HTML Colors & Styles - CSS | HTML for Junior Classes - Class 3 PDF Download
HTML colors are specified with predefined color names, or with RGB, HEX, HSL, RGBA, or HSLA values.
Color Names
In HTML, a color can be specified by using a color name:


HTML supports 140 standard color names.
Background Color
You can set the background color for HTML elements:

Example
<h1 style="background-color:DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="background-color:Tomato;">Lorem ipsum...</p>
Text Color
You can set the color of text:
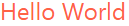
Example
<h1 style="color:Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<p style="color:DodgerBlue;">Lorem ipsum...</p>
<p style="color:MediumSeaGreen;">Ut wisi enim...</p>
Border Color
You can set the color of borders:
Example
<h1 style="border:2px solid Tomato;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
<h1 style="border:2px solid Violet;">Hello World</h1>
Color Values
In HTML, colors can also be specified using RGB values, HEX values, HSL values, RGBA values, and HSLA values.
The following three <div> elements have their background color set with RGB, HEX, and HSL values: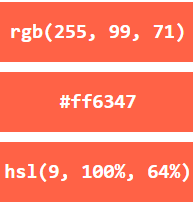
The following two <div> elements have their background color set with RGBA and HSLA values, which adds an Alpha channel to the color (here we have 50% transparency):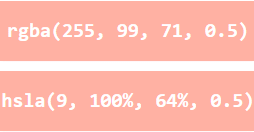
Example
<h1 style="background-color:rgb(255, 99, 71);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:#ff6347;">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsl(9, 100%, 64%);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:rgba(255, 99, 71, 0.5);">...</h1>
<h1 style="background-color:hsla(9, 100%, 64%, 0.5);">...</h1>
HTML RGB and RGBA Colors
An RGB color value represents RED, GREEN, and BLUE light sources.
An RGBA color value is an extension of RGB with an Alpha channel (opacity).
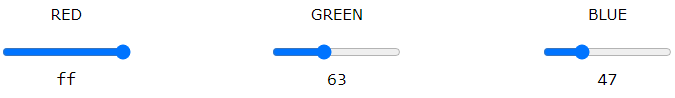
RGB Color Values
- In HTML, a color can be specified as an RGB value, using this formula:
rgb(red, green, blue) - Each parameter (red, green, and blue) defines the intensity of the color with a value between 0 and 255.
- This means that there are 256 x 256 x 256 = 16777216 possible colors!
- For example, rgb(255, 0, 0) is displayed as red, because red is set to its highest value (255), and the other two (green and blue) are set to 0.
- Another example, rgb(0, 255, 0) is displayed as green, because green is set to its highest value (255), and the other two (red and blue) are set to 0.
- To display black, set all color parameters to 0, like this: rgb(0, 0, 0).
- To display white, set all color parameters to 255, like this: rgb(255, 255, 255).
- Experiment by mixing the RGB values below:


Example


Shades of Gray
Shades of gray are often defined using equal values for all three parameters:
Example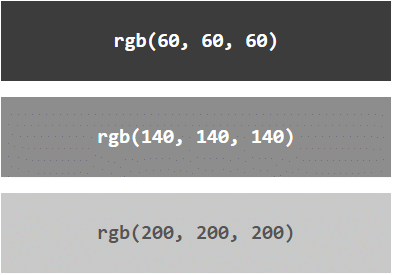

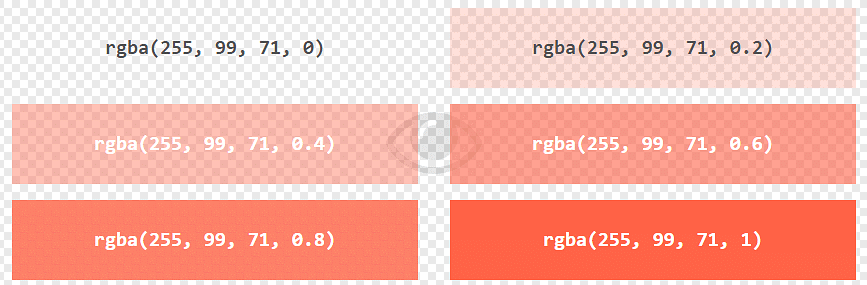
RGBA Color Values
RGBA color values are an extension of RGB color values with an Alpha channel - which specifies the opacity for a color.
An RGBA color value is specified with:
rgba(red, green, blue, alpha)
The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (not transparent at all):
Experiment by mixing the RGBA values below:

