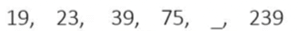Summary & Examples: Number Series | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Number Series is an important topic in competitive exams, with a specific focus as five questions are dedicated solely to this section. It holds significant importance in various exams. Candidates preparing for competitive exams can secure 4-5 marks in just 2-3 minutes by understanding the different types and patterns of number series in both reasoning and quantitative aptitude.
What is Number Series?
- A number series is a sequence of numbers that follow a specific pattern or rule. The sequence can involve various arithmetic or mathematical operations, and the goal is usually to identify the underlying rule or relationship between the numbers.
- In number series, some numbers are mistakenly put into the series, and some numbers are missing. We need to observe first and then find the accurate number to that series.
- In many cases, the next number in the series can be predicted by recognizing the pattern.
- The sequence is the list of numbers written in a specific order.

Common Types of Number Series
Type 1: Addition / Subtraction or Multiplication / Division
These series follow the pattern of addition or subtraction of even or odd numbers. In these number series, each term in the sequence is derived by applying a specific mathematical operation, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division, to the previous term.
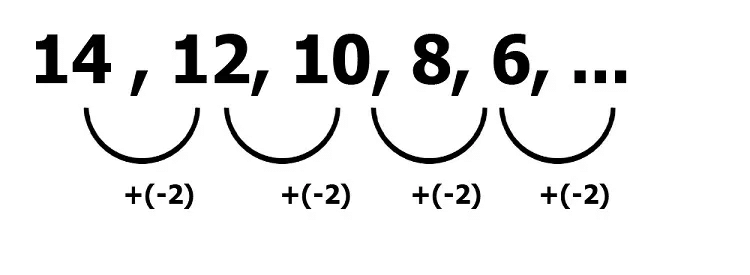
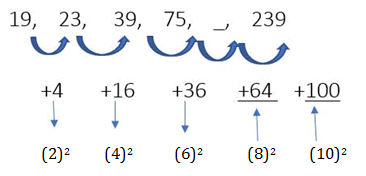
Example 1: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
19, 23, 39, 75, ? , 239.
The most common trick to solve a number series is to solve by checking the difference between two adjacent numbers, but the difference could not only lead to addition/subtraction, but it can also be with multiplication/division.
Therefore, to check whether to think addition-wise or multiplication-wise in increasing sequence, one must assume with the help of the difference between the first and last number of the given sequence.
If the difference seems to be less according to the number of steps used to make the last number from the first, then we should check the addition.
If the difference seems to be large, one must check the multiplication trick between the adjacent numbers.
In Example 1, given above,
The difference between first no. (19) and last number (239) is 220.
Now, a question will arise on how we will assume whether the difference is more or less. We observe the number of steps required to start from the first number till the last number.
In Example 1, 19 becomes 239 in five steps , one of which we have to find out
The difference of 220 between 19 and 239 in five steps logically gives priority to addition over multiplication in an increasing sequence like this.
75 + 64 = 139, 139 + 100 = 239
139 is the correct answer.
Example 2: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
10, 31, 95, 288, ? , 2609
As we can see in the above example, the difference between the first number (10) and the last number (2609) is 2599 in five steps, which indicate us to check multiplication trick between the numbers.
It seems that the terms follow a pattern
10 * 3 + 1 = 31
31 * 3 + 2 = 95
95 * 3 + 3 = 288
288 * 3 + 4 = 868
868 * 3 + 5 = 2609
So the missing term is (288*3) + 4 = 868
Note : While checking multiplication trick always start from right end of the sequence.
Example 3: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
30, 34, 43, 59, 84, 120, ?
(a) 169
(b) 148
(c) 153
(d) 176
(e) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
By analyzing the given series, we observe the differences between consecutive terms:
34 - 30 = 4
43 - 34 = 9
59 - 43 = 16
84 - 59 = 25
120 - 84 = 36
The differences between consecutive terms follow a clear pattern of consecutive perfect squares:
4 = 2², 9 = 3², 16 = 4², 25 = 5², 36 = 6².We can predict the next difference should be the next perfect square, which is 7² = 49.
