Light, Sound and Force Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Light |

|
| Sources of Light |

|
| Sound |

|
| Force |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Light
Imagine you are in a very dark room. The windows and doors are all closed, and there is no light anywhere. It is so dark that you cannot see even your own hands.
Suddenly, you turn on a light switch. Instantly, everything in the room becomes clear and bright. You can see the furniture, the colors, and all the small details around you.
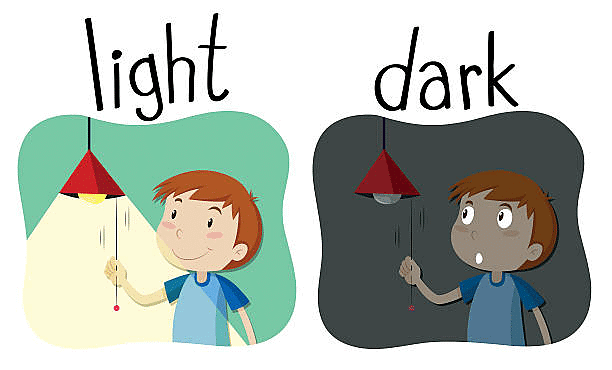
Light is like a superhero for your eyes. It helps you see the beauty of the world and turns darkness into color and shape. Without light, everything remains hidden, but with light, everything comes to life!
Sources of Light
A source of light is anything that gives us light so we can see things around us.Natural Sources of Light:
Some things in nature give off light by themselves. These are called natural sources of light.
Examples:
- The Sun – The biggest and brightest source of light for us!
- The Stars – They twinkle in the night sky and give us light.
- The Moon – It does not make its own light, but it reflects the light from the Sun.
- Glowworms & Fireflies – These little insects glow in the dark!

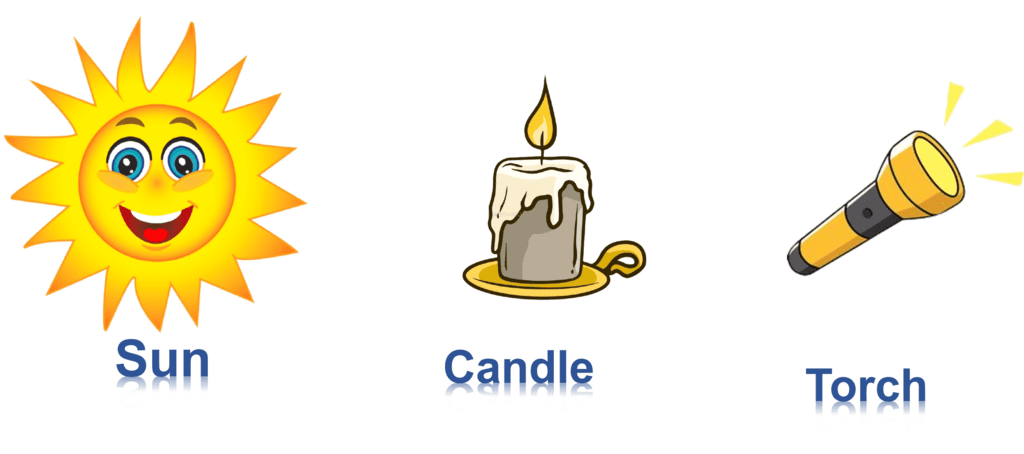
Artificial Sources of Light:
Some light sources are made by humans. These are called artificial sources of light.
Examples:
- Electric Bulb – Lights up our rooms when it's dark.
- Candles & Lamps – We use them when there is no electricity.
- Torches & Flashlights – Help us see in the dark when we go outside.

Luminous Objects:
Things that give off light are known as luminous objects.
- Natural sources like the Sun, Stars, and Glowworms fall into this category.
- Artificial sources such as Electric Bulbs and Candles are also considered luminous objects.
Non-Luminous Objects:
Objects that do not produce their own light are called non-luminous objects.
- They rely on external light sources to become visible.
- Examples include tables, books, and even the Moon (which only reflects the Sun’s light).