HTML HEX Colors
A hexadecimal color is specified with: #RRGGBB, where the RR (red), GG (green) and BB (blue) hexadecimal integers specify the components of the color.
HEX Color Values
In HTML, a color can be specified using a hexadecimal value in the form:
#rrggbb
Where rr (red), gg (green) and bb (blue) are hexadecimal values between 00 and ff (same as decimal 0-255).
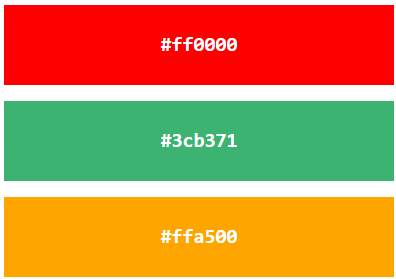
For example, #ff0000 is displayed as red, because red is set to its highest value (ff), and the other two (green and blue) are set to 00.
Another example, #00ff00 is displayed as green, because green is set to its highest value (ff), and the other two (red and blue) are set to 00.
To display black, set all color parameters to 00, like this: #000000.
To display white, set all color parameters to ff, like this: #ffffff.
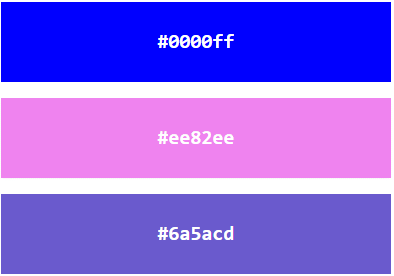
Experiment by mixing the HEX values below:
Example
Shades of Gray
Shades of gray are often defined using equal values for all three parameters:
Example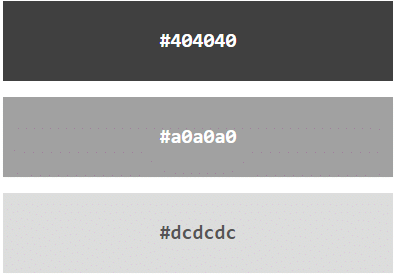

HTML HSL and HSLA Colors
HSL stands for hue, saturation, and lightness.
HSLA color values are an extension of HSL with an Alpha channel (opacity).
HSL Color Values
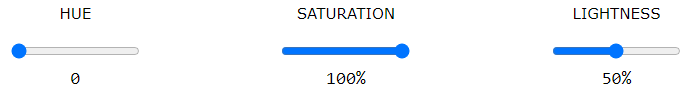
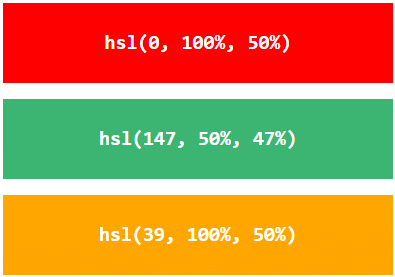
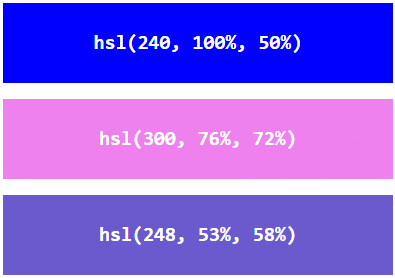
In HTML, a color can be specified using hue, saturation, and lightness (HSL) in the form:
hsl(hue, saturation, lightness)
Hue is a degree on the color wheel from 0 to 360. 0 is red, 120 is green, and 240 is blue.
Saturation is a percentage value, 0% means a shade of gray, and 100% is the full color.
Lightness is also a percentage value, 0% is black, and 100% is white.
Experiment by mixing the HSL values below:

Example
Saturation
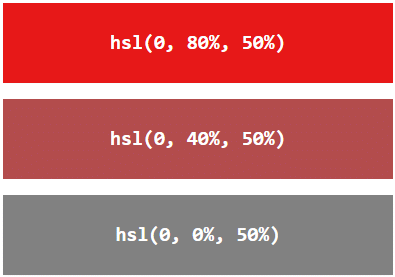
Saturation can be described as the intensity of a color.
100% is pure color, no shades of gray
50% is 50% gray, but you can still see the color.
0% is completely gray, you can no longer see the color.
Example
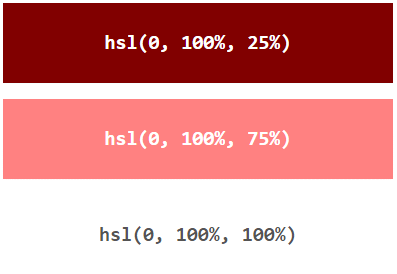
Lightness
The lightness of a color can be described as how much light you want to give the color, where 0% means no light (black), 50% means 50% light (neither dark nor light) 100% means full lightness (white).
Example