Therefore, the missing term is:
120 + 49 = 169.Thus, the correct answer is 169 (Option a).
Example 4: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
40, 54, 82, ? , 180, 250.
(a) 142
(b) 124
(c) 136
(d) 163
(e) None of these
Correct Answer: Option (b)
Explanation:
Let's examine the differences between consecutive terms:54 - 40 = 14
82 - 54 = 28
Notice that the difference between terms is increasing:
The first difference is 14 and the second difference is 28 (which is 14 × 2)
The difference between consecutive terms is increasing by a multiple of 14. So, the next difference should be 42(which is 14 × 3).
Therefore, the missing term is:
82 + 42 = 124.The next difference should then be 56 (42 + 14), and:
124 + 56 = 180, which matches the next given term in the series.Thus, the correct answer is 124 (Option b).
Example 5: Find the wrong number in the below-mentioned series:
0, 1, 3, 8, 18, 35, 264
(a) 264
(b) 35
(c) 18
(d) 8
(e) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
There is a pattern in difference between the consecutive numbers:
0 - 1 = 1 ← 02 + 1
1 - 3 = 2 ← 12 + 1
3 - 8 = 5 ← 22 + 1
8 - 18 = 10 ← 32 + 1
18 - 35 = 17 ← 42 + 1
Next difference should be 52 + 1 i.e. 26.
35 - 61 = 26 ← 52 + 1
From above the correct sequence would be: 0, 1, 3, 8, 18, 35, 61 and
so, the wrong number is: 264
Example 6: Find the wrong number in the below-mentioned series:
6, 7, 9, 13, 26, 37, 69
Options:
(a) 7
(b) 26
(c) 69
(d) 37
(e) 9
Correct Answer: Option (b)
Explanation:
The pattern in the series follows a progression based on doubling the difference between consecutive terms:7 - 6 = 1
9 - 7 = 2
13 - 9 = 4
26 - 13 = 13 (This is the incorrect difference)
37 - 26 = 11
69 - 37 = 32
The correct pattern should have doubled the previous difference. The correct progression should be:
+1, +2, +4, +8, +16, +32
Therefore, the number should be 21 in place of 26
Thus, the wrong number is 26 (Option b).
Example 7: Find the wrong number in the below-mentioned series:
1, 3, 10, 36, 152, 760, 4632
Options:
(a) 3
(b) 36
(c) 4632
(d) 760
(e) 152
Correct Answer: Option (d)
Explanation:
The pattern in the series follows the multiplication of each term with an increasing integer and adding an increasing even number:1 × 1 + 2 = 3
3 × 2 + 4 = 10
10 × 3 + 6 = 36
36 × 4 + 8 = 152
152 × 5 + 10 = 770
760 × 6 + 12 = 4632
The pattern is: ×1 +2, ×2 +4, ×3 +6, ×4 + 8, ×5 +10, ×6 + 12, …
Following this pattern, the correct number should be 770 in place of 760.
Thus, the wrong number is 760 (Option d).
Type 2: Perfect Square or Perfect Cube
A number is a perfect square if its square root is a whole number, and a number is a perfect cube if its cube root is a whole number.
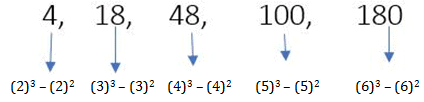
Example 8 : 4, 18, 48, 100, 180, ___.
If case Type-1 is not applicable in a sequence, then in the next step, we must compare given numbers or their differences to the square or cube of natural numbers, as in the above example.
The expression for each term is in the form of:
(2³) - (2²), (3³) - (3²), (4³) - (4²), (5³) - (5²), (6³) - (6²)
Let's break down the calculations:
For the first term: (2³) - (2²) = 8 - 4 = 4 (which matches the first term)
For the second term: (3³) - (3²) = 27 - 9 = 18 (which matches the second term
For the third term: (4³) - (4²) = 64 - 16 = 48 (which matches the third term)
For the fourth term: (5³) - (5²) = 125 - 25 = 100 (which matches the fourth term)
For the fifth term: (6³) - (6²) = 216 - 36 = 180 (which matches the fifth term)
Therefore, for the sixth term (7)3-(7)2 = 294, is the correct answer.