Need for Light Indoors:
- When we're inside a room without sunlight, we need artificial sources like electric bulbs, candles, torches, and lamps to see. These artificial sources replace the natural light and make it possible for us to see things in the dark.
Artificial Sources Created by Humans:
- Artificial sources of light are inventions made by humans to brighten our surroundings.
- These sources play a crucial role in providing light when natural sources are not available.
Light helps us see things, but what happens when something blocks light? That’s when shadows appear!
Shadow
Light travels in a straight line, like a beam from a flashlight. When light shines, it goes in a clear, straight path and creates bright, thin rays.
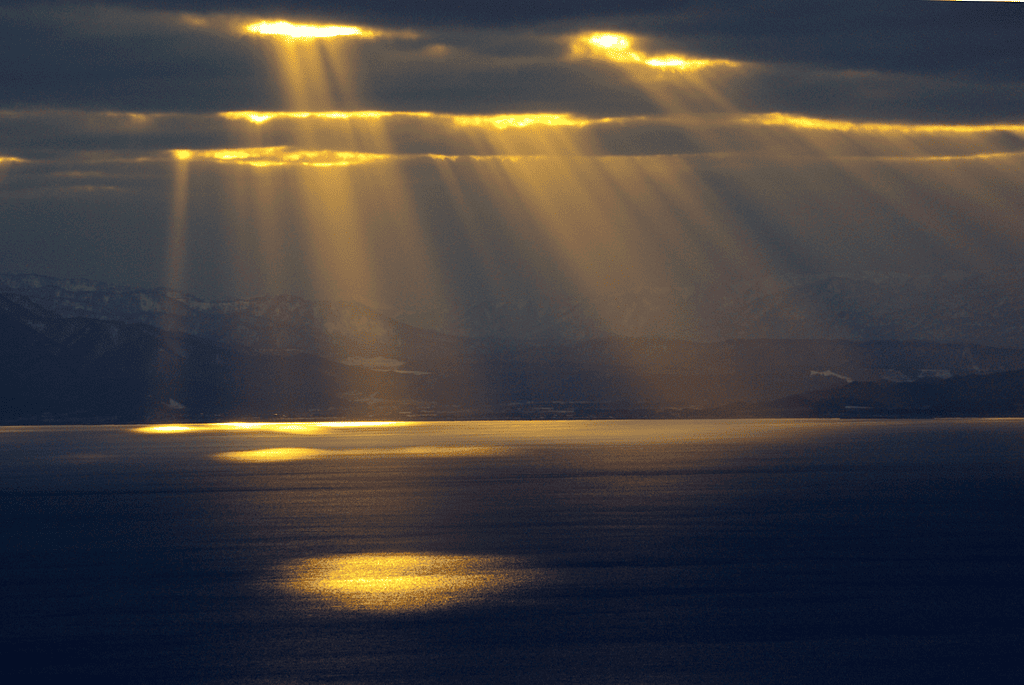 Light travels in straight lines
Light travels in straight lines
When something blocks this straight path of light, a dark shape called a shadow is made. For example, if you stand in the sunlight, your body stops some of the light, and a shadow that looks like you appears on the ground.
Observing Shadows at Different Times:
Morning:
- Shadows are longer in the morning.
- The sun is low on the horizon, causing light to cover a greater distance before reaching the ground, resulting in longer shadows.
Afternoon:
- Shadows are shorter in the afternoon.
- The sun is higher in the sky, making the distance between the object and the shadow shorter.
Evening:
- Similar to the morning, shadows are longer in the evening.
- As the sun descends, the angle of sunlight changes, creating elongated shadows.
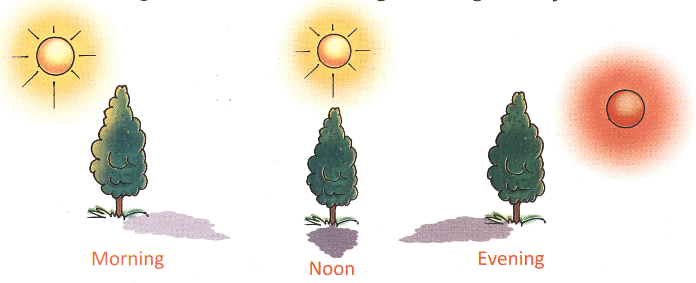 Shadows throughout the Day
Shadows throughout the Day
Factors Affecting Shadow Length:
- The length of shadows depends on the position of the sun in the sky.
- Shadows are longest when the sun is low, and shortest when the sun is high.Question for Chapter Notes: Light, Sound and ForceTry yourself:Which time of day would result in the shortest shadows?View Solution
Properties of Shadow
 Playing with Shadows
Playing with Shadows
- Shape of the shadow is similar to the shape of the object.
- The size of the shadow can be smaller or bigger than the object.
- Shadows are always black in colour.
- Shadow always forms on the opposite side of the source of the light.
Transparent, Translucent And Opaque Objects
1. Transparent Substances: Transparent substances are materials that allow light rays to pass through them clearly. Examples include glass, clear plastic sheets, and transparent water.
Use of Transparent Glass:In homes, we use transparent glass in window panes to allow sunlight to enter rooms and kitchens, enabling us to see outside.

2. Translucent Substances: Translucent substances allow light to pass through them partially. Examples include frosted glass, colored plastic sheets, oiled paper, and light-coloured wet handkerchiefs.
Use of Translucent Frosted Glass:
In areas like bathrooms, where we want light to enter but also desire privacy, we use translucent frosted glass in window panes.
 Translucent Window Glass
Translucent Window Glass
3. Opaque Substances: Opaque substances do not allow light to pass through them at all. Examples are wood, rocks, and metals.
Use of Opaque Substances:
At night, when we switch on lights inside our homes, we use curtains made of opaque material (cloth) to cover windows, ensuring privacy by preventing outsiders from seeing inside.