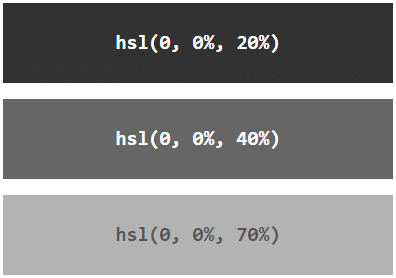
 Shades of Gray
Shades of Gray
Shades of gray are often defined by setting the hue and saturation to 0, and adjust the lightness from 0% to 100% to get darker/lighter shades:
Example

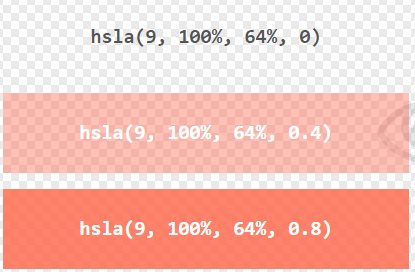
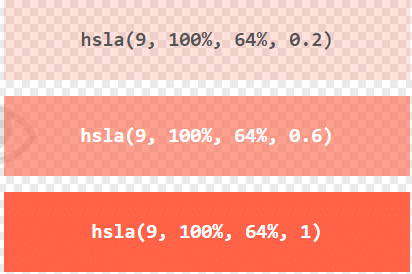
HSLA Color Values
HSLA color values are an extension of HSL color values with an Alpha channel - which specifies the opacity for a color.
An HSLA color value is specified with:
hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, alpha)
The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (not transparent at all):
Experiment by mixing the HSLA values below:

Example
HTML Styles - CSS
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets.
CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once.
What is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is used to format the layout of a webpage.
With CSS, you can control the color, font, the size of text, the spacing between elements, how elements are positioned and laid out, what background images or background colors are to be used, different displays for different devices and screen sizes, and much more!
Tip: The word cascading means that a style applied to a parent element will also apply to all children elements within the parent. So, if you set the color of the body text to "blue", all headings, paragraphs, and other text elements within the body will also get the same color (unless you specify something else)!
Using CSS
CSS can be added to HTML documents in 3 ways:
- Inline: by using the style attribute inside HTML elements
- Internal: by using a <style> element in the <head> section
- External: by using a <link> element to link to an external CSS file
The most common way to add CSS, is to keep the styles in external CSS files. However, in this tutorial we will use inline and internal styles, because this is easier to demonstrate, and easier for you to try it yourself.
Inline CSS
- An inline CSS is used to apply a unique style to a single HTML element.
- An inline CSS uses the style attribute of an HTML element.
The following example sets the text color of the <h1> element to blue, and the text color of the <p> element to red:
Example
<h1 style="color:blue;">A Blue Heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">A red paragraph.</p>
Internal CSS
An internal CSS is used to define a style for a single HTML page.
An internal CSS is defined in the <head> section of an HTML page, within a <style> element.
The following example sets the text color of ALL the <h1> elements (on that page) to blue, and the text color of ALL the <p> elements to red. In addition, the page will be displayed with a "powderblue" background color:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {background-color: powderblue;}
h1 {color: blue;}
p {color: red;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
External CSS
An external style sheet is used to define the style for many HTML pages.
To use an external style sheet, add a link to it in the <head> section of each HTML page:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
The external style sheet can be written in any text editor. The file must not contain any HTML code, and must be saved with a .css extension.
Here is what the "styles.css" file looks like:
"styles.css":
body {
background-color: powderblue;
}
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}
Tip: With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire web site, by changing one file!
CSS Colors, Fonts and Sizes
Here, we will demonstrate some commonly used CSS properties. You will learn more about them later.
The CSS color property defines the text color to be used.
The CSS font-family property defines the font to be used.
The CSS font-size property defines the text size to be used.
Example
Use of CSS color, font-family and font-size properties:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 300%;
}
p {
color: red;
font-family: courier;
font-size: 160%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Border
The CSS border property defines a border around an HTML element.
Tip: You can define a border for nearly all HTML elements.
Example
Use of CSS border property:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
}
CSS Padding
The CSS padding property defines a padding (space) between the text and the border.
Example
Use of CSS border and padding properties:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
padding: 30px;
}
CSS Margin
The CSS margin property defines a margin (space) outside the border.
Example
Use of CSS border and margin properties:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
margin: 50px;
}
Link to External CSS
External style sheets can be referenced with a full URL or with a path relative to the current web page.
Example
This example uses a full URL to link to a style sheet:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://www.w3schools.com/html/styles.css">
Example
This example links to a style sheet located in the html folder on the current web site:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/html/styles.css">
Example
This example links to a style sheet located in the same folder as the current page:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
|
14 videos|31 docs|24 tests
|