(a) Perfect Square Series:
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer, such as 1, 4, 9, 16, and so on. These numbers form the perfect square series, where each term is the square of consecutive integers (1², 2², 3², etc.).
Example 9: In the following options, a few number series are present. One of them has an error; pick the wrong one out:
(a) 3, 9, 15, 21
(b) 9, 81, 225, 441
(c) 441, 529, 676, 841
(d) 900, 841, 784, 729
Answer: (c)
Solution:
Let's analyze each series one by one:Series (a):
3, 9, 15, 21
This is an Arithmetic Progression (A.P.) where the common difference is 6.
Each term is increasing by 6, so this series is correct.Series (b):
9, 81, 225, 441
This is a perfect square series:
9 = 3², 81 = 9², 225 = 15², 441 = 21².
So, this series is also correct.Series (c):
441, 529, 676, 841
This is also a perfect square series, but the squares don't follow the correct pattern.
441 = 21², 529 = 23², 676 = 26², 841 = 29².
If we observe, the numbers should be in increasing order of squares (with no gaps), but instead of 841, we should have 900 = 30².
So, this is the incorrect series.Series (d):
900, 841, 784, 729
This is a perfect square series:
900 = 30², 841 = 29², 784 = 28², 729 = 27².
This series is correct as the numbers follow the pattern of perfect squares in descending order.Thus, the wrong series is Option (c), because the square of 30 (900) should be in place of 841.
Example 10: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
841, ?, 2401, 3481, 4761
Answer: 1521
Solution:
These numbers are squares of certain integers:841 = 29²
The missing term is 1521 = 39²
2401 = 49²
3481 = 59²
4761 = 69²
The missing number is 1521.
8, 12, 21, 37, __
Example 11: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
1, 9, 25, ?, 81, 121
Answer: 49
Solution:
These numbers are squares of certain integers:1 = 1²
9 = 3²
25 = 5²
The missing term is 49 = 7²
81 = 9²
121 = 11²
The missing number is 49.
Example 12: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
289, 225, 169, ?, 81
Answer: 121
Solution:
These numbers are squares of certain integers:289 = 17²
225 = 15²
169 = 13²
The missing term is 121 = 11²
81 = 9²
Numbers are decreasing by 2
Thus missing number is 121.
(b) Perfect Cube Series:
A perfect cube is a number that can be expressed as the cube of an integer, such as 1, 8, 27, 64, and so on. The perfect cube series follows the same pattern, where each term is the cube of consecutive integers (1³, 2³, 3³, etc.)
Example 13: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
3375, ?, 24389, 46656, 79507
Answer: 10648
The given numbers seem to be cubes:
3375 = 15³
The missing number is unknown.
24389 = 29³
46656 = 36³
79507 = 43³
Now, we observe that the numbers in the series are increasing by cubes of consecutive integers.
The pattern follows cubes of integers:
15³, ?, 29³, 36³, 43³.If we examine the progression of the integers, we see that they increase by 7. The missing number must therefore correspond to 22³, which is 10648.
Thus, the missing number is 10648.
Example 14: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
729, 6859, 24389, ?, 117649, 205379
Answer: 59319
Again, we look at the cube roots of the given numbers:
729 = 9³
6859 = 19³
24389 = 29³
The missing number is unknown.
117649 = 49³
205379 = 59³
The pattern follows cubes of integers:
9³, 19³, 29³, ?, 49³, 59³.
If we observe, the integers increase by 10. Therefore, the integer between 29 and 49 is 39 (as it follows the pattern).
So, the missing number corresponds to 39³.
39³ = 59319.Thus, the missing number is 59319.
Example 15: What should come in place of the question mark in the following series:
1000, 8000, 27000, 64000, ?