Sound
Sounds in Our Environment: Sound is all around us. We hear people talking, birds chirping, cars honking, and doorbells ringing. Even leaves create a rustling sound when the wind gently blows through them.How We Make Sounds:
We make sounds too! When we talk, laugh, clap, or run, we create sound waves.
Pleasant Sounds:
- Pleasant sounds are those that make us happy or don't bother us.
- Examples include birds chirping, someone singing, and the gentle ticking of a clock.

Unpleasant Sounds (Noise):
- Unpleasant sounds are irritating and can disturb us. These sounds are also known as noise.
- Examples include vehicles honking in traffic, loud music, and factory noises

Effects of Noise:
- Noise can make us sick and even give us headaches.
- It disturbs our peace and can be harmful to our well-being.
Force
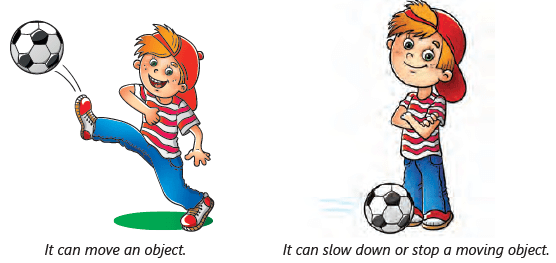
Force is what we use when we want to move something. It's like a magical push or pull that makes things happen.
Pushing Actions:
- When you want to move something away from you, you push it.
- Example: Kicking a football involves giving it a powerful push.
Pulling Actions:
- When you want to bring something closer to you, you pull it.
- Example: Lifting a football with your hands involves a pulling motion.
Everyday Examples:
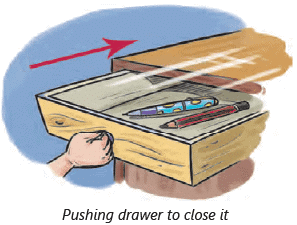
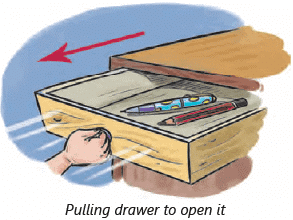
Opening a Drawer:
- You pull a drawer to open it.
- You push to close it.
Sports Activities:
- In cricket, you push a ball with your bat.
- When picking up a book, you pull it towards yourself.
Definition of Force:
- Any action of pushing or pulling on an object is called force.
- It's the invisible friend that helps us move, lift, and change the position of things.
Force in Daily Tasks:
- Throughout the day, we engage in a variety of activities that involve applying force.
- Whether it's opening doors, playing sports, or handling objects, force is always at play.
Effects of Force
- Force and Motion: Force can cause a change in the motion of an object.
- Stationary Objects: Objects stay still until a force makes them move.
- Speed and Direction: Force can change how fast something is going or the way it's moving.
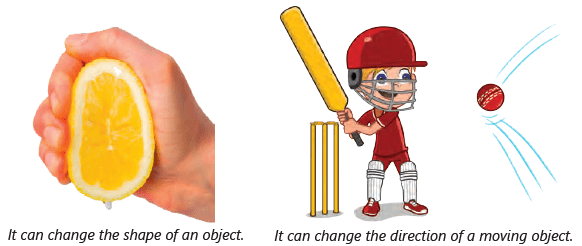
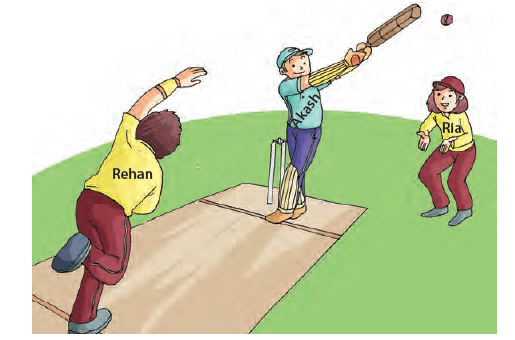
Look at the picture. Rehan is throwing the ball using force. Akash hits the ball and changes the direction of the moving ball. The ball flies and moves towards Ria. Ria catches the ball. She stops the movement of the ball.
Conclusion
In our everyday lives, light, shadows, sound, and force are all around us, helping us see, hear, and interact with the world. From the bright sunshine that makes everything visible to the sounds that fill our environment, these natural and artificial wonders make life exciting and full of learning. Understanding how things like light, force, and sound work helps us appreciate the amazing world we live in and the simple things that make it all happen. So, next time you see a shadow, hear a sound, or push or pull something, remember—you're part of the amazing science that makes everything work!
|
20 videos|203 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Light, Sound and Force Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What are the different sources of light? |  |
| 2. How does sound travel through different mediums? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between force and motion? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of light? |  |
| 5. How do we perceive sound and light differently? |  |
















