Laxmikanth Summary: National Human Rights Commission | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Establishment of the NHRC
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is a statutory body, not a constitutional one.
- It was established in 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993, enacted by the Parliament.
- The NHRC serves as the watchdog for human rights in India, overseeing rights related to life, liberty, equality, and dignity of individuals, as guaranteed by the Constitution or international covenants enforceable by Indian courts.
- The specific objectives for establishing the commission include:
- Strengthening institutional arrangements to address human rights issues more effectively and comprehensively.
- Investigating allegations of government excesses independently, demonstrating the government's commitment to protecting human rights.
- Complementing and enhancing existing efforts to protect and promote human rights.
International Covenants refer to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights. These were adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on December 16, 1966. The Indian government agreed to these covenants on April 10, 1979. Additionally, the term may include other covenants or conventions adopted by the UN General Assembly as specified by the Central Government.
Composition of the Commission
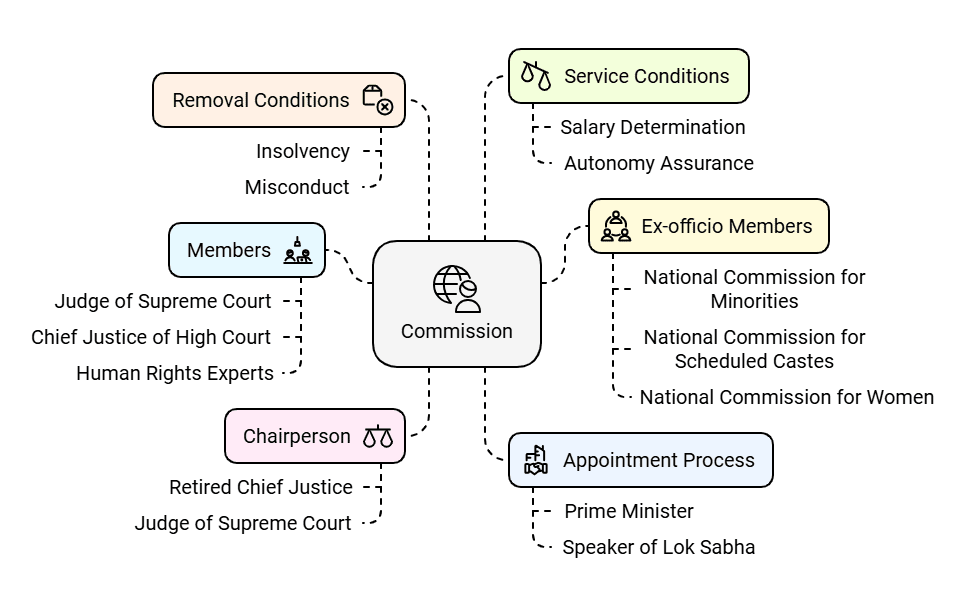
- The commission is made up of multiple members, including a chairperson and five members.
- The chairperson must be a retired chief justice of India or a judge of the Supreme Court.
- The members should include:
- a serving or retired judge of the Supreme Court,
- a serving or retired chief justice of a high court, and
- three individuals with knowledge or practical experience in human rights (at least one of whom must be a woman).
- In addition to these full-time members, the commission has seven ex-officio members:
- The chairpersons of the National Commission for Minorities,
- the National Commission for Scheduled Castes,
- the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes,
- the National Commission for Women,
- the National Commission for Backward Classes, and
- the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights.
- The Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities.
- The President appoints the chairperson and members based on the recommendations of a six-member committee, which includes:
- the prime minister,
- the Speaker of the Lok Sabha,
- the Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha,
- the leaders of the Opposition in both Houses of Parliament, and
- the Central home minister.
- A sitting judge of the Supreme Court or a sitting chief justice of a high court can be appointed only after consulting the Chief Justice of India.
- The chairperson and members serve a term of three years or until they reach the age of 70, whichever comes first, and they are eligible for reappointment.
- After their tenure, they are not eligible for further employment under the Central or state governments.
- The President can remove the chairperson or any member under certain circumstances, such as:
- insolvency,
- engaging in paid employment outside their duties,
- infirmity of mind or body,
- being declared of unsound mind by a competent court, or
- conviction and sentencing for an offense.