Answer: 125000
These numbers are cubes of integers:
1000 = 10³
8000 = 20³
27000 = 30³
64000 = 40³
The pattern follows cubes of consecutive multiples of 10:
10³, 20³, 30³, 40³.
Following this pattern, the next number should be 50³ = 125000.
Thus, the missing number is 125000.
Type 3: Factorisation / Prime Factorisation
If Type 1 and Type 2 are not applicable in a sequence, one must try to make factors of the numbers in the next step. A prime factorization series involves expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. For example:
12 = 2 × 2 × 3 (Prime factorization of 12)
18 = 2 × 3 × 3 (Prime factorization of 18)
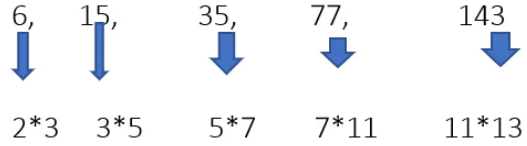
Example 16: 6, 15, 35, 77, 143, __.
In the above example, all the previous tricks are not applicable to get an answer.
Hence, We will make factors of the given numbers.
(2,3,5,7,11,13) all are prime numbers in ascending order.
Hence, 13*17 = 221, is the correct answer.
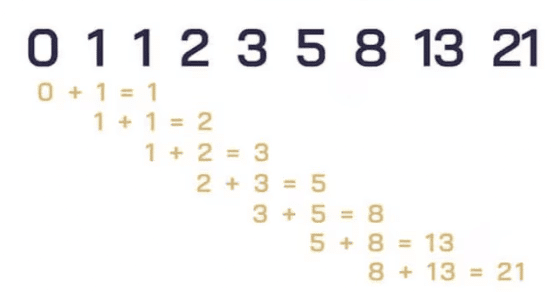
Type 4: Fibonacci Series
- A series in which a number is made by using the previous two numbers is called a Fibonacci series.
- An example of fibonacci series is 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
- Each term is the sum of the previous two terms.
Example 17: 1, 4, 5, 9, 14, 23, ___
Answer: 37
Let's observe the pattern in the sequence:
1 (first term)
4 (second term)
5 (third term): The sum of the first and second terms: 1 + 4 = 5
9 (fourth term): The sum of the second and third terms: 4 + 5 = 9
14 (fifth term): The sum of the third and fourth terms: 5 + 9 = 14
23 (sixth term): The sum of the fourth and fifth terms: 9 + 14 = 23
In the above sequence, all the numbers are the sum of the previous two numbers. Now, to find the next number, we add the fifth and sixth terms:
23 + 14 = 37
Thus, the next number in the sequence is 37.
Type 5: Sum of Digits
In a sum of digits number series, the sequence may follow a pattern based on the sum of the digits of each number.
Some common types of sum of digits series could include:
- A series where each term is the sum of the digits of the previous number.
- A series where the sum of digits of numbers increases or decreases in a regular pattern.
Example 18: Find the next term.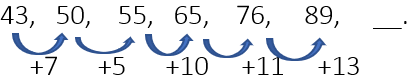
In the given sequence, we calculate the difference between consecutive terms. Upon observation, we notice that the differences for the 1st, 3rd, and 5th terms follow an increasing pattern: +7, +10, +13 (increasing by +3 each time). Similarly, for the 2nd and 4th terms, the differences are +5 and +11 (increasing by +6 ).
Based on this, we predict that the next difference (for the 6th term) will follow the same increasing pattern and be +17. ( +5, +11, +17 and so on)
Thus, the next term is calculated as:
89 + 17 = 106
Example 19: Find the next term.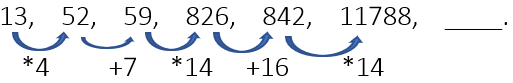
If we disregard the first number and focus on the pattern, we observe that the additions are +7 and +16. The difference between these two additions is 9. Following this, the third addition should be +25, which is an increase of 9 from the previous difference. Thus, the next step is to add 25 to the 6th number in the sequence.
Therefore, the correct calculation is 11788 + 25 = 11813.
