Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Notes > Communication System > Random Processes & Variables
Random Processes & Variables | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction to Random Process and variables
- The concept of a random process allows us to study systems involving signals that are not entirely predictable.
- A random process is the natural extension of the concept of a random variable when dealing with signals.
- A random process is a collection of time functions or signals corresponding to various outcomes of a random experiment.
- Random process represents the mathematical model of these random signals.
- A random process (or stochastic process) is a collection of random variables (functions) indexed by time.
- Random process can be denoted by X(t,s) or X(t), where s is the sample point of the random experiment and t is the time.
- A random variable is an outcome is mapped to a number whereas the Random process is an outcome is mapped to a random waveform that is a function of time.
- These random signals play a fundamental role in the fields of communications, signal processing, control systems, and many other engineering disciplines.
Types of classes of signals in deterministic signals
- Continuous-time and continuous amplitude signals: These are a function of a continuous independent variable, time. The range of the amplitude of the function is also continuous.
- Continuous-time and discrete amplitude signals: These are a function of a continuous independent variable, time—but the amplitude is discrete.
- Discrete-time and continuous amplitude signals: These are functions of a quantized or discrete independent time variable, while the range of amplitudes is continuous.
- Discrete-time and discrete amplitude signals: These are functions where both the independent time variable and the amplitude are discrete.
Mean Function
The mean function of a random process is the expected value of the process.
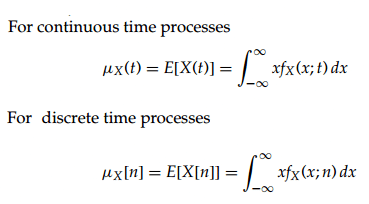
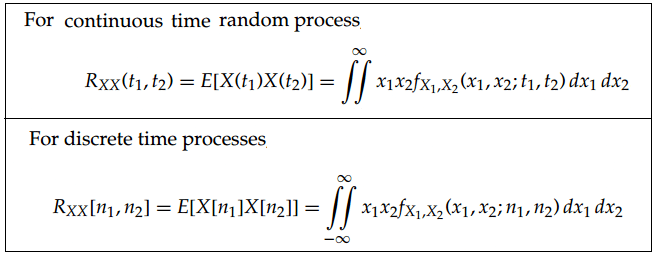
Auto-correlation function
- This represents the relation of a function with its shifted version.
- The autocorrelation function of the random process X(t), denoted by Rxx(t1 ,t2).
- Auto-correlation function is defined as the expected value of the product of X(t1) ,X(t2)
- Rxx(t1, t2) = E [X(t1) X(t2)]
Properties of Auto Correction Function
- The mean square value of a random process can be obtained from the auto-correlation function R(Z).
- R(Z) is even function Z.
- R(Z) is maximum at Z = 0 e.e. |R(Z)| ≤ R(0). In other words, this means the maximum value of R(Z) is attained at Z = 0.
- If R(Z) is the auto-correlation of a stationary random process {x(t)} with no periodic components and with non-zeros means then
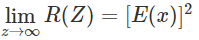
The short time auto-correlation function is usually computed using the following equation: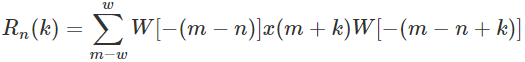
Stationary Process
A process whose statistical properties are independent of a choice of time origin is called as a stationary process.
- A random process is considered stationary (in the strict sense) if its specification is independent of time, i.e., if the joint probability density function of its sample values is independent of time.
- A process X(t) is called as strict-sense stationary, if the statistics of the process are invariant to a time shift.
- A process X(t) is called as wide-sense stationary (WSS), if the mean function and autocorrelation function are invariant to a time shift.
- mx (t) = E [X(t)] = constant (independent of t)
- Rxx (t1t2) depends only on the time difference τ = (t1 – t2) and not on t1 and t2 individually. Rxx (t + τ, t) = Rxx (τ)
- All strict sense stationary random processes are also WSS, provided that the mean and autocorrelation function exist.
- If mx(t) and Rxx (t + τ, t) are periodic with period t, the process is called as the cyclostationary process.
- Rx(0) gives power content of a power signal (if signal is power signal).
- Rx(0) gives energy content of the signal (if a signal is energy signal).
- Fourier transform of Rxx(τ) gives power spectral density for power signal and energy spectral density for energy signal.
Power and Energy of Random Signal
Power content of a random signal X is given by
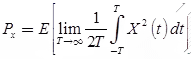

Energy content of random signal is given by
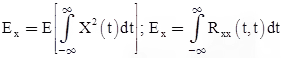
For the case of stationary processes, only power type process is of theoretical and practical interest.
Cross-Correlation
The cross correlation function between two random processes X(t) and Y(t) is
Rx,y(t1, t2) = E[X (t1) Y (t2)];
Rx,y(t1, t2) = Ry,x (t2, t1)
Random Processes and Linear Systems
Let random process X(t) is input to an LTI system having impulse response h(t) and y(t) is output of LTI system then

- If X(t) is stationary process then X(t) and Y(t) will be jointly stationary with
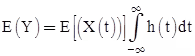
Rxy(τ) = Rx(τ) * h(–τ)
Rx(τ) * h(–τ)
Ry(τ) = Rx(τ) * h(–τ) * h(τ)
Sy(f) = Sx(f)|H(f)|2
where * represents convolution
Power Spectral Density
- A quantity that is related to the auto-correlation function is the power spectral density [PSD, Sxx(f)].
- Note that the power spectral density is only defined for a stationary random process.
- The PSD and the auto-correlation function form a Fourier transform pair.
- Power spectral density of random process X(t):
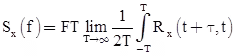
- If the two processes X(t) and Y(t) are uncorrected, then Rxy(τ) = E[X(t)] E[Y(t)], where X(t) and Y(t) are jointly stationary processes.
The document Random Processes & Variables | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) is a part of the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Course Communication System.
All you need of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) at this link: Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
|
13 videos|49 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Random Processes & Variables - Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is a random process? |  |
Ans. A random process is a mathematical model that describes the evolution of a system over time where the outcomes are uncertain. It is a collection of random variables indexed by time, and it provides a statistical description of how the variables change and interact with each other.
| 2. What is a random variable? |  |
Ans. A random variable is a variable that can take on different values based on the outcome of a random event. It represents the uncertain quantity or outcome of an experiment or observation. Random variables can be discrete, taking on a countable number of values, or continuous, taking on any value within a range.
| 3. How are random processes and random variables related? |  |
Ans. Random processes are often defined in terms of random variables. In a random process, the values of the random variables change over time or some other parameter. Each random variable represents the outcome of a specific time instance or parameter value. Random processes provide a statistical description of the behavior of these random variables over time.
| 4. What are some examples of random processes and variables? |  |
Ans. Some examples of random processes include stock market prices, weather patterns, radio signals, and network traffic. In these cases, the values of the random variables change over time, and the random process provides a statistical model for their behavior. Examples of random variables include the number of customers in a queue, the temperature at a certain location, and the outcome of a coin toss.
| 5. How are random processes and variables used in real-world applications? |  |
Ans. Random processes and variables are widely used in various fields such as engineering, finance, telecommunications, and physics. They are used to model and analyze systems with inherent randomness, allowing for predictions and decision-making under uncertain conditions. For example, in finance, random processes are used to model stock prices and exchange rates, while in telecommunications, they are used to analyze and optimize network performance.
Related Searches






















