States of Matter Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| States of Matter |

|
| Three State of Matter |

|
| Change of States |

|
| Conclusion |

|
States of Matter
Everything around us is made of matter! The table we write on, the water we drink, and even the air we breathe are all forms of matter. Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space.

Scientists have found that matter can exist in three main forms:
- Solids – like a table or a pencil, which have a fixed shape.
- Liquids – like water or milk, which flow and take the shape of their container.
- Gases – like air, which we cannot see but can feel when the wind blows.
- Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. The arrangement of these molecules depends on the type of matter.
- For example, the molecules in a solid are packed closely together, while in a liquid, they are more spread out. This is why different things, like water and a rock, feel and behave differently.
Three State of Matter
1. Solids
- Solid is a state of matter that has a fixed shape and volume.
- In solids, molecules are closely packed. That is why solids are hard.
- Solids do not change their shape when moved from one container to another container, i.e., they have a definite shape and a definite volume.
- Examples of solids include everyday objects like a chair, dice, cup, book.

2. Liquid
- Liquids do not have a fixed shape. They flow easily and take the shape of the container they are in.
- Liquid molecules are loosely packed. They are not as tightly packed as solids, so they can move around freely.
- Liquids have a fixed volume. No matter what container you pour them into, the amount of liquid stays the same.
- Examples: Water, oil, milk, and, juice.

3. Gases
- Gases do not have a fixed shape, just like liquids.
- Their tiny particles (molecules) are very loosely packed and move around freely.
- Gases fill the container they are in and spread in all directions.
- Unlike liquids, gases do not have a fixed amount (volume). They can expand or get squeezed.
- Air is a mixture of many gases.
- Examples: Oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen.
Change of States
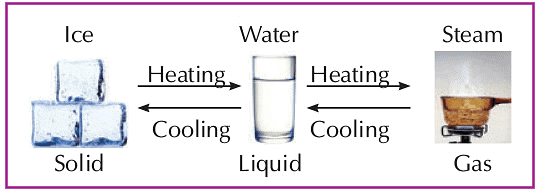
- Matter can change from one state to another.
- A solid can change into a liquid when heated.
- A liquid becomes a gas when heated.
- A gas changes into a liquid when cooled.
- When we freeze a liquid, it becomes a solid.
- Example: When we heat ice (a solid), it melts into water (a liquid). If we heat the water, it changes into vapors (a gas).
Conclusion
Matter around us can exist in three different states: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state has unique properties based on how its molecules are arranged and move. Changes in temperature can cause matter to switch from one state to another, like ice melting into water or water evaporating into vapor. Understanding these states and changes helps us see how things around us work and interact in everyday life.
|
20 videos|121 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on States of Matter Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What are the three main states of matter? |  |
| 2. How do solids, liquids, and gases differ from each other? |  |
| 3. What is meant by 'change of states' in matter? |  |
| 4. What causes the change of states in matter? |  |
| 5. Can matter exist in more than three states? |  |
