Hence, the missing number is 11813.
Type 6: Alternate Pattern Series
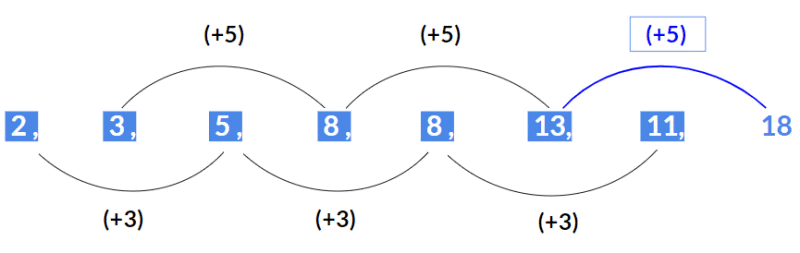
- When numbers given as a hint in a question are more or when a question asks two numbers of a series or the same number comes twice in a series, these all give a hint to alternate pattern series.
Example 20: Find the next terms.
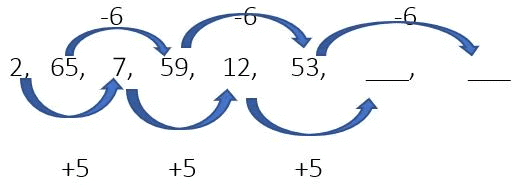
Alternate numbers are increasing by the common sum. i.e +5 and -6.
So the next two numbers are 12+5 = 17, 53-6 = 47
Ans. 17, 47
Example 21: Find the next terms.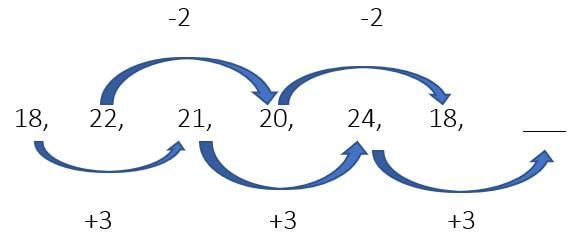
Alternate numbers are increasing by the common sum. i.e +3 and -2.
So, the next number is 24+3 = 27
Ans. 27
Type 7: Decimal Pattern Series
In a decimal pattern series, the terms may involve operations like:
- Multiplying or dividing by powers of 10 (e.g., 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, etc.)
- Adding or subtracting decimals in a regular pattern (e.g., 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, etc.)
- Incrementing or decrementing decimal numbers by a constant or variable amount.
Example 22 : Simple Decimal Series (Increment by 0.1)
Series: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, ___
Solution:
This is an arithmetic series where each term is increasing by 0.1.
- 0.1 + 0.1 = 0.2
- 0.2 + 0.1 = 0.3
- 0.3 + 0.1 = 0.4
Therefore, the next term is:
- 0.4 + 0.1 = 0.5
Thus, the complete series is: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5.
Example 23: Decimal Series with Multiplication by Powers of 10
Series: 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, ___
Solution:
Each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by 1/10 or dividing by 10.
- 1 × 0.1 = 0.1
- 0.1 × 0.1 = 0.01
- 0.01 × 0.1 = 0.001
Thus, the next term is:
- 0.001 × 0.1 = 0.0001
Therefore, the complete series is: 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001.
Example 24: Find the missing term.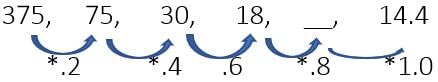
We can observe the multiplication between the numbers. Pattern is the multiplication of 0.2, 0.4, 06, 0.8 and so on
So, the answer is 18 * 0.8 = 14.4
Example 25: Find the next term.
16, 24, 60, 210, 945, __
The pattern is:
16 x 1.5 = 24
24 x 2.5 =60
60 x 3.5 = 210
210 x 4.5 = 945
945 x 5.5 = 5197.5The missing number is 5197.5
Type 8: Bracket Pattern Series
These series often combine both arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.) and the concept of grouping numbers using brackets, resulting in a sequence that follows a specific pattern. While using the bracket pattern, we might multiply the number or do addition or subtraction before multiplying.