- Additionally, the President can remove the chairperson or a member for proved misconduct or incapacity, but these cases must be referred to the Supreme Court for inquiry.
- The Supreme Court's recommendation is necessary for removal in such cases.
- The Central government determines the salaries, allowances, and other conditions of service for the chairperson and members, but these cannot be varied to their disadvantage after appointment.
- These provisions aim to ensure the autonomy, independence, and impartiality of the Commission's functioning.
Functions of the Commission
The functions of the Commission include:
- Inquiring into violations: The Commission can investigate any violation of human rights or negligence in preventing such violations by a public servant, either on its own initiative, based on a petition, or by court order.
- Intervening in legal proceedings: The Commission has the authority to intervene in court cases involving allegations of human rights violations.
- Visiting jails and detention facilities: The Commission can visit jails and other detention places to assess the living conditions of inmates and make recommendations for improvements.
- Reviewing legal safeguards: The Commission reviews constitutional and legal safeguards for protecting human rights and suggests measures for their effective implementation.
- Examining factors inhibiting human rights: The Commission studies factors, including acts of terrorism, that hinder the enjoyment of human rights and recommends remedial actions.
- Studying international treaties: The Commission analyzes international treaties and instruments related to human rights and recommends ways for their effective implementation.
- Promoting research: The Commission undertakes and promotes research in the field of human rights.
- Spreading human rights awareness: The Commission works to increase awareness of human rights and the safeguards available for their protection among the general public.
- Supporting NGOs: The Commission encourages the efforts of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) working in the field of human rights.
- Undertaking additional functions: The Commission can perform any other functions it deems necessary for promoting human rights.
As part of its primary objective to protect and promote human rights, the Commission is actively working to raise awareness about human rights across the country. This effort is supported by civil society, NGOs, human rights activists, and the media. The Commission's initiatives, such as camp sittings and open hearings in various regions, aim to deliver justice to victims of human rights violations directly.
The complaints received by the Commission cover a wide array of issues, including:
- Alleged human rights violations due to negligence by public servants.
- Custodial deaths and torture.
- Fake encounters and police misconduct.
- Violations by security forces.
- Conditions in prisons.
- Atrocities against women, children, and vulnerable groups.
- Communal violence.
- Bonded and child labor.
- Non-payment of retirement benefits.
- Negligence by public authorities.
- Atrocities against Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
The Commission also takes note of incidents reported in the media and those brought to its attention by its officials during visits to different parts of the country.
Working of the National Human Rights Commission
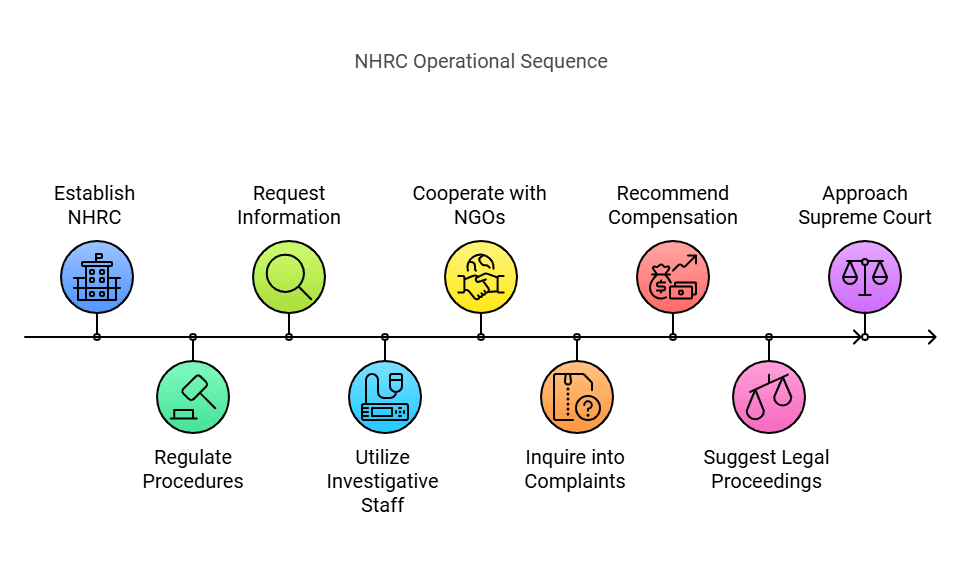
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is headquartered in Delhi, but it has the authority to establish offices in other locations across India.
