Living and Non-Living Things Class 3 Notes Science
Introduction
Look around you! You can see trees, birds, toys, books, and even your friends. But do you know that some of these things are living and some are non-living? How can we say if something is living or non-living? Let's learn about these in detail.
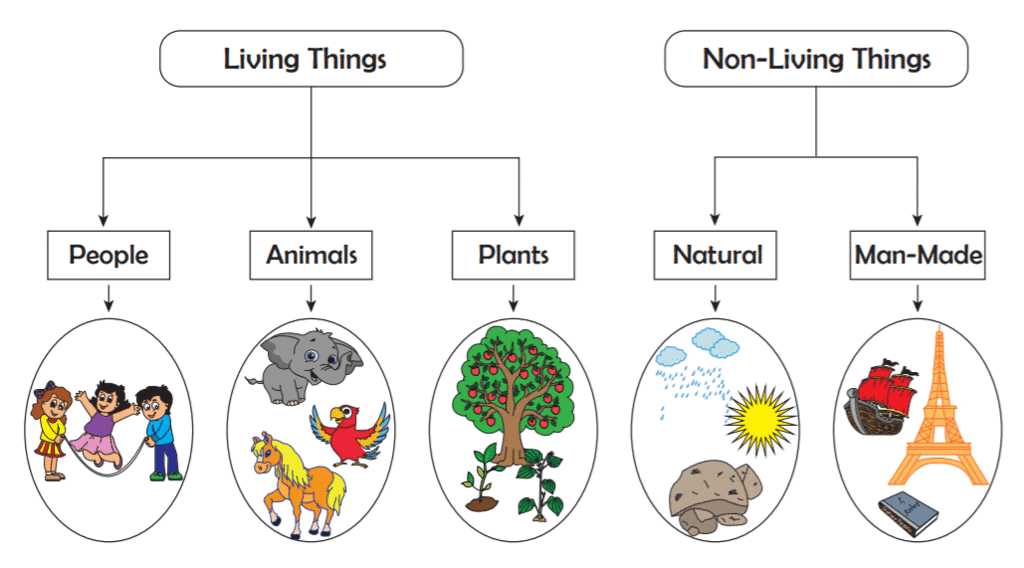
What are Living Things?
Living things are anything that can grow, move, and respond to their surroundings. They eat, breathe, reproduce, and can change over time. Animals, plants, fungi, and even small bacteria are examples of living things.

Living things are alive. They are made by nature, not by humans. Plants and animals are examples of living things.
What are Non-Living Things?
Non-living things are objects that don't have life. They don't grow, move on their own, or react to their environment like living things do. Things like rocks, water, air, and even your toys or books are non-living. They are very important because they help all living things stay alive, just like water and air!

Types of Non-Living Things
Non-living things can be categorized as either natural or man-made.
- Natural non-living things are found in nature, like the sun, moon, stars, rivers, oceans, and mountains.
- Man-made non-living things are things people make, like airplanes, cars, books, tables, and chairs!
Characteristics of Living Things
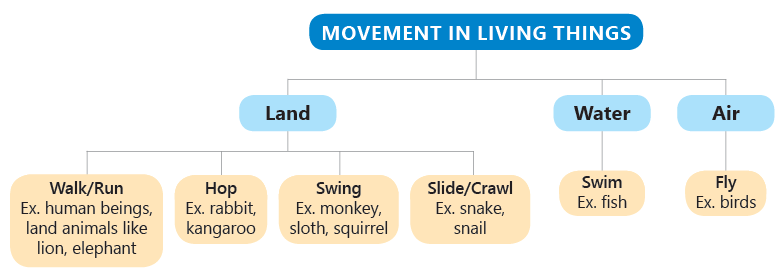
1. Living Things Move
Animals move from place to place to find food, water, shelter and to stay safe from enemies. This movement is called locomotion.

Different animals move in different ways:
- Humans walk, run, jog, and skip.
- Deer, leopards, and buffaloes walk and run with the help of their legs.
- Kangaroos and rabbits hop using their body parts.
- Most of the insects and birds move by flying using their wings and legs.
- Fish swim with the help of their fins and tails. Birds like ducks and geese use their webbed feet to swim in water.
- Some animals, which do not have limbs, use other parts of the body to move. Snails, snakes, and earthworms can slide/crawl on the ground using their muscles.
- Monkeys swing from tree to tree using their limbs and tails.
Various plants also show movement in different ways:
 Sunflowers turn towards light
Sunflowers turn towards light
- A sunflower turns to face the sun.
- The tips of young plants bend towards light.
- Climbers grow with support.
- Plant roots move down into the ground to absorb water.
2. Living Things Need Food And Water
All living things need food and water to live. Food gives the energy to do different life activities.