Example 26: 3, 28, 180, ____, 3676
The pattern is :
(3+1)x7 = 28
(28+2)x6 =180
(180+3)x5 = 915
(915+4)x4 = 3676
Ans. 915
Example 27: 37, 31, 52, 144, __, 2810
The pattern is :
(37-6)x1=31
(31-5)x2=52
(52-4)x3=144
(144-3)x4=564
(564-2)x5=2810
Ans. 564
Type 9: Dual Pattern Series
A dual pattern series refers to a sequence of numbers that follows two different patterns or operations alternately. The pattern of the first series can also be used to find the missing numbers of the second series.
Example 28:
15, 9, 8, 12, 36, 170
19, a, b, __, d, e,
The pattern is :
(15-6)x1=9
(9-5)x2=8
(8-4)x3=12
Similarly:
(19-6)x1=13
(13-5)x2=16
(16-4)x3=36
Ans. 36
Type 10: Factorial Based Series
A factorial number series is a sequence where each term is the factorial of a number. The factorial of a number (denoted as n!) is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to that number.
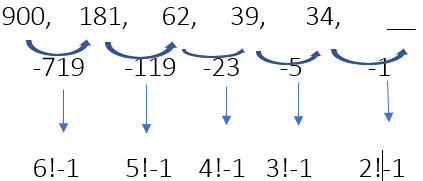
Example 29: Find the next term.
Ans. 34-1= 33The first term, 900, is based on 6! - 1.
The second term, 181, is based on 5! - 1.
The third term, 62, is based on 4! - 1.
The fourth term, 39, is based on 3! - 1.
The fifth term, 34, is based on 2! - 1.
The sixth term should be 33
Example 30: Find the next term.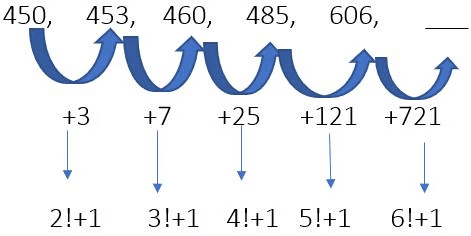
Ans. 1327
The pattern involves adding factorials to the numbers:
2! + 1 = 2 × 1 + 1 = 3
The first term is 450. Adding 3 to it gives:
450 + 3 = 453.3! + 1 = 6 + 1 = 7
The second term is 453. Adding 7 gives:
453 + 7 = 460.4! + 1 = 24 + 1 = 25
The third term is 460. Adding 25 gives:
460 + 25 = 485.5! + 1 = 120 + 1 = 121
The fourth term is 485. Adding 121 gives:
485 + 121 = 606.Now, for the missing term: 6! + 1 = 720 + 1 = 721
The fifth term is 606. Adding 721 gives:
606 + 721 = 1327.
Type 11: Arithmetic Series
A series in which the next term is obtained by adding or subtracting a constant number to its previous term.
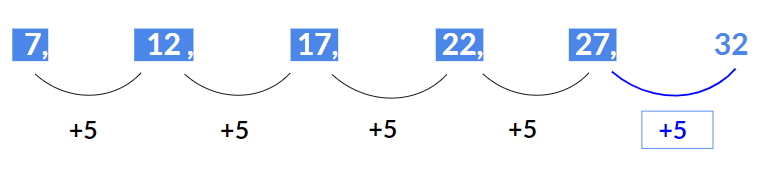
Example 31: Find the next term 7, 12, 17, 22, 27, ?
Solution:
The above series is an Arithmetic series where 5 is added to each term to get the next term i.e.12 = 7 + 5
17 = 12 + 5
22 = 17 + 5
27 = 22 + 5
Hence, the next term will be 27 + 5 = 32
Example 32: Write the missing term 29, 23, 17, 11, ?
Solution:
The above series is an Arithmetic series where 6 is subtracted from each term to get the next term i.e.29 – 6 = 23
23 – 6 = 17
17 – 6 = 11
Hence, next term will be 11 - 6 = 5.
