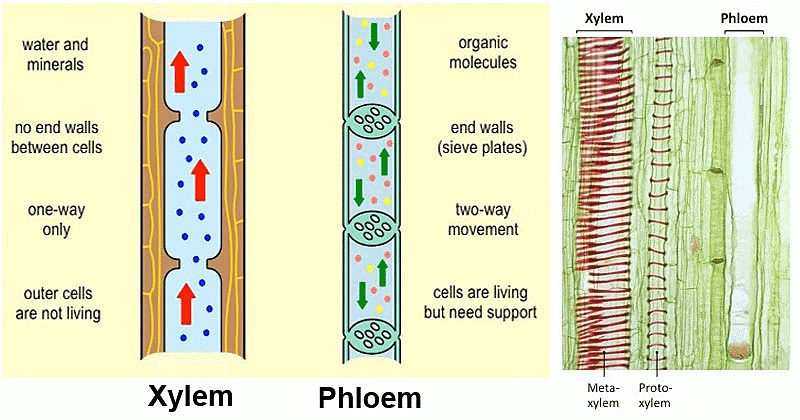
- Translocation of food and other substances takes place in the sieve tubes with the help of adjacent companion cells, in both upward and downward directions. Material like sucrose is transferred into phloem tissue using energy from ATP, which increases the osmotic pressure of the tissue, causing water to move into it. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to tissues with less pressure.
Excretion in Humans
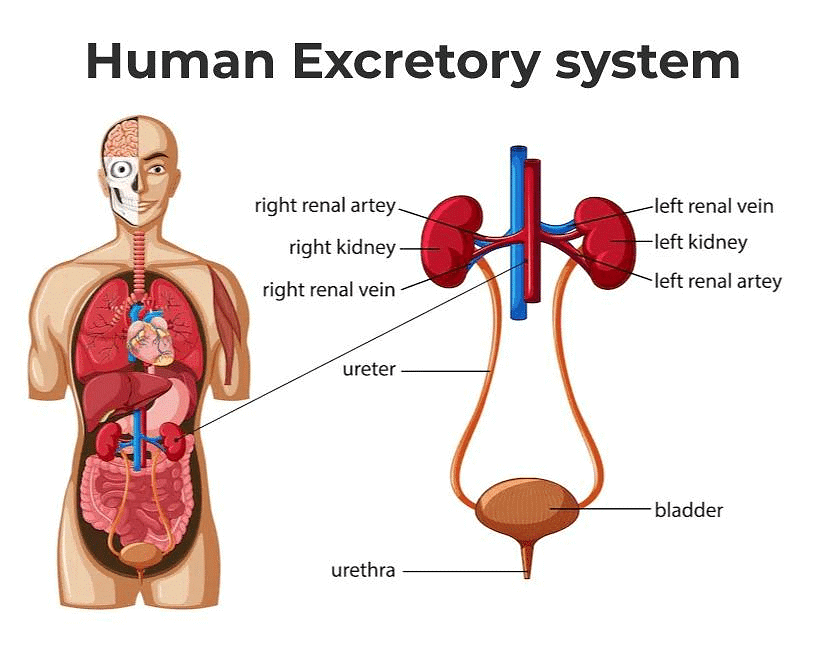
The biological process involved in the removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body is known as excretion. Different organisms employ various strategies for this purpose. In complex multicellular organisms like humans, specialized organs carry out this function. 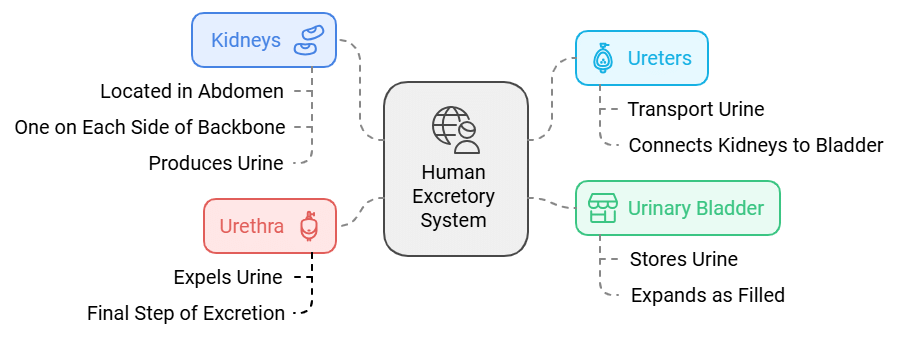
The excretory system of humans comprises a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra. The kidneys are situated in the abdomen, one on each side of the backbone. Urine produced in the kidneys travels through the ureters to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled through the urethra.
Functions of the Kidneys
- Each kidney contains numerous filtering units called nephrons, densely packed together.
- Each nephron consists of a cup-shaped structure known as Bowman’s capsule (which contains a cluster of capillaries called glomerulus), a convoluted tube, and a collecting duct.
- As the glomerular filtrate moves through the nephron's tubular part, useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, mineral ions, and water are reabsorbed by the blood capillaries surrounding the nephron.
- Each kidney filters approximately 180 liters of blood daily, but only about one to two liters of urine is excreted since the rest of the filtrate is reabsorbed by kidney tubules.
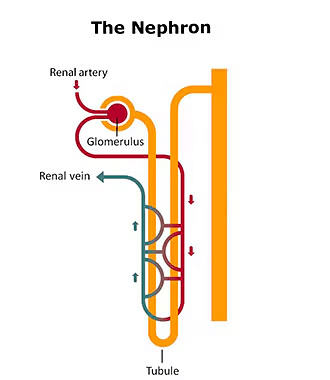
- The kidneys play a crucial role in excretion, filtering soluble nitrogen compounds as waste products.
- Kidneys perform two essential functions: (i) filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood, and (ii) osmoregulation, which maintains the appropriate balance of water and ions in the body.
- An artificial kidney is utilized to filter the blood of patients. The process of purifying blood using an artificial kidney is referred to as hemodialysis.
- The urinary bladder is muscular and regulated by the nervous system, allowing for the control of the urge to urinate.
Excretion in Plants
Plants employ completely different strategies for excretion than those of animals. Oxygen itself can be thought of as a waste product generated during photosynthesis! We have discussed earlier how plants deal with oxygen as well as carbon dioxide. They can get rid of excess water by transpiration.
- Plants use the fact that many of their tissues consist of dead cells.
- They can even lose some parts, such as leaves.
- Many plant waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles.
- Waste products may also be contained in leaves that fall off.
- Other waste products are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem.
- Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
|
80 videos|512 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Life Processes - 2 Chapter Notes - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the process of glycolysis and where does it occur in the cell? |  |
| 2. How does respiration in humans differ from that in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the main types of blood vessels in the human circulatory system? |  |
| 4. What role does lymph play in the human body? |  |
| 5. How do excretion processes differ in humans and plants? |  |