Introduction to Ethics | UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude PDF Download
What are 'Ethics'?
- At its simplest, ethics is a system of moral principles. The investigative study of 'What is the right thing to do?' They affect how people make decisions and lead their lives.
- The term 'ethics' is derived from the Greek word 'ethikos', which can mean custom, habit, character or disposition.
- Ethics is a moral principle system that helps us differentiate between right and wrong, good and bad, fair and unfair. These can be said to be the guiding light for human conduct.
- The change in human behaviour and action due to applying ethical principles helps us build a humane society where everyone can live in peace and harmony.
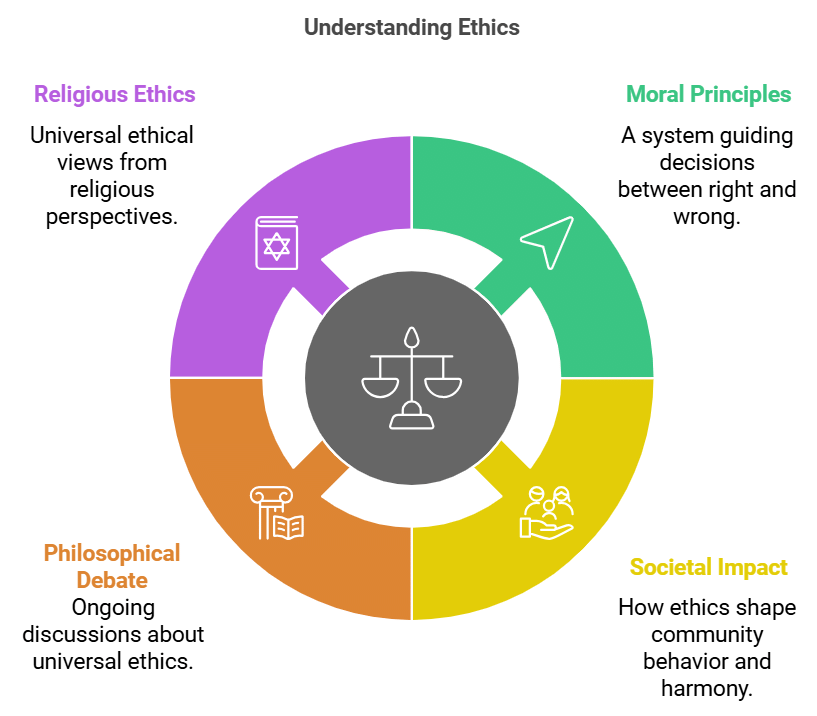
- Whether or not any universal moral principles can be applied irrespective of person or circumstance is a debate that philosophers have had throughout history.
- Every society has tried to codify the principles of good or acceptable conduct many times. Immoral or unacceptable behaviour has been discouraged or punished.
- Religious views on ethics, for example, tend to be universal. As proposed by Immanuel Kant (covered later), the concept of Categorical Imperative gives a test of determining an act's universality.
The Essence of Ethics
- The essence is the intrinsic nature or indispensable quality of something which determines its character. It implies the core of the substantive portion, the most important quality.
- The essence of ethics lies in the requirement of common ethical principles to ensure peace, harmony, and society's stability. It can be best reflected in values of accountability, empathy, honesty, integrity, probity, compassion etc.
- The most basic need for ethics lies in the fact that we do not automatically know what will benefit our lives and what will be detrimental.