Type 11: Geometric Series
A series where each successive number is obtained by either multiplying or dividing the previous number by a specific number.
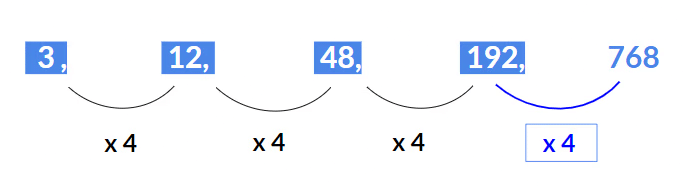
Example 33: Find the missing term 3, 12, 48, 192, ?
Solution:
Here, each number is multiplied by 4 to get the next number, i.e.12 = 3 x 4
48 = 12 x 4
192 = 48 x 4
Hence next term will be 192 x 4 = 768.
Example 34: Find the next term 729, 243, 81, 27, ?
Solution.
Here each number is divided by 3 to get the next number.729/3 = 243
243/3 = 81
81/3 = 27
Hence next term will be 27/3 = 9
Type 12: Mixed Series
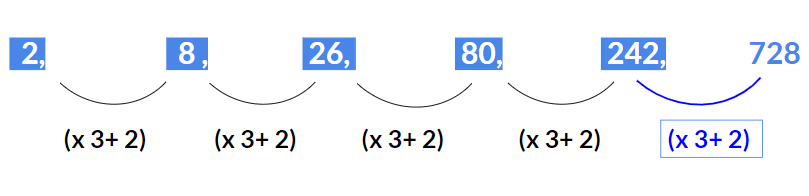
A series where more than one pattern is arranged in a single series.Example 35: Find the missing term 2, 8, 26, 80, 242, ?
Solution:
Here the pattern is (x 3 + 2).2 x 3 + 2 = 8
8 x 3 + 2 = 26
26 x 3 + 2 = 80
80 x 3 + 2 = 242
Hence missing term will be 242 x 3 + 2 = 728
Example 36: Find the next term 5, 12, 27, 59, ?
Solution:
Here each term is multiplied by 2 and consecutive prime numbers are added.5 x 2 + 2 = 12
12 x 2 + 3 = 27
27 x 2 + 5 = 59
Hence next term will be 59 x 2 + 7 = 125
Type 13: Arithmetic – Geometric Series
A series that is a combination of Arithmetic and Geometric series.
Example 37: Find the next term 3, 5, 10, 12, 24, 26, ?
Solution:
Here the pattern is (+ 2, x 2, + 2, x 2 …..)
- 3 + 2 = 5
- 5 x 2 = 10
- 10 + 2 = 12
- 12 x 2 = 24
- 24 + 2 = 26
Hence, the next term will be 26 x 2 = 52
Type 14: Alternate Series
A series where two series are combined into a single series.
Example 38: Find the next term 2, 3, 5, 8, 8, 13, 11, ?
Solution:
Here alternate terms starting with 2 form an Arithmetic series with a common difference of +3. (2, 5, 8, 11)
Also, alternate terms starting with 3 form another Arithmetic series with a common difference as +5. ( 3, 8, 13,..)Hence next term will be 18.
Example 39: Find the next term 3, 5, 7, 10, 11, 15, 15, ?
Solution:
Here, alternate terms starting with 3 form an Arithmetic series with a common difference of +4 (3, 7, 11, 15)
Also, alternate terms starting with 5 form a Geometric series with a common ratio of +2 (5, 10, 15)
Hence, the next term will be 15 + 5= 20.
Type 15: Prime Number Series
A series is based on prime numbers in a specific order, and generally, one number is missing or wrongly placed.
Example 40: Find the next term of the series 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, ……...
Solution:
- In the above series, all numbers are odd, but we don’t have 9 after 7.
- Therefore, we need to look for some other pattern.
- We observe all numbers are prime; hence, it’s a prime number series, and the next term will be 17.