- Animals get their food directly or indirectly from plants. Animals like cows, deer, sheep, and elephants eat leaves and grass, while others like lions, tigers, and bears eat other animals.
- Plants cannot move from one place to another like animals for food. They make their own food. Green plants are the only living things that can make their own food using water, air, and sunlight.
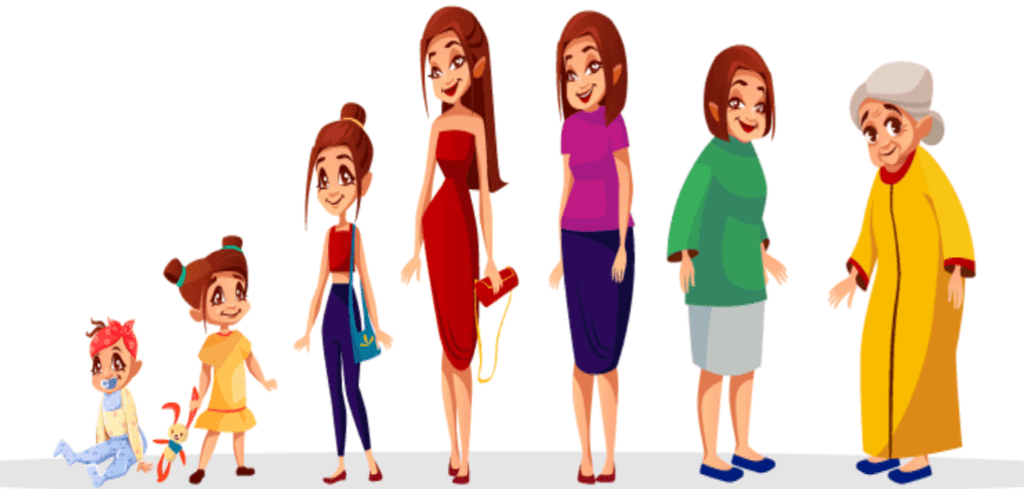
3. Living Things Grow
All animals are born small but as time passes they become bigger. Look at your childhood pictures. You have grown from a baby to a child. All animals also grow.
- A baby chick comes out of an egg and grows into a henor rooster.
- A tadpole grows and becomes a frog.
- A caterpillar changes into a butterfly.
- A seed grows into a small baby plant that further grows into a big plant.
- Living things grow and change in height, size, and shape. When they get old, they die.

4. Living Things Breathe
Place your hand on your chest. What do you feel? We feel our chest moving up and down. This is due to breathing. Animals breathe by different means
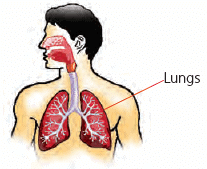
- Animals like cows, cats, and dogs that live on land have lungs to breathe.
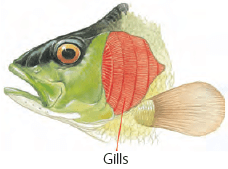
- Fish and some other animals that live in water use gills to breathe.
- We cannot observe breathing in plants but they also take in air from tiny holes present on leaves called stomata (Stoma: singular)
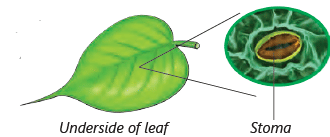
5. Living Things Can Feel
All living things can feel. When we feel cold, we cover ourselves with woolen clothes.
- Ants come to find out sugar (if kept in an open place) no matter how far off they are.
- We are able to feel because of our sense organs.
- We have five sense organs—eyes, nose, ears, tongue, and skin.
- Just like humans and animals, plants can also feel. They do feel changes around them, but they do not have sense organs.

6. Living Things Reproduce
All living thingsreproduce, that is, they produce other living beings of their own kind. This is called reproduction.
Different ways of reproduction are: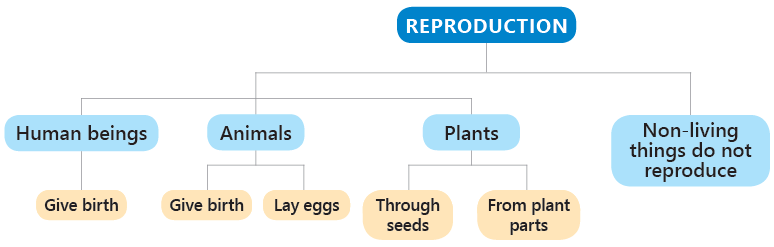
- Animals that Give Birth: Some animals, like cows, monkeys, dogs, tigers, elephants, and rabbits, give birth to their young ones.
- Animals that Lay Eggs: Some animals like birds, snakes, crocodiles, and lizards lay eggs, and their babies come out of them.
- Plants and Seeds: Most plants grow new plants by making seeds. Some plants can also grow from parts like stems, roots, or leaves.
Reproduction is crucial for the survival and continuation of species.

7. Living Things Go Through A Life Cycle
Living things are born, grow, reproduce, get old and die after some time. However, non-living things do not show such life cycle.

Characteristics of Non-Living Things
These are the following characteristics of non-living things:
1. Non-living things cannot move.
2. They do not need food and water.
3. They cannot grow.
4. Non-living things cannot breathe.
5. They cannot feel.
6. They cannot reproduce.
7. They cannot go through a lifecycle.
We can see that non-living things are just opposite of living things in their characteristics.
Differences Between Living Things and Non-living Things
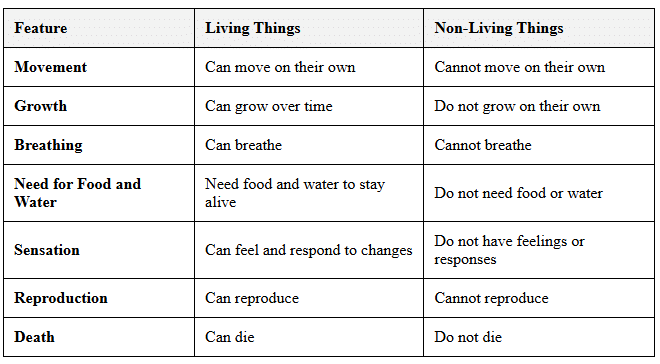
Summary
- Everything is either living or non-living.
- Plants and animals are living because they grow, breathe, need food, respond to changes, make babies, and can die.
- Plants can feel changes around them but don’t have special body parts for it.
- Female animals can give birth to babies either by giving birth or laying eggs that grow into babies.
- Non-living things don’t grow, breathe, eat, or make babies. They can’t feel anything.
|
20 videos|121 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Living and Non-Living Things Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What are the main differences between living things and non-living things? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of living and non-living things? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of living things? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to understand the differences between living and non-living things? |  |
| 5. How do non-living things affect living things? |  |

