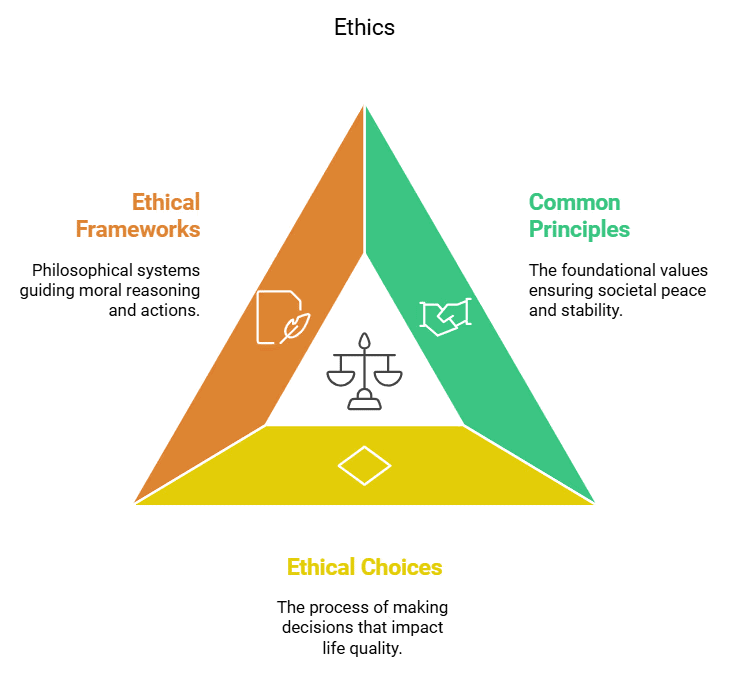
- We continuously face choices that affect the length and quality of our lives. We must choose our values, where to live, how to spend our time, whom to associate with, whom to believe? We must decide what to think about and how to achieve our goals. Which character traits to acquire, and which to eliminate? Which of our emotional responses are beneficial, and which, detrimental? What criteria should we judge others, and on what basis to interact with them? To the extent that we default on deliberation, we are at the mercy of social and emotional factors that may be far from optimal.
- Ethics or Moral philosophy contemplates what is wrong or right. As a discipline, it has three branches - Meta-ethics, Normative ethics and Applied ethics. Meta-ethics investigates the broader questions, such as 'how can morality be defined?', 'What is justice?' etc. Normative ethics is concerned with what we ought to do.
- It provides a framework for deciding what is right or wrong. Various philosophers have tried to give this framework through reasoning, e.g. deontological ethics of Kant, utilitarianism of Jeremy Bentham and Juan Stuart Mill, virtue ethics of Aristotle, et al. Finally, Applied Ethics deals with practical issues of moral importance such as capital punishment, surrogacy, and dilemmas in day-to-day life, etc.
Meta-Ethics
Deals with the “after” or “beyond, and questions such as: “What is goodness?” and “How can we tell good from bad?” It also questions the origin of ethical principles, whether they are human or divine in origin. It also deals with questions like: What are the meanings of ethical terms: right, wrong, love, compassion? It also questions whether moral judgments are universal or relative, and if they are of one kind or many.
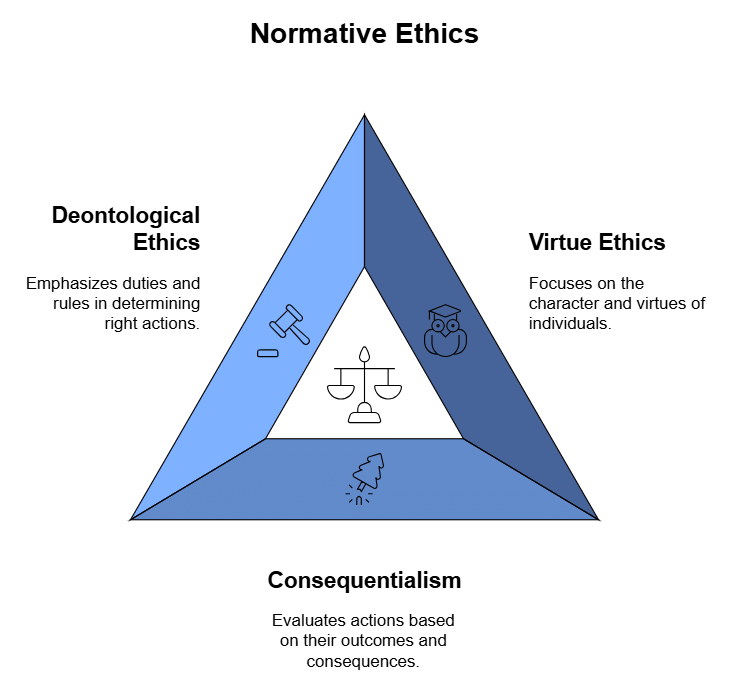
Prescriptive Ethics (Normative Ethics)
Normative Ethics is concerned with the criteria of what is right or wrong. IT includes the formulation of moral rules that directly implications for what human actions, institutions and ways of life should be like. It deals with questions like: How should people act? What is the correct action?