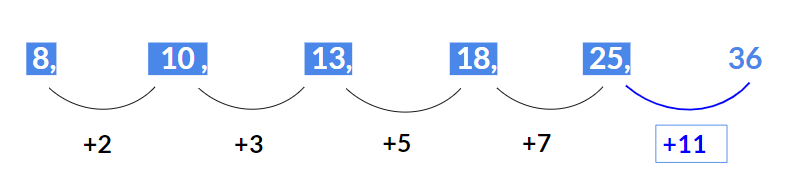
Example 41: Find the term in place of the question mark 8, 10, 13, 18, 25, ?
Solution:
Here the difference between consecutive terms :10 – 8 = 2
13 – 10 = 3
18 – 13 = 5
25 – 18 = 7.
Hence the differences 2, 3, 5 , 7 form a prime number series.
Hence the next difference should be the next prime number after 7, which is 11.
Therefore, the next missing term will be 25 + 11 = 36.
Example 42: 5 , 24 , 122 , 340, ?
Solution:
In the above series, the pattern that is being followed is as given below:First term 5 = 23 – 3
Second term 24 = 33 – 3
Third term 122 = 53 – 3
Fourth term 340 = 73 – 3
We observe that the series is [(prime)3 – 3].
Hence, the next term should be 113 – 3 = 1331 - 3 = 1328.
Important Points to Remember
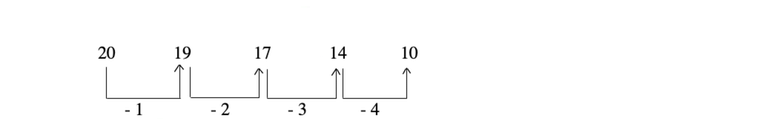
1. If the change is slow or gradual, then it is a difference series.
e.g.
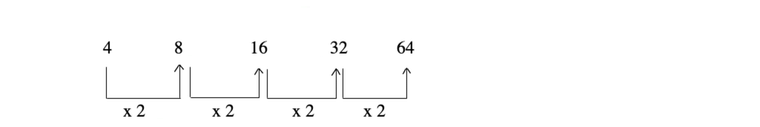
2. If the change is equally sharp, then it is a ratio series.
e.g.
3. If the rise is sharp initially, but slows down later, then it is formed by adding squared or cubed numbers.
e.g.
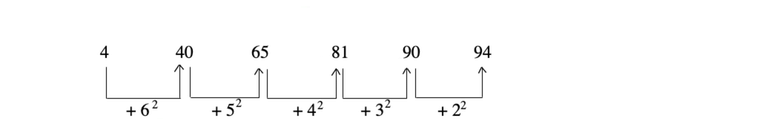
4. If the series is alternating, then it may be either a mixed series or two different operations going on alternately.
e.g.
(2,3,5,7,11,13) All are prime numbers in ascending order.
Hence, 13*17 = 221 is the correct answer.
Tips:
Here are some tips for solving number series problems:
- Identify the Pattern: Look for arithmetic (addition/subtraction), geometric (multiplication/division), or alternating patterns.
- Check Differences: Subtract consecutive terms to find a common difference (arithmetic), or check second/third differences for quadratic or cubic patterns.
- Factorial Patterns: Look for terms involving factorials (1!, 2!, 3!, etc.).
- Powers and Roots: Check for squares, cubes, or square roots.
- Multiplicative/Divisive Patterns: Look for terms obtained by multiplying or dividing by a constant.
- Special Sequences: Recognize sequences like Fibonacci or primes.
- Trial and Error: Test different operations to find a matching pattern.
- Work Backwards: If stuck, try working from the end of the series to the beginning.
- Practice: Regular practice helps improve pattern recognition and speed.
These strategies will help you tackle most number series problems efficiently.
|
207 videos|276 docs|138 tests
|
FAQs on Summary & Examples: Number Series - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What are the different types of number series? |  |
| 2. How do you identify an addition or subtraction series? |  |
| 3. What is the Fibonacci series, and how is it generated? |  |
| 4. How can perfect squares or cubes be identified in a number series? |  |
| 5. What is an alternate pattern series, and how does it work? |  |