DNA Fingerprinting | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology (RGCB) in Thiruvananthapuram, in collaboration with the Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics (CDFD), is leveraging advanced DNA fingerprinting techniques, including next-generation sequencing, to identify victims of natural disasters like the Ockhi storm. These methods are also pivotal in criminal investigations and conservation efforts.
What exactly is DNA fingerprinting? And how does it differ from portrayals in TV crime shows?
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
- It is a technique for identifying individuals by analyzing unique DNA markers, such as Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs).
- DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic acid, is the fundamental building block of life, encoding all genetic information and facilitating trait inheritance across generations.
- Each individual’s DNA comprises Bases [Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C)], Sugar, and a Phosphate, with bases forming hydrogen-bonded pairs.
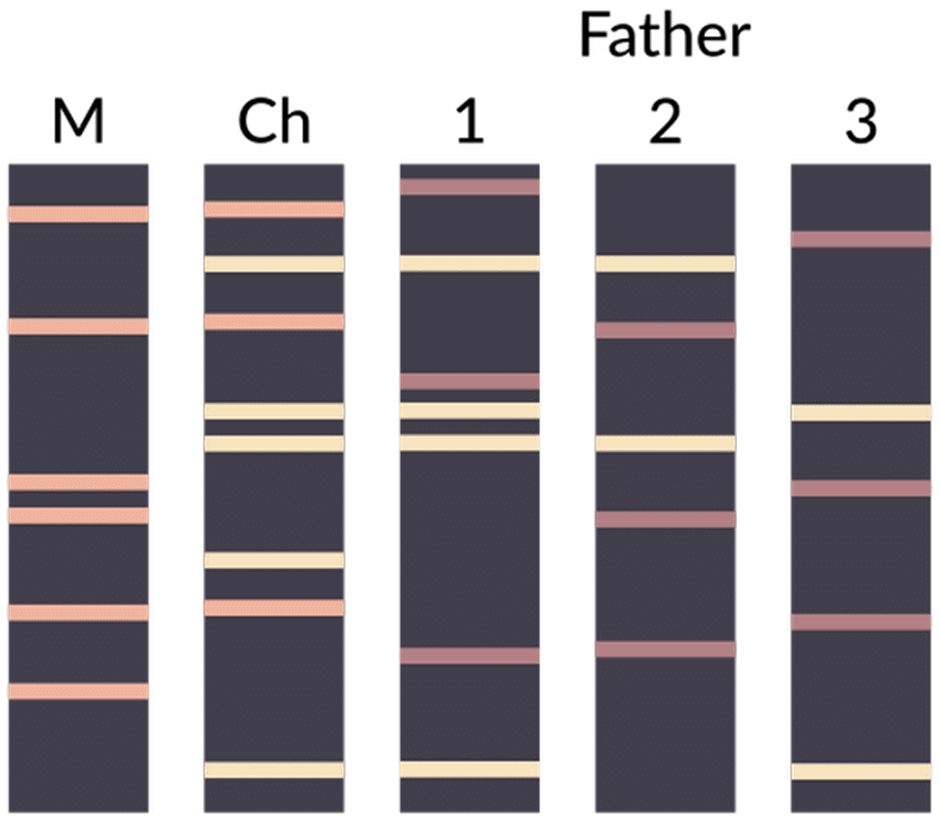
- “Humans have three billion base pairs, with 99.7% similarity between individuals. The 0.3% variation, analyzed via STRs and SNPs, enables precise identification. Parent-child matches show 50% similarity, siblings range from 25% to 75%, and monozygotic twins exhibit a 100% match,” explains Dr. Madhusudan Reddy, staff scientist at CDFD, Hyderabad, emphasizing modern STR-based profiling.
Can DNA Fingerprinting Be Done Only with Blood Samples?
- DNA can be extracted from blood, bones, hair with root, saliva, semen, teeth, tissue, and even trace amounts like touch DNA from skin cells.
- “For Ockhi victims, we analyzed bone and sternum samples using advanced techniques. Relatives provide buccal swabs or blood for comparison, ensuring accurate matches,” says an official from RGCB’s DNA fingerprinting facility, highlighting minimally invasive sampling.
How is DNA Fingerprinting Done?
- DNA is extracted from samples using specific protocols. Fragments are amplified via Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to generate sufficient material for analysis.
- Amplified DNA is analyzed using capillary electrophoresis or next-generation sequencing (NGS). These methods produce unique STR or SNP profiles, which are compared using AI-driven software for rapid, accurate matching, surpassing older gel electrophoresis techniques.
What are its uses?
DNA fingerprinting supports forensics, paternity testing, and conservation
- For criminal identification, aiding India’s justice system.
- To resolve disputes of maternity/paternity, ensuring legal clarity.
- To identify mutilated remains, as in disaster victim identification.
- In cases of baby exchanges in hospitals, ensuring family reunification.
- In forensic wildlife and conservation (e.g., tracking endangered species like tigers), medical diagnostics, and ancestry tracing, reflecting its interdisciplinary scope.
Can Anyone Get Their DNA Checked with Their Parents?
- An RGCB official noted that paternity/maternity disputes require a court order, with testing conducted under police and judicial supervision to ensure legality.
Are There Any Laws in India Regarding DNA Fingerprinting?
- The DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Bill, proposed in 2019, remains under parliamentary review in 2025, aiming to regulate DNA profiling and establish national DNA databanks.
- The Bill addresses identification of missing persons, disaster victims, and criminals, while raising privacy and ethical concerns, aligning with India’s biotech governance framework.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on DNA Fingerprinting - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is DNA fingerprinting? |  |
| 2. How is DNA fingerprinting used in forensic science? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of DNA fingerprinting in paternity testing? |  |
| 4. Can DNA fingerprinting be used to establish familial relationships other than paternity? |  |
| 5. What are some limitations of DNA fingerprinting? |  |

