The different branches are:
- Virtue Ethics
- Consequentialism
- Deontological Ethics
Descriptive Ethics
Descriptive ethics studies people’s belief about morality. Describes and compares between objectives of different ethical theories. It deals with questions like: What do people think is right? It is different from normative and applied ethics.
Applied Ethics
Applied ethics is a philosophical examination from a moral standpoint of particular issues in private and public life that are moral judgments. This uses application of moral knowledge to practical problems and uses philosophical methods to identify the morally correct course of action in various fields of human life.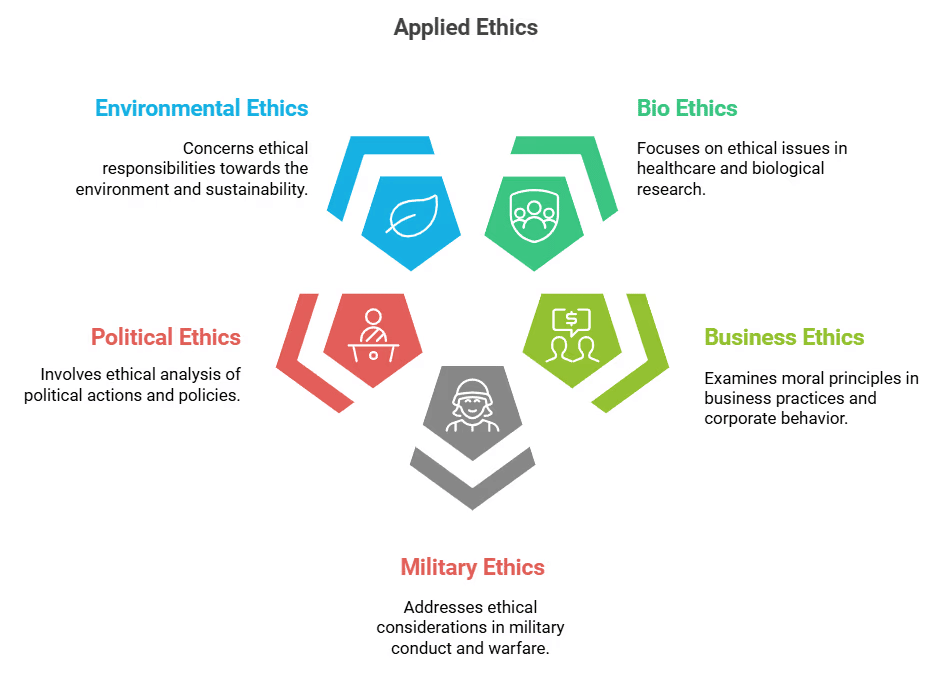
The different branches are:
- Bio Ethics
- Business Ethics
- Military Ethics
- Political Ethics
- Environmental Ethics
- Publication Ethics
|
78 videos|132 docs
|
FAQs on Introduction to Ethics - UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude
| 1. What is the definition of ethics? |  |
| 2. Why is ethics important in public administration? |  |
| 3. What are the main branches of ethics? |  |
| 4. How can ethical dilemmas be resolved? |  |
| 5. What role do cultural differences play in ethics? |  |






