- The NHRC is responsible for regulating its own procedures and operates with the powers of a civil court, giving its proceedings a judicial character.
- It can request information or reports from the Central and state governments or any subordinate authorities.
- The commission has its own investigative staff to look into complaints of human rights violations, but it can also utilize officers or investigation agencies from the Central or state governments.
- The NHRC has established effective cooperation with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that have firsthand information about human rights violations.
- However, the commission cannot inquire into matters that occurred more than one year prior to the complaint.
During or after an inquiry, the NHRC can take several actions:
- Recommend compensation or damages to the victim from the concerned government or authority.
- Suggest legal proceedings or other actions against guilty public servants.
- Propose interim relief for the victim.
- Approach the Supreme Court or the relevant High Court for necessary directions, orders, or writs.
Role of the National Human Rights Commission
- The functions of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) are primarily recommendatory in nature. This means that the NHRC does not have the power to punish those who violate human rights or to provide any form of relief, including monetary compensation, to victims.
- While the NHRC's recommendations are not legally binding on the government or relevant authorities, they hold significant weight. The government is required to inform the NHRC about the actions taken in response to its recommendations within one month.
- A former member of the NHRC noted that although the commission's role is advisory, the cases it forwards are taken seriously by the government. This indicates that the NHRC, despite its limited powers, has substantial influence and authority. No government can easily disregard its recommendations.
- The NHRC's jurisdiction is also limited regarding human rights violations by members of the armed forces. In such cases, the commission can request reports from the Central government and make recommendations. The Central government is then obliged to inform the NHRC of the actions taken on these recommendations within three months.
- Additionally, the NHRC submits its annual or special reports to the Central and state governments. These reports are presented to the respective legislatures, accompanied by a memorandum detailing the actions taken on the commission's recommendations and the reasons for any non-acceptance.
Problems Faced by the National Human Rights Commission
1. Administrative Constraints: The commission adheres to the Paris Principles, which emphasize the need for National Human Rights Institutions to have appropriate infrastructure, including adequate funding and staff. This is essential for the commission's independence from the government and financial control, ensuring its impartiality in human rights matters.
- The commission handles around one lakh complaints each year, reflecting the growing trust of Indian citizens.
- To manage this increasing workload, there is a need to delegate more administrative and financial powers to the Chairperson of the commission.
2. Financial Constraints: The commission receives annual grants-in-aid from the Government of India, specifically from the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- While this provides a level of financial independence, the commission seeks greater autonomy, particularly in purchasing vehicles, which is currently not delegated.
3. Manpower Constraints: Since its establishment, the commission has never operated at its full sanctioned strength.
- Due to the high volume of complaints, it has been necessary to hire retired government officers as consultants on a contract basis.
- The commission is struggling to meet the expectations of victims of human rights violations and is unable to fulfill its mandate effectively.
- There is a need for the creation of various posts to enhance its operational capacity.
- The shortage of experienced investigating officers, who are supposed to be provided by the government, has impacted the commission's ability to conduct spot inquiries into incidents such as custodial deaths, torture, and illegal detentions.
- The Law Division, critical to the commission's functioning, is also facing challenges due to manpower shortages, affecting its ability to handle and dispose of a large number of complaints.
- In 2017, the Supreme Court expressed concern over the commission's manpower issues and urged the Government of India to address these concerns promptly.
|
154 videos|981 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: National Human Rights Commission - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India? |  |
| 2. How is the NHRC constituted and who are its members? |  |
| 3. What powers does the NHRC hold to investigate human rights violations? |  |
| 4. Can the NHRC take action against government authorities for human rights violations? |  |
| 5. How can individuals file a complaint with the NHRC? |  |






















